

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2016, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 849-858.DOI: 10.11983/CBB15149 cstr: 32102.14.CBB15149
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jinhong Yuan1,2, Jingrui Li2,3, Haiyan Zhang1,2*
Received:2015-08-14
Accepted:2016-02-01
Online:2016-11-01
Published:2016-12-02
Contact:
Zhang Haiyan
About author:# Co-first authors
Jinhong Yuan, Jingrui Li, Haiyan Zhang. Structure and Function of Copper Transporters in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(6): 849-858.
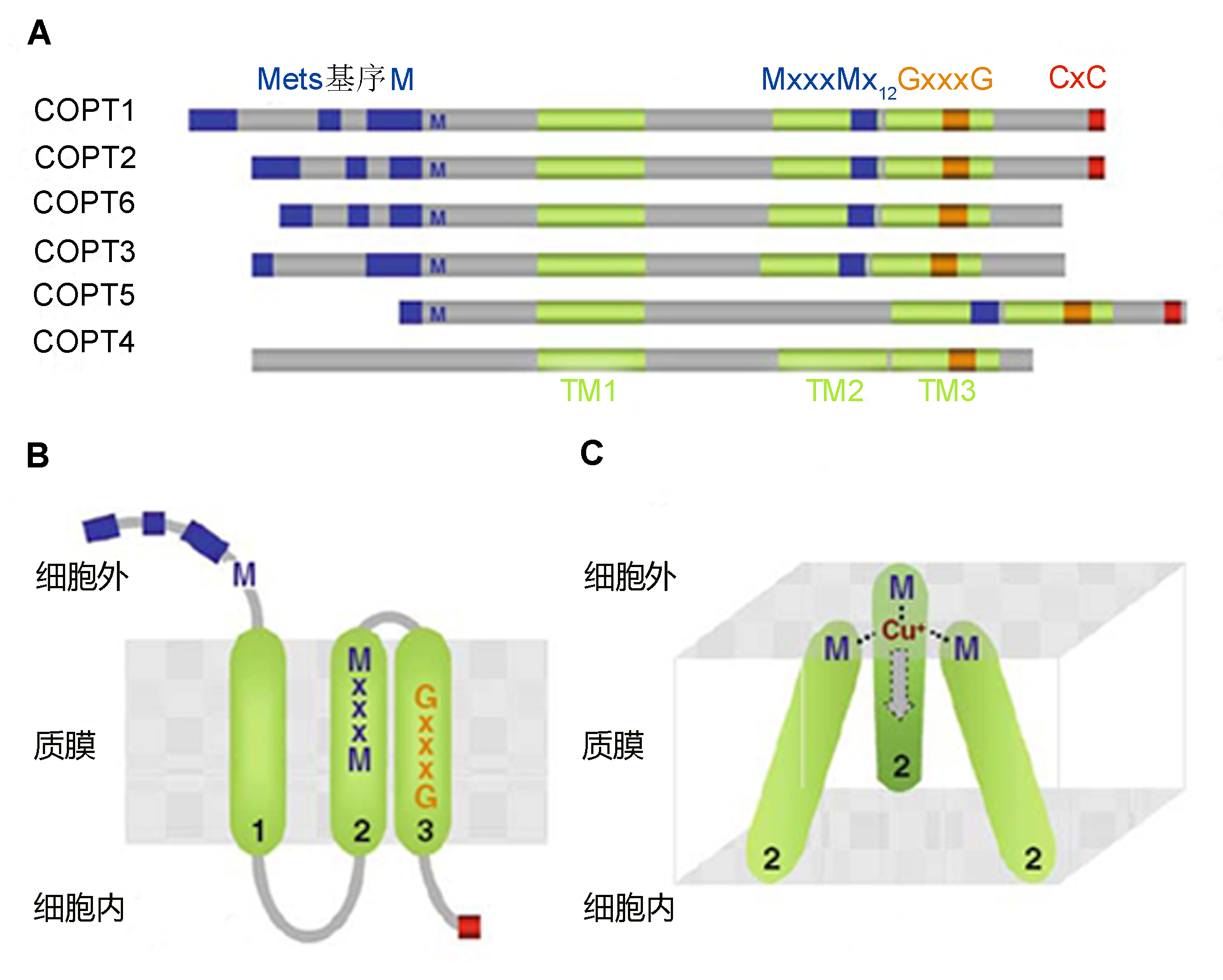
Figure 1 The COPT family of Cu transport proteins (modified from Peñarrubia et al., 2010)(A) Alignment of the putative Arabidopsis thaliana COPT Cu transporters; (B) The proposed topological structure of the COPT proteins; (C) The spatial disposition of TM2 in the human Ctr1 homotrimer complex. M: Met; G: Gly; C: Cys
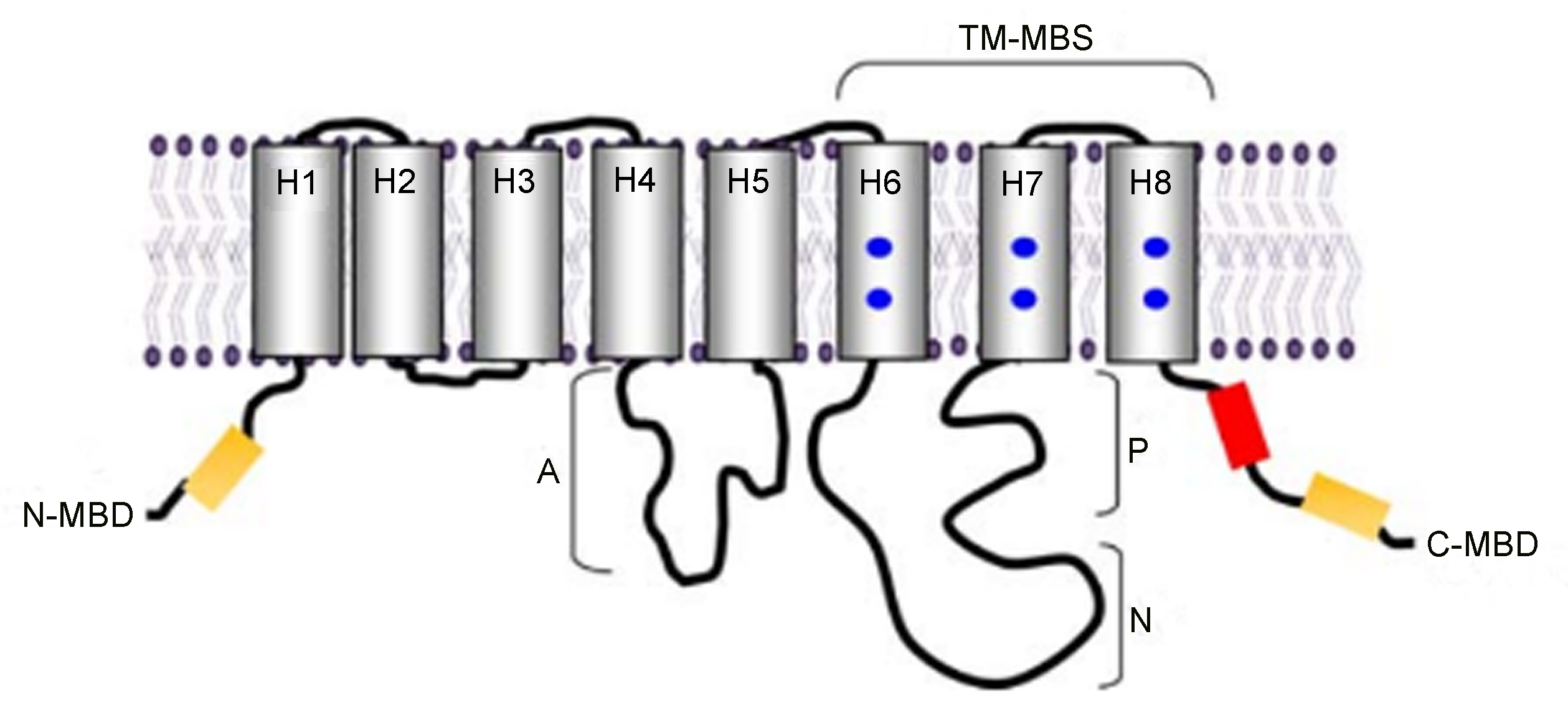
Figure 2 Schematic illustration of the topology and main domains present in P1B-type ATPases (Arguello et al., 2007)H1-H8: Transmembrane segments; TM-MBS: Transmembrane metal binding sites; N-MBD: N-terminal metal binding domain; C-MBD: C-terminal metal binding domain. A, P and N: The maindo-mains present in P1B-type ATPases
| [1] | 陈涛, 张劲松 (2006). 乙烯的生物合成与信号传递. 植物学通报 23, 519-530. |
| [2] | 房茜, 李鹏, 靳思, 印莉萍 (2007). 酵母和植物中铜的转运系统及其调控. 植物学通报 24, 807-815. |
| [3] | 贺瑶, 周惜时, 夏妍, 郭攀, 王桂萍, 沈振国, 陈亚华 (2015). 铜排斥型植物黄花月见草(Oenothera glazioviana)对铜胁迫的响应以及在铜污染土壤上的合理利用. 农业环境科学学报 34, 449-460. |
| [4] | 金勇, 付庆灵, 郑进, 康薇, 刘永红, 胡红青 (2012). 超积累植物修复铜污染土壤的研究现状. 中国农业科技导报 14, 93-100. |
| [5] | 唐莲, 刘振中, 蒋任飞 (2003). 重金属污染土壤植物修复法. 环境保护科学 29, 33-36. |
| [6] | 王夏芳 (2015). 铜离子对环境危害现状及对策研究. 国土与自然资源研究 1, 55-57. |
| [7] | 王兆苏, 王新军, 陈学萍, 朱永官 (2015). 微生物铁氧化作用对砷迁移转化的影响. 环境科学学报 31, 328-333. |
| [8] | 伍自力, 余孟瑶, 陈露, 魏静, 王晓琴, 胡勇, 闫妍, 万平 (2015). 小立碗藓对重金属镉胁迫的应答特征. 植物学报50, 171-179. |
| [9] | 袁祖丽, 孙晓楠, 刘秀敏 (2008). 植物耐受和解除重金属毒性研究进展. 生态环境 17, 2494-2502. |
| [10] | 张红晓, 张芬琴 (2011). 铜在植物细胞中的运输和分布. 洛阳理工学院学报 21, 1-5. |
| [11] | 张玉秀, 张媛雅, 孙涛, 柴团耀 (2010). 植物重金属转运蛋白P1B-ATPase结构和功能研究进展. 生物工程学报 26, 715-725. |
| [12] | 赵雪芹, 张海燕, 刘维仲 (2012). 植物铜转运相关蛋白研究进展. 广西植物 32, 280-284. |
| [13] | 钟茜, 李韶山 (2013). 水稻P1B-型ATPase重金属转运蛋白的结构与功能研究进展. 宁夏师范学院学报 34, 62-69. |
| [14] | Abdel-Ghany SE, Burkhead JL, Gogolin KA, Andres- Colas N, Bodecker JR, Puig S, Peñarrubia L, Pilon M (2005a). AtCCS is a functional homolog of the yeast copper chaperone Ccs1/Lys7.FEBS Lett 579, 2307-2312. |
| [15] | Abdel-Ghany SE, Muller-Moule P, Niyogi KK, Pilon M, Shikanai T (2005b). Two P-type ATPases are required for copper delivery in Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts.Plant Cell 17, 1233-1251. |
| [16] | Andres-Colas N, Perea-Garcia A, Puig S, Peñarrubia L (2010). Deregulated copper transport affects Arabidopsis development especially in the absence of environmental cycles.Plant Physiol 153, 170-184. |
| [17] | Andrés-Colás N, Sancenón V, Rodriguez-Navarro S, Mayo S, Thiele DJ, Ecker JR, Puig S, Peñarrubia L (2006). The Arabidopsis heavy metal P-type ATPase HMA5 interacts with metallochaperones and functions in copper detoxification of roots.Plant J 45, 225-236. |
| [18] | Arguello JM, Eren E, Gonzalez-Guerrero M (2007). The structure and function of heavy metal transport P1B-ATP- ases.Biometals 20, 233-248. |
| [19] | Axelsen KB, Palmgren MG (2001). Inventory of the superfamily of P-type ion pumps in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 126, 696-706. |
| [20] | Balandin T, Castresana C (2002). AtCOX17, an Arabidopsis homolog of the yeast copper chaperone COX17.Plant Physiol 129, 1852-1857. |
| [21] | Beard SJ, Hashim R, Membrillo-Hernández J, Hughes MN, Poole RK (1997). Zinc(II) tolerance in Escherich coli K-12: evidence that the zntA gene (o732) encodes a cation transport ATPase.Mol Microbiol 25, 883-891. |
| [22] | Blaby-Haas CE, Padilla-Benavides T, Stube R, Arguello JM, Merchant SS (2014). Evolution of a plant-specific copper chaperone family for chloroplast copper homeostasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, E5480-E5487. |
| [23] | Brumbarova T, Bauer P, Ivanov R (2015). Molecular mechanisms governing Arabidopsis iron uptake.Trends Plant Sci 20, 124-133. |
| [24] | Burkhead JL, Reynolds KAG, Abdel-Ghany SE, Cohu CM, Pilon M (2009). Copper homeostasis.New Phytol 182, 799-816. |
| [25] | Carrio-Segui A, Garcia-Molina A, Sanz A, Peñarrubia L (2015). Defective copper transport in the copt5 mutant affects cadmium tolerance.Plant Cell Physiol 56, 442-454. |
| [26] | Changela A, Chen K, Xue Y, Holschen J, Outten CE, O’Halloran TV, Mondragon A (2003). Molecular basis of metal-ion selectivity and zeptomolar sensitivity by CueR.Science 301, 1383-1387. |
| [27] | Chu HH, Chiecko J, Punshon T, Lanzirotti A, Lahner B, Salt DE, Walker EL (2010). Successful reproduction requires the function of Arabidopsis Yellow Stripe-Like1 and Yellow Stripe-Like3 metal-nicotianamine transporters in both vegetative and reproductive structures.Plant Physiol 154, 197-210. |
| [28] | Colangelo EP, Guerinot ML (2006). Put the metal to the petal: metal uptake and transport throughout plants.Curr Opin Plant Biol 9, 322-330. |
| [29] | Deng F, Yamaji N, Xia J, Ma JF (2013). A member of the heavy metal P-type ATPase OsHMA5 is involved in xylem loading of copper in rice.Plant Physiol 163, 1353-1362. |
| [30] | DiDonato Jr RJ, Roberts LA, Sanderson T, Eisley RB, Walker EL (2004). Arabidopsis Yellow Stripe-Like2 (YSL2): a metal-regulated gene encoding a plasma mem- brane transporter of nicotianamine-metal complexes.Plant J 39, 403-414. |
| [31] | Garcia-Molina A, Andres-Colas N, Perea-Garcia A, del Valle-Tascon S, Peñarrubia L, Puig S (2011). The intracellular Arabidopsis COPT5 transport protein is required for photosynthetic electron transport under severe copper deficiency.Plant J 65, 848-860. |
| [32] | Garcia-Molina A, Andres-Colas N, Perea-Garcia A, Neumann U, Dodani SC, Huijser P, Peñarrubia L, Puig S (2013). The Arabidopsis COPT6 transport protein functions in copper distribution under copper-deficient conditions.Plant Cell Physiol 54, 1378-1390. |
| [33] | Garcia L, Welchen E, Gonzalez DH (2014). Mitochondria and copper homeostasis in plants.Mitochondrion 19, 269-274. |
| [34] | Gratao PL, Polle A, Lea PJ, Azevedo RA (2005). Making the life of heavy metal-stressed plants a little easier.Funct Plant Biol 32, 481-494. |
| [35] | Guerinot ML (2000). The ZIP family of metal transporters.BBA-Biomembranes 1465, 190-198. |
| [36] | Hansch R, Mendel RR (2009). Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl).Curr Opin Plant Biol 12, 259-266. |
| [37] | Himelblau E, Mira H, Lin SJ, Culotta VC, Peñarrubia L, Amasino RM (1998). Identification of a functional homolog of the yeast copper homeostasis gene ATX1 from Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 117, 1227-1234. |
| [38] | Jung HI, Gayomba SR, Rutzke MA, Craft E, Kochian LV, Vatamaniuk OK (2012). COPT6 is a plasma membrane transporter that functions in copper homeostasis in Arabidopsis and is a novel target of SQUAMOSA promoter-binding protein-like 7.J Biol Chem 287, 33252-33267. |
| [39] | Koike S, Inoue H, Mizuno D, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2004). OsYSL2 is a rice metal- nicotianamine transporter that is regulated by iron and expressed in the phloem.Plant J 39, 415-424. |
| [40] | Lee S, Kim YY, Lee Y, An G (2007). Rice P1B-type heavy-metal ATPase, OsHMA9, is a metal efflux protein.Plant Physiol 145, 831-842. |
| [41] | Li HX, Fan R, Li LB, Wei B, Li GL, Gu LQ, Wang XP, Zhang XQ (2014). Identification and characterization of a novel copper transporter gene family TaCT1 in common wheat.Plant Cell Environ 37, 1561-1573. |
| [42] | Migocka M (2015). Copper-transporting ATPases: the evolutionarily conserved machineries for balancing copper in living systems.IUBMB Life 67, 737-745. |
| [43] | Mills RF, Krijger GC, Baccarini PJ, Hall JL, Williams LE (2003). Functional expression of AtHMA4, a P1B-type ATPase of the Zn/Co/Cd/Pb subclass.Plant J 35, 164-176. |
| [44] | Milner MJ, Seamon J, Craft E, Kochian LV (2013). Transport properties of members of the ZIP family in plants and their role in Zn and Mn homeostasis.J Exp Bot 64, 369-381. |
| [45] | Mira H, Martinez-García F, Peñarrubia L (2001). Evidence for the plant-specific intercellular transport of the Arabidopsis copper chaperone CCH.Plant J 25, 521-528. |
| [46] | Palmgren MG, Axelsen KB (1998). Evolution of P-type ATPases.BBA-Bioenergetics 1365, 37-45. |
| [47] | Peñarrubia L, Andres-Colas N, Moreno J, Puig S (2010). Regulation of copper transport in Arabidopsis thaliana: a biochemical oscillator?J Biol Inorg Chem 15, 29-36. |
| [48] | Peñarrubia L, Romero P, Carrió-Seguí A, Andrés- Bordería A, Moreno J, Sanz A (2015). Temporal aspects of copper homeostasis and its crosstalk with hormones.Front Plant Sci 6, 255. |
| [49] | Perea-Garcia A, Garcia-Molina A, Andres-Colas N, Vera- Sirera F, Perez-Amador MA, Puig S, Peñarrubia L (2013). Arabidopsis copper transport protein COPT2 participates in the cross talk between iron deficiency responses and low-phosphate signaling.Plant Physiol 162, 180-194. |
| [50] | Pilon M, Abdel-Ghany SE, Cohu CM, Gogolin KA, Ye H (2006). Copper cofactor delivery in plant cells.Curr Opin Plant Biol 9, 256-263. |
| [51] | Puig S, Mira H, Dorcey E, Sancenón V, Andrés-Colás N, Garcia-Molina A, Burkhead JL, Gogolin KA, Abdel-Ghany SE, Thiele DJ, Ecker JR, Pilon M, Peñarrubia L (2007). Higher plants possess two different types of ATX1-like copper chaperones.Biochem Bioph Res Co 354, 385-390. |
| [52] | Raven JA, Evans MCW, Korb RE (1999). The role of trace metals in photosynthetic electron transport in O2-evolving organisms.Photosynth Res 60, 111-149. |
| [53] | Rodrigo-Moreno A, Andres-Colas N, Poschenrieder C, Gunse B, Peñarrubia L, Shabala S (2013). Calcium- and potassium-permeable plasma membrane transporters are activated by copper in Arabidopsis root tips: linking copper transport with cytosolic hydroxyl radical production.Plant Cell Environ 36, 844-855. |
| [54] | Rodriguez FI, Esch JJ, Hall AE, Binder BM, Schaller GE, Bleecker AB (1999). A copper cofactor for the ethylene receptor ETR1 from Arabidopsis.Science 283, 996-998. |
| [55] | Sancenón V, Puig S, Mateu-AndrésI, Dorcey E, Thiele DJ, Peñarrubia L (2004). The Arabidopsis copper transporter COPT1 functions in root elongation and pollen development.J Biol Chem 279, 15348-15355. |
| [56] | Sancenón V, Puig S, Mira H, Thiele DJ, Peñarrubia L (2003). Identification of a copper transporter family in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Mol Biol 51, 577-587. |
| [57] | Sautron E, Mayerhofer H, Giustini C, Pro D, Crouzy S, Ravaud S, Pebay-Peyroula E, Rolland N, Catty P, Seiǵneurin-Berny D (2015). HMA6 and HMA8 are two chloroplast Cu+-ATPases with different enzymatic properties.Biosci Rep 35, e00201. |
| [58] | Shikanai T (2003). PAA1, a P-type ATPase of Arabidopsis, functions in copper transport in chloroplasts.Plant Cell 15, 1333-1346. |
| [59] | Shin LJ, Lo JC, Yeh KC (2012). Copper chaperone antioxidant protein1 is essential for copper homeostasis. Plant Physiol 159, 1099-1110. |
| [60] | Tapken W, Kim J, Nishimura K, Wijk KJ, Pilon M (2015). The Clp protease system is required for copper ion- dependent turnover of the PAA2/HMA8 copper transporter in chloroplasts.New Phytol 205, 511-517. |
| [61] | Tapken W, Ravet K, Shahbaz M, Pilon M (2015). Regulation of Cu delivery to chloroplast proteins.Plant Signal Behav 10, e1046666. |
| [62] | Ueno D, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2009). Further characterization of ferric-phytosiderophore transporters ZmYS1 and Hv- YS1 in maize and barley.J Exp Bot 60, 3513-3520. |
| [63] | Wakuta S, Mineta K, Amano T, Toyoda A, Fujiwara T, Naito S, Takano J (2015). Evolutionary divergence of plant borate exporters and critical amino acid residues for the polar localization and boron-dependent vacuolar sor- ting of AtBOR1.Plant Cell Physiol 56, 852-862. |
| [64] | Wang JW, Li Y, Zhang YX, Chai TY (2013). Molecular cloning and characterization of a Brassica juncea yellow stripe-like gene, BjYSL7, whose overexpression incre- ases heavy metal tolerance of tobacco.Plant Cell Rep 32, 651-662. |
| [65] | Waters BM, Chu HH, Didonato RJ, Roberts LA, Eisley RB, Lahner B, Salt DE, Walker EL (2006). Mutations in Arabidopsis yellow stripe-like1 and yellow stripe-like3 reveal their roles in metal ion homeostasis and loading of metal ions in seeds.Plant Physiol 141, 1446-1458. |
| [66] | Waters BM, McInturf SA, Stein RJ (2012). Rosette iron deficiency transcript and microRNA profiling reveals links between copper and iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana.J Exp Bot 63, 5903-5918. |
| [67] | Williams LE, Mills RF (2005). P1B-ATPases—an ancient family of transition metal pumps with diverse functions in plants.Trends Plant Sci 10, 491-502. |
| [68] | Wintz H, Fox T, Wu YY, Feng V, Chen W, Chang HS, Zhu T, Vulpe C (2003). Expression profiles of Arabidopsis thaliana in mineral deficiencies reveal novel transporters involved in metal homeostasis.J Biol Chem 278, 47644-47653. |
| [69] | Wintz H, Vulpe C (2002). Plant copper chaperones.Biochem Soc T 30, 732-735. |
| [70] | Yruela I (2009). Copper in plants acquisition, transport and interactions. Funct Plant Biol 36, 409-430. |
| [71] | Yu ZL, Zhang JG, Wang XC, Chen J (2008). Excessive copper induces the production of reactive oxygen species, which is mediated by phospholipase D, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase and antioxidant systems.J Integr Plant Biol 50, 157-167. |
| [72] | Yuan M, Chu Z, Li X, Xu C, Wang S (2010). The bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae overcomes rice defenses by regulating host copper redistribution.Plant Cell 22, 3164-3176. |
| [73] | Yuan M, Li X, Xiao J, Wang S (2011). Molecular and functional analyses of COPT/Ctr-type copper transporter-like gene family in rice.BMC Plant Biol 11, 69. |
| [74] | Zelazny E, Vert G (2015). Regulation of iron uptake by IRT1: endocytosis pulls the trigger.Mol Plant 8, 977-979. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||