

植物学报 ›› 2015, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 628-636.DOI: 10.11983/CBB14119 cstr: 32102.14.CBB14119
收稿日期:2014-07-14
接受日期:2014-11-13
出版日期:2015-09-01
发布日期:2015-10-09
通讯作者:
陈彤
作者简介:? 共同第一作者
基金资助:Dongchao Ji, Kai Song, Jingjing Xing, Tong Chen*, Shiping Tian
Received:2014-07-14
Accepted:2014-11-13
Online:2015-09-01
Published:2015-10-09
Contact:
Chen Tong
About author:? These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 溶解素基序(LysM)是一类普遍存在于大多数有机体中的蛋白质结构域。植物细胞中含有LysM结构域的蛋白能够识别不同种类含有N-乙酰葡糖胺结构的配体分子, 从而启动植物对病原菌的特异防御反应。作为一种重要的模式识别受体, LysM结构域蛋白通过不同形式的寡聚化、受体类胞质激酶BIK1和MAPK级联反应向下游传递信号, 而病原菌能够通过其分泌的效应蛋白特异性识别或修饰模式识别受体, 规避植物细胞中病原体相关分子模式诱导的免疫反应。该文主要综述受体激酶/蛋白在病原菌激发子识别和防卫反应启动中的作用。
季东超, 宋凯, 邢晶晶, 陈彤, 田世平. LysM蛋白介导植物免疫防卫反应及其信号激发的研究进展. 植物学报, 2015, 50(5): 628-636.
Dongchao Ji, Kai Song, Jingjing Xing, Tong Chen, Shiping Tian. Studies of Innate Immunity Mediated by Lysin Motif Protein and Its Signaling Priming. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(5): 628-636.
| 基因名称 (别称) | 基因号 | LysM结构域布局 | 配体 | 受体 类型 | 是否为功能性 激酶(激酶类型) | 突变体对几 丁质处理 后的响应 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AtCERK1 (AtLYK1, LysM RLK1) | At3g21630 | I + II + IV | 几丁质 | LysM-RLK-I LYK | 是 (RD kinase) | 不敏感 | 参与肽聚糖感知; LjNFR1横向同源 |
| AtLYK2 | At3g01840 | * + * + V | 未知 | LysM-RLK-II LYR | 否 (Pseudo kinase) | 正常 | LjNFR5横向同源II |
| AtLYK3 | At1g51940 | * + VII + * | 未知 | LysM-RLK-I LYK | 是 (RD kinase) | 正常 | |
| AtLYK4 | At2g23770 | I + II + III | 几丁质 | LysM-RLK-II LYR | 否 (Pseudo kinase) | 中等敏感 | LjNFR5横向同源I |
| AtLYK5 | At2g33580 | I + II + III | 几丁质 | LysM-RLK-II LYR | 否 (Pseudo kinase) | 正常 | |
| AtLYP1 (CEBiP-like1, LYM2) | At2g17120 | * + VI + VII | 几丁质 | LYP | - | 正常 | C末端包含GPI锚定信号; OsCEBiP直系同源 |
| AtLYP2 (CEBiP-like2, LYM1) | At1g21880 | * + VI + VIII | 肽聚糖 | LYP | - | 正常 | C末端包含GPI锚定信号; 与OsLYP4和OsLYP6直系同源 |
| AtLYP3 (CEBiP-like3, LYM3) | At1g77630 | * + VI + VIII | 肽聚糖 | LYP | - | 正常 | C末端包含GPI锚定信号; 与OsLYP4和OsLYP6直系同源 |
表1 拟南芥基因组中的LysM受体激酶/蛋白(Mendes et al., 2011)
Table 1 LysM-containing receptors / proteins in Arabidopsis (Mendes et al., 2011)
| 基因名称 (别称) | 基因号 | LysM结构域布局 | 配体 | 受体 类型 | 是否为功能性 激酶(激酶类型) | 突变体对几 丁质处理 后的响应 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AtCERK1 (AtLYK1, LysM RLK1) | At3g21630 | I + II + IV | 几丁质 | LysM-RLK-I LYK | 是 (RD kinase) | 不敏感 | 参与肽聚糖感知; LjNFR1横向同源 |
| AtLYK2 | At3g01840 | * + * + V | 未知 | LysM-RLK-II LYR | 否 (Pseudo kinase) | 正常 | LjNFR5横向同源II |
| AtLYK3 | At1g51940 | * + VII + * | 未知 | LysM-RLK-I LYK | 是 (RD kinase) | 正常 | |
| AtLYK4 | At2g23770 | I + II + III | 几丁质 | LysM-RLK-II LYR | 否 (Pseudo kinase) | 中等敏感 | LjNFR5横向同源I |
| AtLYK5 | At2g33580 | I + II + III | 几丁质 | LysM-RLK-II LYR | 否 (Pseudo kinase) | 正常 | |
| AtLYP1 (CEBiP-like1, LYM2) | At2g17120 | * + VI + VII | 几丁质 | LYP | - | 正常 | C末端包含GPI锚定信号; OsCEBiP直系同源 |
| AtLYP2 (CEBiP-like2, LYM1) | At1g21880 | * + VI + VIII | 肽聚糖 | LYP | - | 正常 | C末端包含GPI锚定信号; 与OsLYP4和OsLYP6直系同源 |
| AtLYP3 (CEBiP-like3, LYM3) | At1g77630 | * + VI + VIII | 肽聚糖 | LYP | - | 正常 | C末端包含GPI锚定信号; 与OsLYP4和OsLYP6直系同源 |
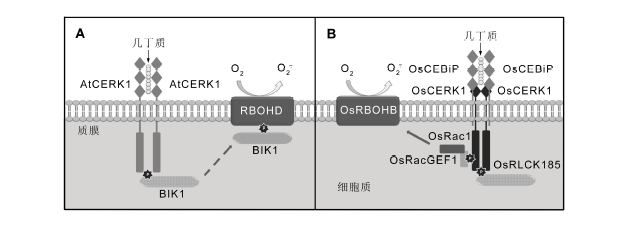
图1 拟南芥和水稻中CERK1受体复合物及可能的信号激发机制(改自Macho and Zipfel, 2014) (A) 几丁质诱导AtCERK1同源二聚化和激活, 在此过程中BIK1对于NADPH氧化酶产生活性氧爆发是必需的; (B) 水稻中的几丁质受体复合物由OsCEBiP、OsCERK1和一些相关的胞质蛋白组成; 受几丁质刺激后, OsCERK1磷酸化OsRLCK185, 后者从受体复合物上解离下来并参与下游信号转导; 另外, OsCERK1激活OsRacGEF1/OsRac1, 从而引起活性氧爆发。CERK1: 几丁质激发子受体激酶; CEBiP: 几丁质激发子结合蛋白; BIK1: 葡萄胞属诱导激酶1; GEF1: 鸟嘌呤交换因子1; RLCK185: 细胞质类受体激酶185
Figure 1 CERK1 receptor complexes and signaling mechanism in Arabidopsis and rice (modified from Macho and Zipfel, 2014)(A) Chitin induces AtCERK1 homo-dimerization and activation, while BIK1 is required for subsequent reactive oxygen species burst from NADPH oxidase (RBOHD) during this process; (B) The chitin receptor complex is composed of OsCEBiP, OsCERK1 and several associated cytoplasmic proteins in rice; Upon stimuli from chitin, OsCERK1 phosphorylates OsRLCK185, which is released from the receptor complex and contributes to down-streaming signal transduction; Additionally, OsCERK1 activates the OsRacGEF1/OsRac1, which contributes to chitin-induced ROS burst. CERK1: Chitin elicitor receptor kinase1; CEBiP: Chitin elicitor binding protein; BIK1: Botrytis-induced kinase1; GEF1: Guanine exchange factor1; RLCK185: Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase185
| 1 | 陈晓亚, 薛红卫 (2012). 植物生理与分子生物学(第4版). 北京: 高等教育出版社. pp. 695-698. |
| 2 | 江聪, 黄敏仁, 徐立安 (2014). LysM结构域及其与植物-真菌相互作用的关系. 植物学报 49, 221-228. |
| 3 | Arrighi JF, Barre A, Ben Amor B, Bersoult A, Soriano LC, Mirabella R, de Carvalho-Niebel F, Journet EP, Ghérardi M, Huguet T, Geurts R, Dénarié J, Rougé P, Gough C (2006). The Medicago truncatula lysine motif- receptor-like kinase gene family includes NFP and new nodule-expressed genes.Plant Physiol 142, 265-279. |
| 4 | Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu WL, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, Sheen J (2002). MAP kinase signaling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity.Nature 415, 977-983. |
| 5 | Bateman A, Bycroft M (2000). The structure of a LysM domain from E. coli membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D (MltD).J Mol Biol 299, 1113-1119. |
| 6 | Bielnicki J, Devedjiev Y, Derewenda U, Dauter Z, Joachimiak A, Derewenda ZS (2006). B. subtilis ykuD protein at 2.0 Å resolution: insights into the structure and function of a novel, ubiquitous family of bacterial enzy- mes.Proteins 62, 144-151. |
| 7 | Boller T, Felix G (2009). A renaissance of elicitors: perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors.Annu Rev Plant Biol 60, 379-406. |
| 8 | Buist G, Kok J, Leenhouts KJ, Dabrowska M, Venema G, Haandrikman AJ (1995). Molecular cloning and nucleo- tide sequence of the gene encoding the major peptidoglycan hydrolase of Lactococcus lactis, a muramidase needed for cell separation.J Bacteriol 177, 1554-1563. |
| 9 | Buist G, Steen A, Kok J, Kuipers OP (2008). LysM, a widely distributed protein motif for binding to (peptido) glycans.Mol Microbiol 68, 838-847. |
| 10 | Chen LT, Hamada S, Fujiwara M, Zhu TH, Thao NP, Wong HL, Krishna P, Ueda T, Kaku H, Shibuya N, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K (2010). The Hop/Sti1-Hsp90 chaperone complex facilitates the maturation and transport of a PAMP receptor in rice innate immunity.Cell Host Microbe 7, 185-196. |
| 11 | de Jonge R, van Esse HP, Kombrink A, Shinya T, Desaki Y, Bours R, van der Krol S, Shibuya N, Joosten MHAJ, Thomma BPHJ (2010). Conserved fungal LysM effector Ecp6 prevents chitin-triggered immunity in plants.Science 329, 953-955. |
| 12 | De Wit PJGM, Mehrabi R, Van Den Burg HA, Stergio- poulos I (2009). Fungal effector proteins: past, present and future.Mol Plant Pathol 10, 735-747. |
| 13 | Dou DL, Zhou JM (2012). Phytopathogen effectors sub- verting host immunity: different foes, similar battleground.Cell Host Microbe 12, 484-495. |
| 14 | Erbs G, Silipo A, Aslam S, De Castro C, Liparoti V, Flagiello A, Pucci P, Lanzetta R, Parrilli M, Molinaro A, Newman MA, Cooper RM (2008). Peptidoglycan and muropeptides from pathogens Agrobacterium and Xanthomonas elicit plant innate immunity: structure and activity. Chem Biol 15, 438-448. |
| 15 | Faulkner C, Petutschnig E, Benitez-Alfonso Y, Beck M, Robatzek S, Lipka V, Maule AJ (2013). LYM2-depend- ent chitin perception limits molecular flux via plasmo- desmata.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 9166-9170. |
| 16 | Felix G, Regenass G, Boller T (1993). Specific perception of subnanomolar concentrations of chitin fragments by tomato cells: induction of extracellular alkalinization, changes in protein phosphorylation, and establishment of a refractory state.Plant J 4, 307-316. |
| 17 | Fliegmann J, Uhlenbroich S, Shinya T, Martinez Y, Lefebvre B, Shibuya N, Bono JJ (2011). Biochemical and phylogenetic analysis of CEBiP-like LysM domain- containing extracellular proteins in higher plants.Plant Physiol Biochem 49, 709-720. |
| 18 | Gimenez-Ibanez S, Hann DR, Ntoukakis V, Petutschnig E, Lipka V, Rathjen JP (2009). AvrPtoB targets the lysM receptor kinase CERK1 to promote bacterial virulence on plants.Curr Biol 19, 423-429. |
| 19 | Glauner B, Höltje JV, Schwarz U (1988). The composition of the murein of Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem 263, 10088-10095. |
| 20 | Gough C, Cullimore J (2011). Lipo-chitooligosaccharide signaling in endosymbiotic plant-microbe interactions.Mol Plant Microbe Interact 24, 867-878. |
| 21 | Gust AA, Biswas R, Lenz HD, Rauhut T, Ranf S, Kemmerling B, Götz F, Glawischnig E, Lee J, Felix G, Nürnberger T (2007). Bacteria-derived peptidoglycans constitute pathogen-associated molecular patterns trig- gering innate immunity in Arabidopsis.J Biol Chem 282, 32338-32348. |
| 22 | Gust AA, Willmann R, Desaki Y, Grabherr HM, Nürnberger T (2012). Plant LysM proteins: modules mediating symbiosis and immunity.Trends Plant Sci 17, 495-502. |
| 23 | Hamel LP, Beaudoin N (2010). Chitooligosaccharide sensing and downstream signaling: contrasted outcomes in pathogenic and beneficial plant-microbe interactions.Planta 232, 787-806. |
| 24 | Hayafune M, Berisio R, Marchetti R, Silipo A, Kayama M, Desaki Y, Arima S, Squeglia F, Ruggiero A, Tokuyasu K, Molinaro A, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2014). Chitin-induced activation of immune signaling by the rice receptor CEBiP relies on a unique sandwich-type dimerization.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, E404-E413. |
| 25 | Ichimura K, Shinozaki K, Tena G, Sheen J, Henry Y, Champion A, Kreis M, Zhang SQ, Hirt H, Wilson C, Heberle-Bors E, Ellis BE, Morris PC, Innes RW, Ecker JR, Scheel D, Klessig DF, Machida Y, Mundy J, Ohashi Y, Walker JC (2002). Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature.Trends Plant Sci 7, 301-308. |
| 26 | Iriti M, Faoro F (2009). Chitosan as a MAMP, searching for a PRR.Plant Signal Behav 4, 66-68. |
| 27 | Kaku H, Nishizawa Y, Ishii-Minami N, Akimoto-Tomiyama C, Dohmae N, Takio K, Minami E, Shibuya N (2006). Plant cells recognize chitin fragments for defense signal- ing through a plasma membrane receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 11086-11091. |
| 28 | Kim SH, Oikawa T, Kyozuka J, Wong HL, Umemura K, Kishi-Kaboshi M, Takahshi A, Kawano Y, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K (2012). The bHLH Rac immunity 1 (RAI 1) is activated by OsRac1 via OsMAPK3 and MAPK6 in rice immunity.Plant Cell Physiol 53, 740-754. |
| 29 | Kishimoto K, Kouzai Y, Kaku H, Shibuya N, Minami E, Nishizawa Y (2010). Perception of the chitin oligosac- charides contributes to disease resistance to blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae in rice.Plant J 64, 343-354. |
| 30 | Kombrink A, Sánchez-Vallet A, Thomma BPHJ (2011). The role of chitin detection in plant-pathogen interactions.Microbes Infect 13, 1168-1176. |
| 31 | Lieberherr D, Thao NP, Nakashima A, Umemura K, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K (2005). A sphingolipid elicitor-inducible mitogen-activated protein kinase is regulated by the small GTPase OsRac1 and heterotrimeric G- protein in rice.Plant Physiol 138, 1644-1652. |
| 32 | Limpens E, Franken C, Smit P, Willemse J, Bisseling T, Geurts R (2003). LysM domain receptor kinases regulat- ing rhizobial Nod factor-induced infection.Science 302, 630-633. |
| 33 | Liu B, Li JF, Ao Y, Qu JW, Li ZQ, Su JB, Zhang Y, Liu J, Feng DR, Qi KB, He YM, Wang JF, Wang HB (2012a). Lysin motif-containing proteins LYP4 and LYP6 play dual roles in peptidoglycan and chitin perception in rice innate immunity.Plant Cell 24, 3406-3419. |
| 34 | Liu TT, Liu ZX, Song CJ, Hu YF, Han ZF, She J, Fan FF, Wang JW, Jin CW, Chang JB, Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2012b). Chitin-induced dimerization activates a plant immune receptor.Science 336, 1160-1164. |
| 35 | Macho AP, Zipfel C (2014). Plant PRRs and the activation of innate immune signaling.Mol Cell 54, 263-272. |
| 36 | Madsen EB, Madsen LH, Radutoiu S, Olbryt M, Rakwalska M, Szczyglowski K, Sato S, Kaneko T, Tabata S, Sandal N, Stougaard J (2003). A receptor kinase gene of the LysM type is involved in legume perception of rhizobial signals.Nature 425, 637-640. |
| 37 | Mendes R, Kruijt M, de Bruijn I, Dekkers E, van der Voort M, Schneider JHM, Piceno YM, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Bakker PAHM, Raaijmakers JM (2011). Deciphering the rhizosphere microbiome for disease-suppressive bacteria.Science 332, 1097-1100. |
| 38 | Miya A, Albert P, Shinya T, Desaki Y, Ichimura K, Shirasu K, Narusaka Y, Kawakami N, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2007). CERK1, a LysM receptor kinase, is essential for chitin elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 19613-19618. |
| 39 | Mulder L, Lefebvre B, Cullimore J, Imberty A (2006). LysM domains of Medicago truncatula NFP protein involved in Nod factor perception. Glycosylation state, molecular modeling and docking of chitooligosaccharides and Nod factors.Glycobiology 16, 801-809. |
| 40 | Nürnberger T, Brunner F, Kemmerling B, Piater L (2004). Innate immunity in plants and animals: striking similarities and obvious differences.Immunol Rev 198, 249-266. |
| 41 | Ohnuma T, Onaga S, Murata K, Taira T, Katoh E (2008). LysM domains from Pteris ryukyuensis chitinase-A: a stability study and characterization of the chitin-binding site.J Biol Chem 283, 5178-5187. |
| 42 | Oldroyd GED, Robatzek S (2011). The broad spectrum of plant associations with other organisms.Curr Opin Plant Biol 14, 347-350. |
| 43 | Ono E, Wong HL, Kawasaki T, Hasegawa M, Kodama O, Shimamoto K (2001). Essential role of the small GTPase Rac in disease resistance of rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 759-764. |
| 44 | Op den Camp R, Streng A, De Mita S, Cao QQ, Polone E, Liu W, Ammiraju JSS, Kudrna D, Wing R, Untergasser A, Bisseling T, Geurts R (2011). LysM-type mycorrhizal receptor recruited for rhizobium symbiosis in nonlegume Parasponia.Science 331, 909-912. |
| 45 | Petutschnig EK, Jones AME, Serazetdinova L, Lipka U, Lipka V (2010). The lysin motif receptor-like kinase (LysM-RLK) CERK1 is a major chitin-binding protein in Arabidopsis thaliana and subject to chitin-induced phosphorylation.J Biol Chem 285, 28902-28911. |
| 46 | Ponting CP, Aravind L, Schultz J, Bork P, Koonin EV (1999). Eukaryotic signaling domain homologues in archaea and bacteria. Ancient ancestry and horizontal gene transfer.J Mol Biol 289, 729-745. |
| 47 | Radutoiu S, Madsen LH, Madsen EB, Felle HH, Umehara Y, Grønlund M, Sato S, Nakamura Y, Tabata S, Sandal N, Stougaard J (2003). Plant recognition of symbiotic bacteria requires two LysM receptor-like kinases.Nature 425, 585-592. |
| 48 | Ren YY, West CA (1992). Elicitation of diterpene biosynthesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by chitin.Plant Physiol 99, 1169-1178. |
| 49 | Schleifer KH, Kandler O (1972). Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications.Bacteriol Rev 36, 407-477. |
| 50 | Shibuya N, Minami E (2001). Oligosaccharide signaling for defence responses in plant.Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 59, 223-233. |
| 51 | Shimizu T, Nakano T, Takamizawa D, Desaki Y, Ishii- Minami N, Nishizawa Y, Minami E, Okada K, Yamane H, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2010). Two LysM receptor molecules, CEBiP and OsCERK1, cooperatively regulate chitin elicitor signaling in rice.Plant J 64, 204-214. |
| 52 | Shinya T, Yamaguchi K, Desaki Y, Yamada K, Narisawa T, Kobayashi Y, Maeda K, Suzuki M, Tanimoto T, Takeda J, Nakashima M, Funama R, Narusaka M, Narusaka Y, Kaku H, Kawasaki T, Shibuya N (2014). Selective regulation of the chitin-induced defense response by the Arabidopsis receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase PBL27.Plant J 79, 56-66. |
| 53 | Shiya T, Motoyama N, Ikeda A, Wada M, Kamiya K, Hayafune M, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2012). Functional characterization of CEBiP and CERK1 homologs in Arabidopsis and rice reveals the presence of different chitin receptor systems in plants.Plant Cell Physiol 53, 1696-1706. |
| 54 | Tanaka K, Nguyen CT, Liang Y, Cao YR, Stacey G (2013). Role of LysM receptors in chitin-triggered plant innate immunity.Plant Signal Behav 8, e22598. |
| 55 | Tena G, Boudsocq M, Sheen J (2011). Protein kinase signaling networks in plant innate immunity.Curr Opin Plant Biol 14, 519-529. |
| 56 | van den Burg HA, Harrison SJ, Joosten MHAJ, Vervoort J, de Wit PJGM (2006). Cladosporium fulvum Avr4 protects fungal cell walls against hydrolysis by plant chitinases accumulating during infection.Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19, 1420-1430. |
| 57 | van Esse HP, Bolton MD, Stergiopoulos L, de Wit PJGM, Thomma BPHJ (2007). The chitin-binding Cladosporium fulvum effector protein Avr4 is a virulence factor.Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20, 1092-1101. |
| 58 | Wan JR, Tanaka K, Zhang XC, Son GH, Brechenmacher L, Nguyen THN, Stacey G (2012). LYK4, a lysin motif receptor-like kinase, is important for chitin signaling and plant innate immunity in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 160, 396-406. |
| 59 | Wan JR, Zhang SQ, Stacey G (2004). Activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in Arabidopsis by chitin.Mol Plant Pathol 5, 125-135. |
| 60 | Wan JR, Zhang XC, Neece D, Ramonell KM, Clough S, Kim SY, Stacey MG, Stacey G (2008). A LysM receptor-like kinase plays a critical role in chitin signaling and fungal resistance in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 20, 471-481. |
| 61 | Willmann R, Lajunen HM, Erbs G, Newman MA, Kolb D, Tsuda K, Katagiri F, Fliegmann J, Bono JJ, Cullimore JV, Jehle AK, Götz F, Kulik A, Molinaro A, Lipka V, Gust AA, Nürnberger T (2011). Arabidopsis lysin-motif proteins LYM1 LYM3 CERK1 mediate bacterial peptidoglycan sensing and immunity to bacterial infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 19824-19829. |
| 62 | Yamaguchi K, Yamada K, Ishikawa K, Yoshimura S, Hayashi N, Uchihashi K, Ishihama N, Kishi-Kaboshi M, Takahashi A, Tsuge S, Ochiai H, Tada Y, Shimanoto K, Yoshioka H, Kawasaki T (2013). A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase targeted by a plant pathogen effector is directly phosphorylated by the chitin receptor and mediates rice immunity.Cell Host Microbe 13, 347-357. |
| 63 | Yamaguchi T, Minami E, Ueki J, Shibuya N (2005). Elicitor-induced activation of phospholipases plays an important role for the induction of defense responses in suspension-cultured rice cells.Plant Cell Physiol 46, 579-587. |
| 64 | Zhang B, Ramonell K, Somerville S, Stacey G (2002). Characterization of early, chitin-induced gene expression in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15, 963-970. |
| 65 | Zhang J, Li W, Xiang TT, Liu ZX, Laluk K, Ding XJ, Zou Y, Gao MH, Zhang XJ, Chen S, Mengiste T, Zhang YL, Zhou JM (2010). Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases integrate signaling from multiple plant immune receptors and are targeted by a Pseudomonas syringae effector.Cell Host Microbe 7, 290-301. |
| 66 | Zhang XC, Cannon SB, Stacey G (2009). Evolutionary genomics of LysM genes in land plants.BMC Evol Biol 9, 183. |
| 67 | Zipfel C (2008). Pattern-recognition receptors in plant innate immunity.Curr Opin Immunol 20, 10-16. |
| 68 | ——————————————— |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
