

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (4): 602-611.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22091 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22091
收稿日期:2022-04-29
接受日期:2022-09-07
出版日期:2023-07-01
发布日期:2022-09-30
通讯作者:
*E-mail: minl@gzhu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shengyu Liu, Xiaobin Liu, Jiafu Zhu, Jing Su, Zhicheng Dong, Min Liu( )
)
Received:2022-04-29
Accepted:2022-09-07
Online:2023-07-01
Published:2022-09-30
Contact:
*E-mail: minl@gzhu.edu.cn
摘要: Tn5是一种细菌转座子。经改造的Tn5能够高效地切割DNA, 同时连接上特定的接头序列, 因而广泛应用于高通量二代测序文库构建中。CUT&Tag (Cleavage Under Target & Tagmentation)是一种改进的研究蛋白质与DNA互作的技术, 具有重复性好、信噪比高及操作简便等优点。该技术采用pA (Protein A)或pG (Protein G)与Tn5形成融合蛋白, 定位于特定抗体(用于识别目标蛋白), 利用Tn5的特性, 在目标位点附近打断DNA的同时引入测序接头, 随后提取DNA, 再进行PCR扩增即可获得测序文库。但不同类型的抗体与pA或pG的亲和力不同, 因此限制了部分抗体在CUT&Tag技术中的应用。为克服这一局限, 该文构建了pG与Tn5的融合蛋白表达载体, 通过原核表达及亲和纯化的方式获得pG-Tn5重组蛋白; 并以RNA聚合酶II (Pol II)特异性抗体Pol II Ser5P (小鼠IgG1型抗体和兔IgG型抗体)为例, 在模式植物拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)中评估pA-Tn5与pG-Tn5在不同类型抗体的CUT&Tag测序文库构建中的效果。结果表明, IgG1型抗体与pG-Tn5的亲和力更高, 构建的文库质量更好, 而IgG型抗体与2种酶的亲和力相当; 同时, 较低起始量的植物材料也能获得较好的效果, 证明了CUT&Tag的应用优势。该研究优化了CUT&Tag技术, 可为后续CUT&Tag实验中针对不同抗体时Tn5融合蛋白的选择提供参考。
刘晟宇, 刘晓斌, 朱家富, 苏京, 董志诚, 刘敏. Tn5转座酶融合蛋白在CUT&Tag实验中的优化及评价. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 602-611.
Shengyu Liu, Xiaobin Liu, Jiafu Zhu, Jing Su, Zhicheng Dong, Min Liu. Optimization and Evaluation of Tn5 Transposase Fusion Protein in CUT&Tag. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 602-611.
| Buffer | Component | Concentration | Buffer | Component | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEGX buffer | NaCl | 0.8 mol·L-1 | HBC buffer | Tris-HCl, pH7.5 | 20 mmol·L-1 |
| Glycerol | 10% | Sucrose | 352 mmol·L-1 | ||
| TritonX-100 | 0.2% | MgCl2 | 8 mmol·L-1 | ||
| HEPES-KOH, pH7.2 | 20 mmol·L-1 | TritonX-100 | 0.08% | ||
| EDTA | 1 mmol·L-1 | β-mercaptoethanol | 8 mmol·L-1 | ||
| Storage buffer | NaCl | 0.8 mol·L-1 | Glycerol | 20% | |
| Glycerol | 10% | 10× binding buffer | HEPES-KOH, pH8.0 | 20 mmol·L-1 | |
| Tris-HCl, pH7.5 | 50 mmol·L-1 | KCl | 100 mmol·L-1 | ||
| EDTA | 0.2 mmol·L-1 | CaCl2 | 10 mmol·L-1 | ||
| DTT | 2 mmol·L-1 | MnCl2 | 10 mmol·L-1 | ||
| Annealing buffer | Tris-HCl, pH7.0 | 5 mmol·L-1 | Spermidine | 5 mmol·L-1 | |
| EDTA | 0.5 mmol·L-1 | Blocking buffer | HEPES-KOH, pH7.5 | 20 mmol·L-1 | |
| NaCl | 50 mmol·L-1 | NaCl | 150 mmol·L-1 | ||
| 5× Tagmentation buffer | TAPS-NaOH, pH8.5 | 50 mmol·L-1 | Spermidine | 0.5 mmol·L-1 | |
| MgCl2 | 25 mmol·L-1 | BSA | 0.1% | ||
| Lysis buffer | HEPES-KOH, pH7.2 | 50 mmol·L-1 | EDTA | 2 mmol·L-1 | |
| NaCl | 150 mmol·L-1 | Wash buffer | HEPES-KOH, pH7.5 | 20 mmol·L-1 | |
| EDTA | 1 mmol·L-1 | NaCl | 150 mmol·L-1 | ||
| TritonX-100 | 1% | Spermidine | 0.5 mmol·L-1 | ||
| Glycerol | 10% | BSA | 0.1% | ||
| β-mercaptoethanol | 5 mmol·L-1 | Pepstatin A | 1 μg·mL-1 | ||
| Pepstatin A | 1 μg·mL-1 | Aprotinin | 1 μg·mL-1 | ||
| Aprotinin | 1 μg·mL-1 | PMSF | 1 mmol·L-1 | ||
| PMSF | 1 mmol·L-1 | TE buffer | Tris-HCl, pH8.0 | 1 mmol·L-1 | |
| HBB buffer | Tris-HCl, pH7.5 | 25 mmol·L-1 | EDTA | 0.1 mmol·L-1 | |
| Sucrose | 0.44 mol·L-1 | Dissolution buffer | NaCl | 300 mmol·L-1 | |
| MgCl2 | 10 mmol·L-1 | EDTA | 1 mmol·L-1 | ||
| TritonX-100 | 0.1% | ||||
| β-mercaptoethanol | 10 mmol·L-1 |
表1 缓冲液
Table 1 Buffer used in this study
| Buffer | Component | Concentration | Buffer | Component | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEGX buffer | NaCl | 0.8 mol·L-1 | HBC buffer | Tris-HCl, pH7.5 | 20 mmol·L-1 |
| Glycerol | 10% | Sucrose | 352 mmol·L-1 | ||
| TritonX-100 | 0.2% | MgCl2 | 8 mmol·L-1 | ||
| HEPES-KOH, pH7.2 | 20 mmol·L-1 | TritonX-100 | 0.08% | ||
| EDTA | 1 mmol·L-1 | β-mercaptoethanol | 8 mmol·L-1 | ||
| Storage buffer | NaCl | 0.8 mol·L-1 | Glycerol | 20% | |
| Glycerol | 10% | 10× binding buffer | HEPES-KOH, pH8.0 | 20 mmol·L-1 | |
| Tris-HCl, pH7.5 | 50 mmol·L-1 | KCl | 100 mmol·L-1 | ||
| EDTA | 0.2 mmol·L-1 | CaCl2 | 10 mmol·L-1 | ||
| DTT | 2 mmol·L-1 | MnCl2 | 10 mmol·L-1 | ||
| Annealing buffer | Tris-HCl, pH7.0 | 5 mmol·L-1 | Spermidine | 5 mmol·L-1 | |
| EDTA | 0.5 mmol·L-1 | Blocking buffer | HEPES-KOH, pH7.5 | 20 mmol·L-1 | |
| NaCl | 50 mmol·L-1 | NaCl | 150 mmol·L-1 | ||
| 5× Tagmentation buffer | TAPS-NaOH, pH8.5 | 50 mmol·L-1 | Spermidine | 0.5 mmol·L-1 | |
| MgCl2 | 25 mmol·L-1 | BSA | 0.1% | ||
| Lysis buffer | HEPES-KOH, pH7.2 | 50 mmol·L-1 | EDTA | 2 mmol·L-1 | |
| NaCl | 150 mmol·L-1 | Wash buffer | HEPES-KOH, pH7.5 | 20 mmol·L-1 | |
| EDTA | 1 mmol·L-1 | NaCl | 150 mmol·L-1 | ||
| TritonX-100 | 1% | Spermidine | 0.5 mmol·L-1 | ||
| Glycerol | 10% | BSA | 0.1% | ||
| β-mercaptoethanol | 5 mmol·L-1 | Pepstatin A | 1 μg·mL-1 | ||
| Pepstatin A | 1 μg·mL-1 | Aprotinin | 1 μg·mL-1 | ||
| Aprotinin | 1 μg·mL-1 | PMSF | 1 mmol·L-1 | ||
| PMSF | 1 mmol·L-1 | TE buffer | Tris-HCl, pH8.0 | 1 mmol·L-1 | |
| HBB buffer | Tris-HCl, pH7.5 | 25 mmol·L-1 | EDTA | 0.1 mmol·L-1 | |
| Sucrose | 0.44 mol·L-1 | Dissolution buffer | NaCl | 300 mmol·L-1 | |
| MgCl2 | 10 mmol·L-1 | EDTA | 1 mmol·L-1 | ||
| TritonX-100 | 0.1% | ||||
| β-mercaptoethanol | 10 mmol·L-1 |
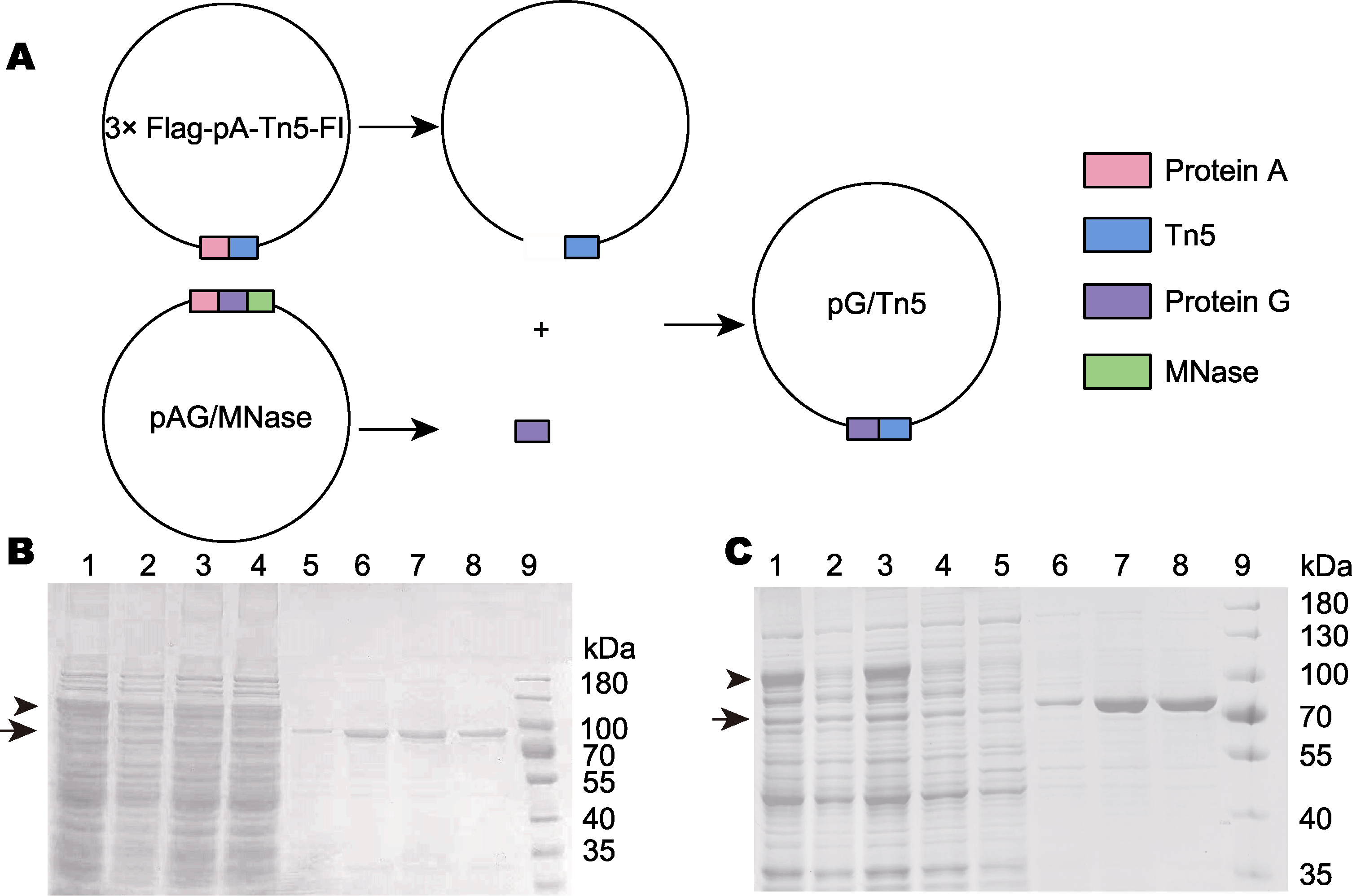
图1 pG/Tn5表达载体的构建及pA-Tn5和pG-Tn5的制备 (A) 利用PCR及同源重组的方式构建pG/Tn5; (B) pA-Tn5利用几丁质亲和标签的亲和纯化(泳道1-4为纯化前的蛋白混合物, 表示纯化前带有几丁质结合结构域和intein的pA-Tn5蛋白; 泳道5-8为洗脱后纯度较高的pA-Tn5, 表示纯化后的蛋白; 泳道9: 蛋白分子量标准); (C) pG-Tn5利用几丁质亲和标签的亲和纯化(泳道1-5为纯化前的蛋白混合物, 表示纯化前的蛋白; 泳道6-8为洗脱后纯度较高的pG-Tn5, 表示纯化后的蛋白; 泳道9: 蛋白分子量标准)
Figure 2 Construction of the pG/Tn5 expression vector and preparation of pA-Tn5 and pG-Tn5 (A) pG/Tn5 was constructed by PCR and homologous recombination; (B) pA-Tn5 was affinity purified by the chitin-binding domain (lanes 1-4 are the protein mixture before purification, represents the protein before purification; lanes 5-8 are pA-Tn5 with high purity after elution, represents the purified protein; lane 9: Protein molecular weight marker); (C) pG-Tn5 is affinity purified by chitin-binding domain (lanes 1-5 are the protein mixture before purification, represents the protein before purification; lanes 6-8 are pG-Tn5 with high purity after elution, represents the purified protein; lane 9: Protein molecular weight marker)
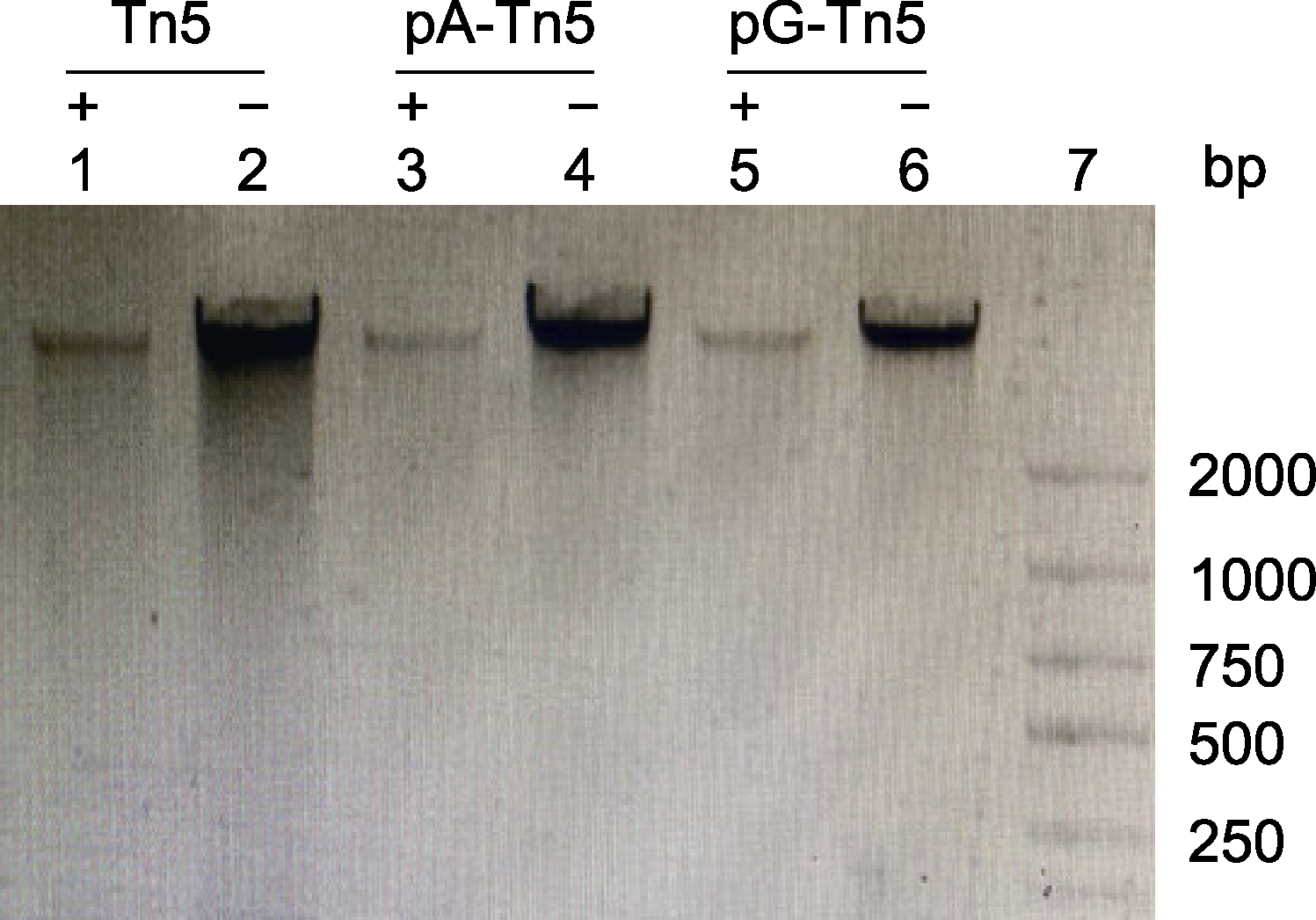
图2 pA-Tn5和pG-Tn5的活力测定 泳道1: 大豆基因组DNA+Tn5; 泳道3: 大豆基因组DNA+pA- Tn5; 泳道5: 大豆基因组DNA+pG-Tn5; 泳道2、4和6: 大豆基因组DNA; 泳道7: Marker
Figure 2 Evaluation of the activities of pA-Tn5 and pG-Tn5 Lane 1: Soybean genomic DNA+Tn5; Lane 3: Soybean genomic DNA+pA-Tn5; Lane 5: Soybean genomic DNA+pG- Tn5; Lanes 2, 4 and 6: Soybean genomic DNA without enzyme; Lane 7: Marker
| Group | Enzyme type | Antibody | Dosage of Tn5 (μg) | Dosage of plant material (μL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | pA-Tn5 | Ser5P Mouse IgG1 | 0.2 | 150 |
| 2 | pA-Tn5 | Ser5P Mouse IgG1 | 1 | 150 |
| 3 | pG-Tn5 | Ser5P Mouse IgG1 | 0.2 | 150 |
| 4 | pG-Tn5 | Ser5P Mouse IgG1 | 1 | 150 |
| 5 | pG-Tn5 | IgG | 0.2 | 150 |
| 6 | pG-Tn5 | IgG | 1 | 150 |
| 7 | pA-Tn5 | Ser5P Rabbit IgG | 0.5 | 30 |
| 8 | pA-Tn5 | Ser5P Rabbit IgG | 1 | 150 |
| 9 | pG-Tn5 | Ser5P Rabbit IgG | 0.5 | 30 |
| 10 | pG-Tn5 | Ser5P Rabbit IgG | 1 | 150 |
| 11 | pA-Tn5 | IgG | 1 | 150 |
| 12 | pG-Tn5 | IgG | 1 | 150 |
表2 实验组设计
Table 2 Experimental group design
| Group | Enzyme type | Antibody | Dosage of Tn5 (μg) | Dosage of plant material (μL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | pA-Tn5 | Ser5P Mouse IgG1 | 0.2 | 150 |
| 2 | pA-Tn5 | Ser5P Mouse IgG1 | 1 | 150 |
| 3 | pG-Tn5 | Ser5P Mouse IgG1 | 0.2 | 150 |
| 4 | pG-Tn5 | Ser5P Mouse IgG1 | 1 | 150 |
| 5 | pG-Tn5 | IgG | 0.2 | 150 |
| 6 | pG-Tn5 | IgG | 1 | 150 |
| 7 | pA-Tn5 | Ser5P Rabbit IgG | 0.5 | 30 |
| 8 | pA-Tn5 | Ser5P Rabbit IgG | 1 | 150 |
| 9 | pG-Tn5 | Ser5P Rabbit IgG | 0.5 | 30 |
| 10 | pG-Tn5 | Ser5P Rabbit IgG | 1 | 150 |
| 11 | pA-Tn5 | IgG | 1 | 150 |
| 12 | pG-Tn5 | IgG | 1 | 150 |
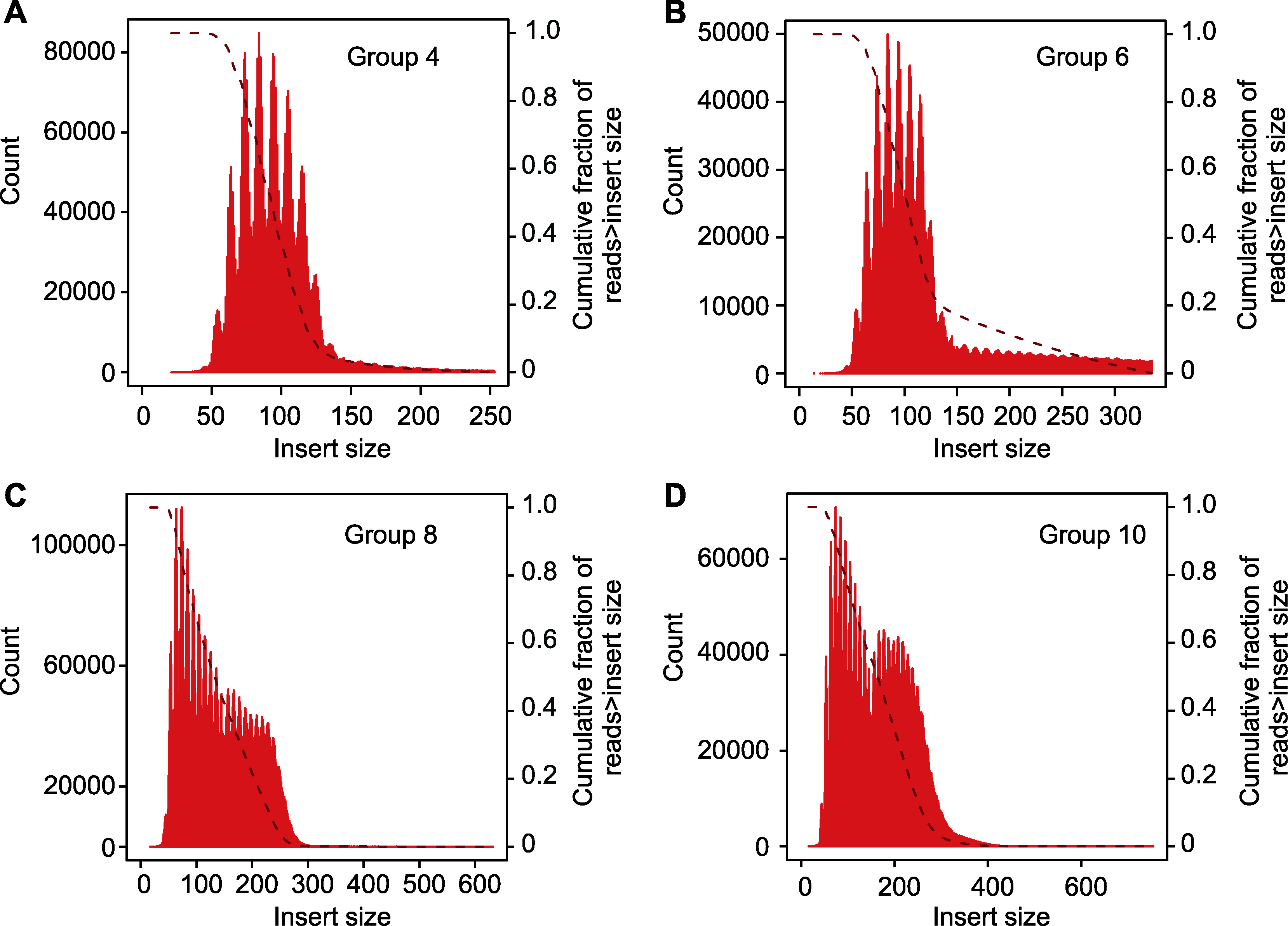
图3 插入片段长度分布 (A) 实验组4插入片段长度分布; (B) 实验组6插入片段长度分布; (C) 实验组8插入片段长度分布; (D) 实验组10插入片段长度分布。Group 4、6、8和10同表2。
Figure 3 Library insert size (A) Library insert size in experimental group 4; (B) Library insert size in experimental group 6; (C) Library insert size in experimental group 8; (D) Library insert size in experimental group 10. Group 4, 6, 8 and 10 are the same as shown in Table 2.
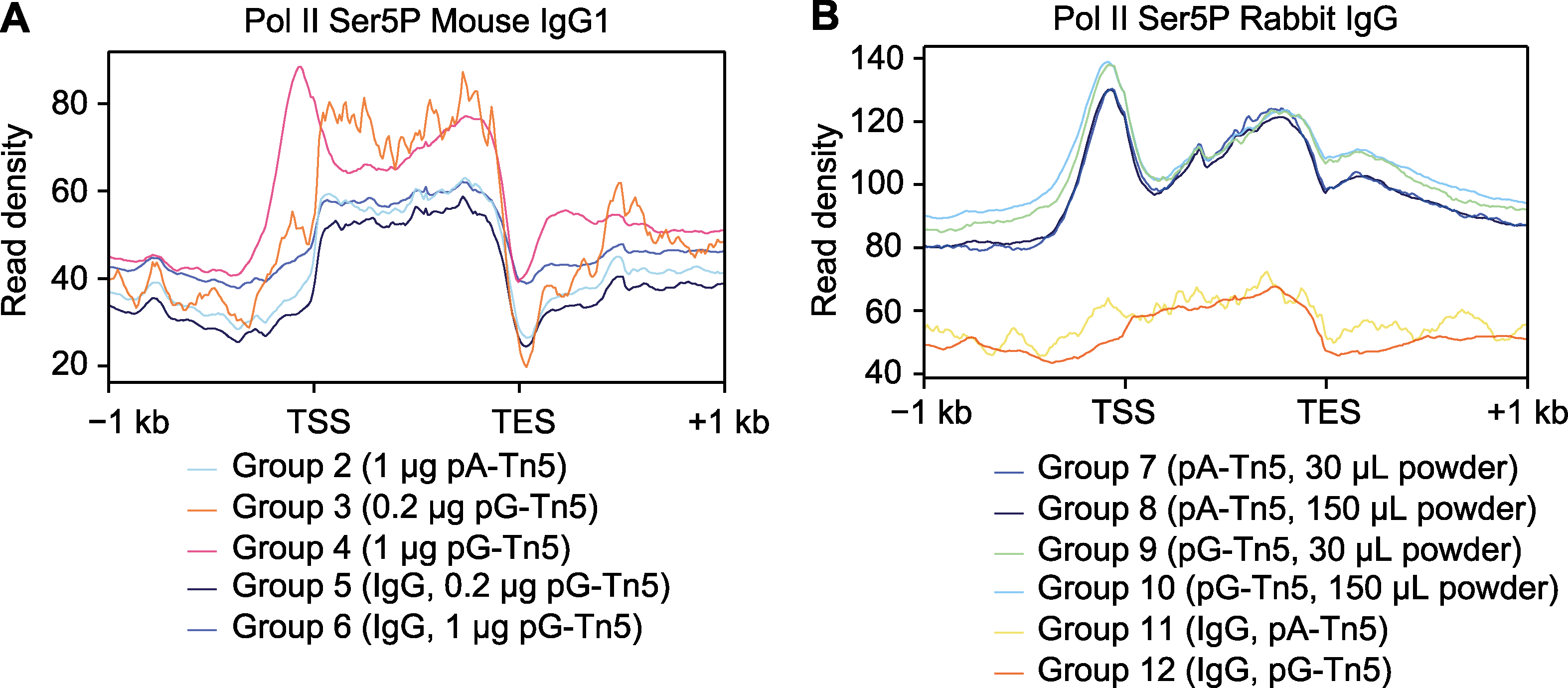
图4 CUT&Tag信号在基因上的平均分布 (A) 小鼠IgG1型抗体的CUT&Tag信号在基因上的平均分布; (B) 兔IgG型抗体的CUT&Tag信号在基因上的平均分布。TSS: 转录起始位点; TES: 转录终止位点
Figure 4 Average distribution of CUT&Tag signals on genes (A) Average distribution of CUT&Tag signals on genes of mouse IgG1 antibody; (B) Average distribution of CUT&Tag signals on genes of rabbit IgG antibody. TSS: Transcription start site; TES: Transcription end site
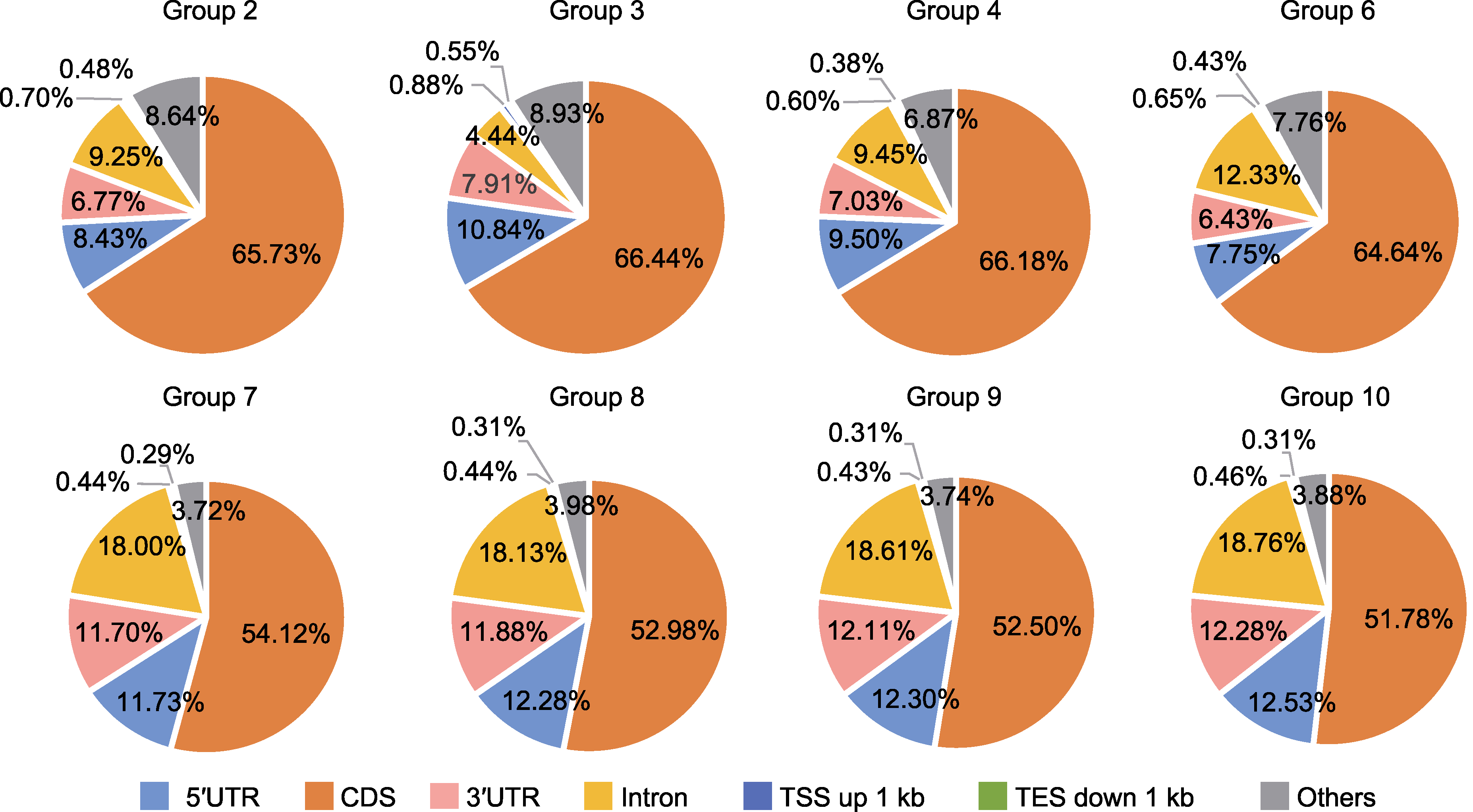
图5 CUT&Tag信号在染色体上的分布 CDS: 蛋白质编码区; 5′UTR: 5′非翻译区; 3′UTR: 3′非翻译区。TSS和TES同图4。Group 2、3、4、6、7、8、9和10同表2。
Figure 5 Distribution of CUT&Tag signals on chromosome CDS: Coding sequence; 5′UTR: 5′ untranslated region; 3′UTR: 3′ untranslated region. TSS and TES are the same as shown in Figure 4. Group 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 are the same as shown in Table 2.
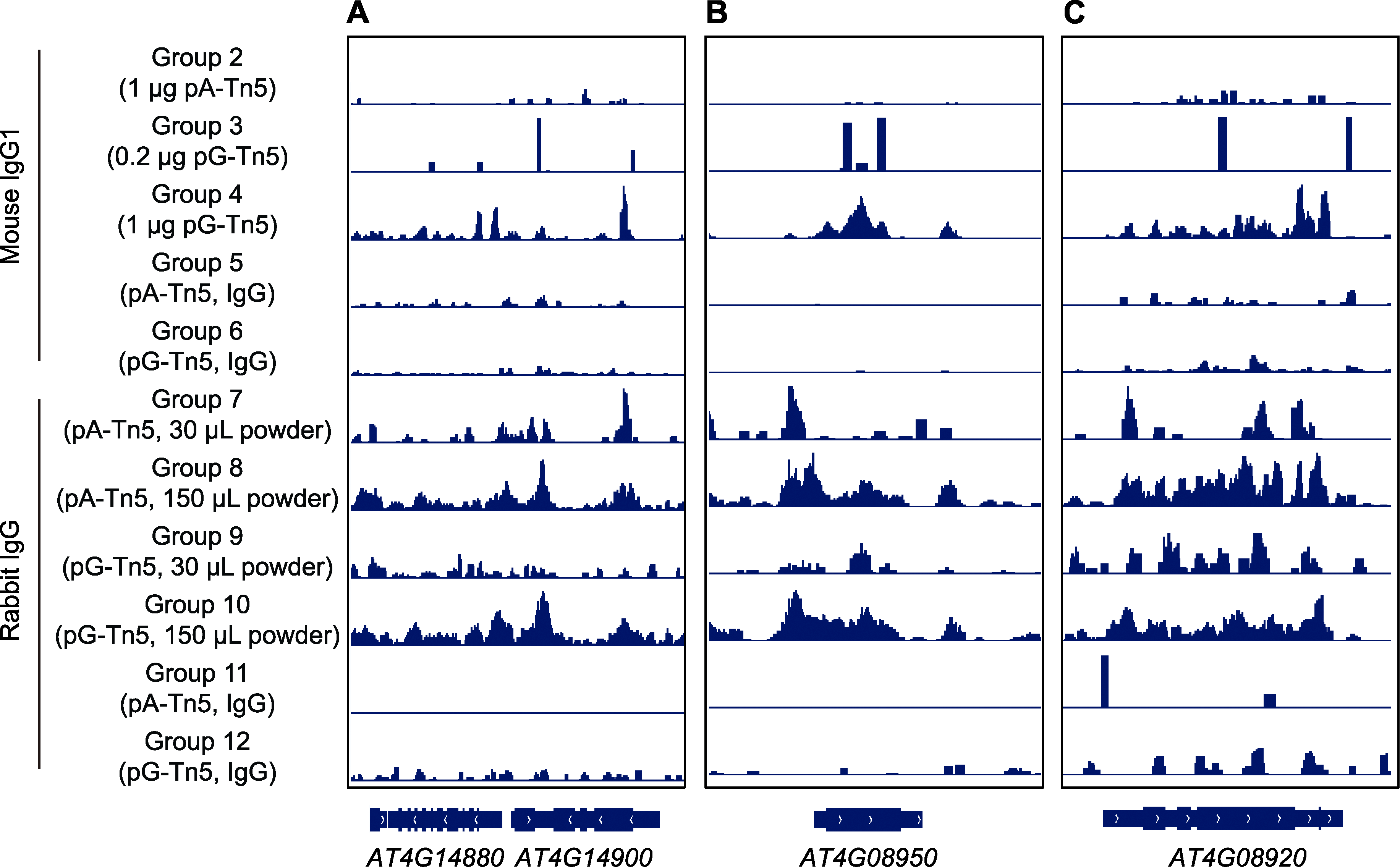
图6 利用IGV展示CUT&Tag信号在个别基因上的分布 (A) 基因AT4G14880-AT4G14900区段的CUT&Tag信号; (B) 磷响应蛋白基因EXO的CUT&Tag信号; (C) 蓝光受体基因CRY1的CUT&Tag信号。从上至下分别对应实验组2-12的实验数据。
Figure 6 Distribution of CUT&Tag signals on individual genes by IGV (A) CUT&Tag signal of gene AT4G14880 to AT4G14900; (B) CUT&Tag signals of phosphorus responsive protein gene EXO; (C) CUT&Tag signals of blue light receptor gene CRY1. From top to bottom, it corresponds to the experimental data of experimental groups 2-12.
| [1] |
陈威, 杨颖增, 陈锋, 周文冠, 舒凯 (2019). 表观遗传修饰介导的植物胁迫记忆. 植物学报 54, 779-785.
DOI |
| [2] |
杜康兮, 沈文辉, 董爱武 (2018). 表观遗传调控植物响应非生物胁迫的研究进展. 植物学报 53, 581-593.
DOI |
| [3] |
王泓力, 焦雨铃 (2020). 染色质免疫共沉淀实验方法. 植物学报 55, 475-480.
DOI |
| [4] |
杨同文, 李成伟 (2014). 植物叶片衰老的表观遗传调控. 植物学报 49, 729-737.
DOI |
| [5] |
Brahma S, Henikoff S (2019). RSC-associated subnucleosomes define MNase-sensitive promoters in yeast. Mol Cell 73, 238-249.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Buenrostro JD, Giresi PG, Zaba LC, Chang HY, Greenleaf WJ (2013). Transposition of native chromatin for fast and sensitive epigenomic profiling of open chromatin, DNA-binding proteins and nucleosome position. Nat Methods 10, 1213-1218.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Dancette OP, Taboureau JL, Tournier E, Charcosset C, Blond P (1999). Purification of immunoglobulins G by protein A/G affinity membrane chromatography. J Chromatogr B: Biomed Sci Appl 723, 61-68.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Di L, Fu Y, Sun YS, Li J, Liu L, Yao JC, Wang GB, Wu YL, Lao KQ, Lee RW, Zheng GH, Xu J, Oh J, Wang D, Xie XS, Huang YY, Wang JB (2020). RNA sequencing by direct tagmentation of RNA/DNA hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117, 2886-2893. |
| [9] |
Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M, Gingeras TR (2013). STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29, 15-21.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Kaya-Okur HS, Wu SJ, Codomo CA, Pledger ES, Bryson TD, Henikoff JG, Ahmad K, Henikoff S (2019). CUT& Tag for efficient epigenomic profiling of small samples and single cells. Nat Commun 10, 1930.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Kharchenko PV, Tolstorukov MY, Park PJ (2008). Design and analysis of ChIP-seq experiments for DNA-binding proteins. Nat Biotechnol 26, 1351-1359.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Lindmark R, Thorén-Tolling K, Sjöquist J (1983). Binding of immunoglobulins to protein A and immunoglobulin levels in mammalian sera. J Immunol Methods 62, 1-13.
PMID |
| [13] |
Lovell S, Goryshin IY, Reznikoff WR, Rayment I (2002). Two-metal active site binding of a Tn5 transposase synaptic complex. Nat Struct Biol 9, 278-281.
PMID |
| [14] | Martin M (2011). Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet.Journal 17, 10-12. |
| [15] | Meers MP, Bryson TD, Henikoff JG, Henikoff S (2019). Improved CUT&RUN chromatin profiling tools. eLife 8, e46314. |
| [16] | Ouyang WZ, Zhang XW, Peng Y, Zhang Q, Cao ZL, Li GL, Li XW (2021). Rapid and low-input profiling of histone marks in plants using nucleus CUT&Tag. Front Plant Sci 12, 734679. |
| [17] |
Picelli S, Björklund ÅK, Reinius B, Sagasser S, Winberg G, Sandberg R (2014). Tn5 transposase and tagmentation procedures for massively scaled sequencing projects. Genome Res 24, 2033-2040.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Ramírez F, Ryan DP, Grüning B, Bhardwaj V, Kilpert F, Richter AS, Heyne S, Dündar F, Manke T (2016). DeepTools2: a next generation web server for deep-sequencing data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 44, W160-W165. |
| [19] |
Schmidt D, Wilson MD, Spyrou C, Brown GD, Hadfield J, Odom DT (2009). ChIP-seq: using high-throughput sequencing to discover protein-DNA interactions. Methods 48, 240-248.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Skene PJ, Henikoff S (2017). An efficient targeted nuclease strategy for high-resolution mapping of DNA binding sites. eLife 6, e21856. |
| [21] |
Tao XY, Feng SL, Zhao T, Guan XY (2020). Efficient chromatin profiling of H3K4me3 modification in cotton using CUT&Tag. Plant Methods 16, 120.
DOI |
| [22] |
Thakur J, Henikoff S (2018). Unexpected conformational variations of the human centromeric chromatin complex. Genes Dev 32, 20-25.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Thorvaldsdóttir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP (2013). Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform 14, 178-192.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Wang LG, Wang SQ, Li W (2012). RSeQC: quality control of RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 28, 2184-2185.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Zheng XY, Gehring M (2019). Low-input chromatin profiling in Arabidopsis endosperm using CUT&RUN. Plant Reprod 32, 63-75.
DOI |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||