

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2016, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 639-649.DOI: 10.11983/CBB15122 cstr: 32102.14.CBB15122
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yao Bingnan1, Chen Baozhang2,3,*( ), Che Mingliang2,3
), Che Mingliang2,3
Received:2015-07-07
Accepted:2016-02-22
Online:2016-09-01
Published:2018-08-10
Contact:
Chen Baozhang
About author:# Co-first authors
Yao Bingnan, Chen Baozhang, Che Mingliang. Spatial-temporal Change of Gross Primary Productivity in the Poyang Lake Basin from 2000 to 2013 and Correlation with Meteorologic Factors[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(5): 639-649.
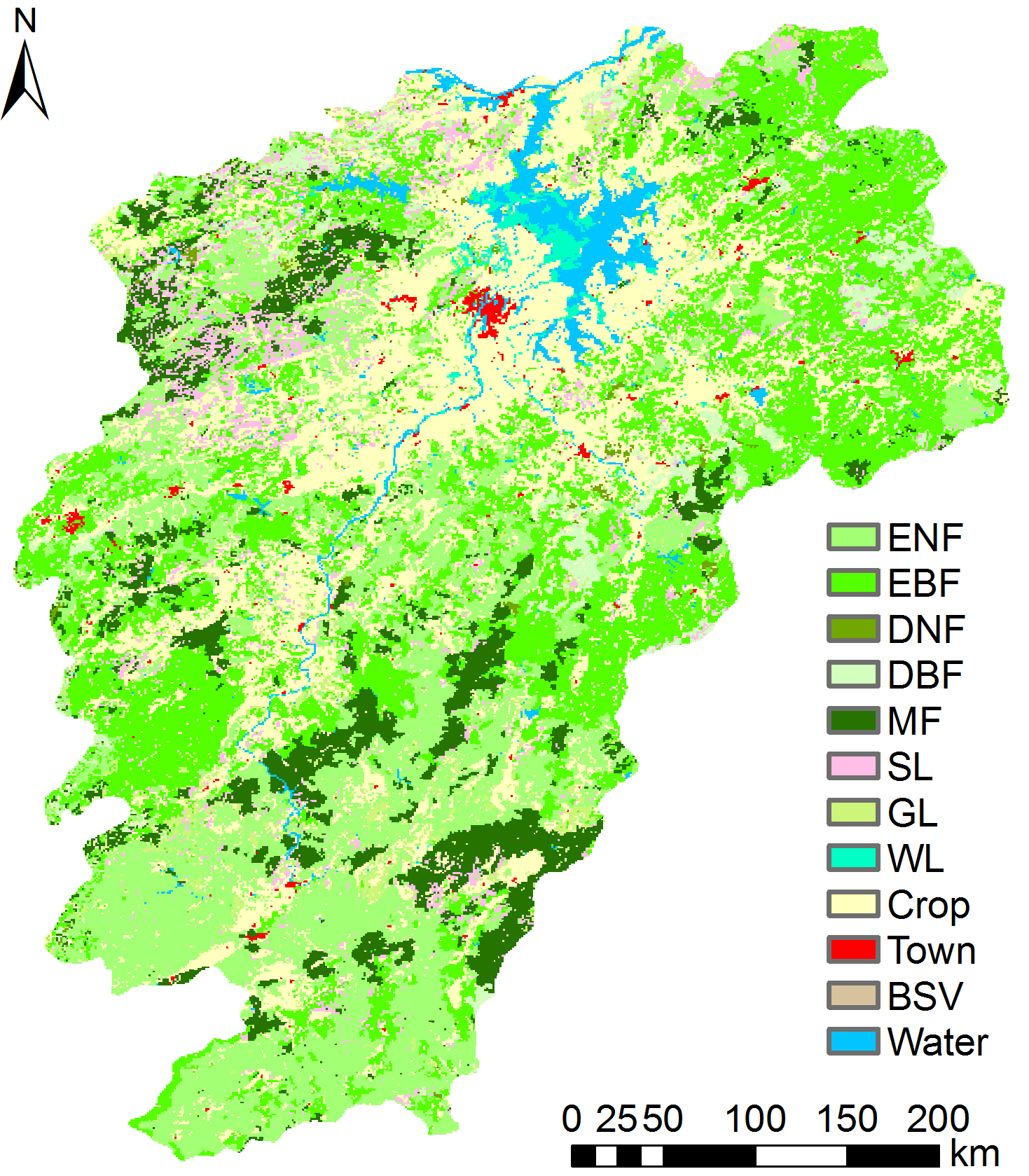
Figure 1 The Poyang Lake basin and the distribution of land cover types ENF: Evergreen needleleaf forests; EBF: Evergreen broadleaf forests; DNF: Deciduous needleleaf forests; DBF: Deciduous broadleaf forests; MF: Mixed forests; SL: Shrubland; GL: Grassland; WL: Wetland; Crop: Cropland; BSV: Barren or sparsely vegetated
| Year | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 14 annual mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 40 | 77 | 14 | 83 | 83 | 76 | 86 | 66 | 76 | 23 | 84 | 71 | 62 | 83 | 88 |
| Maximum | 2378 | 2526 | 2497 | 2508 | 2671 | 2435 | 2544 | 2603 | 2554 | 2630 | 2501 | 2458 | 2471 | 2494 | 2493 |
| Mean | 1247 | 1377 | 1410 | 1363 | 1470 | 1307 | 1388 | 1439 | 1348 | 1348 | 1328 | 1298 | 1342 | 1391 | 1361 |
Table 1 Statistical characteristics of annual GPP in the Poyang Lake basin area from 2000 to 2013 (gC·m-2·a-1)
| Year | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 14 annual mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 40 | 77 | 14 | 83 | 83 | 76 | 86 | 66 | 76 | 23 | 84 | 71 | 62 | 83 | 88 |
| Maximum | 2378 | 2526 | 2497 | 2508 | 2671 | 2435 | 2544 | 2603 | 2554 | 2630 | 2501 | 2458 | 2471 | 2494 | 2493 |
| Mean | 1247 | 1377 | 1410 | 1363 | 1470 | 1307 | 1388 | 1439 | 1348 | 1348 | 1328 | 1298 | 1342 | 1391 | 1361 |
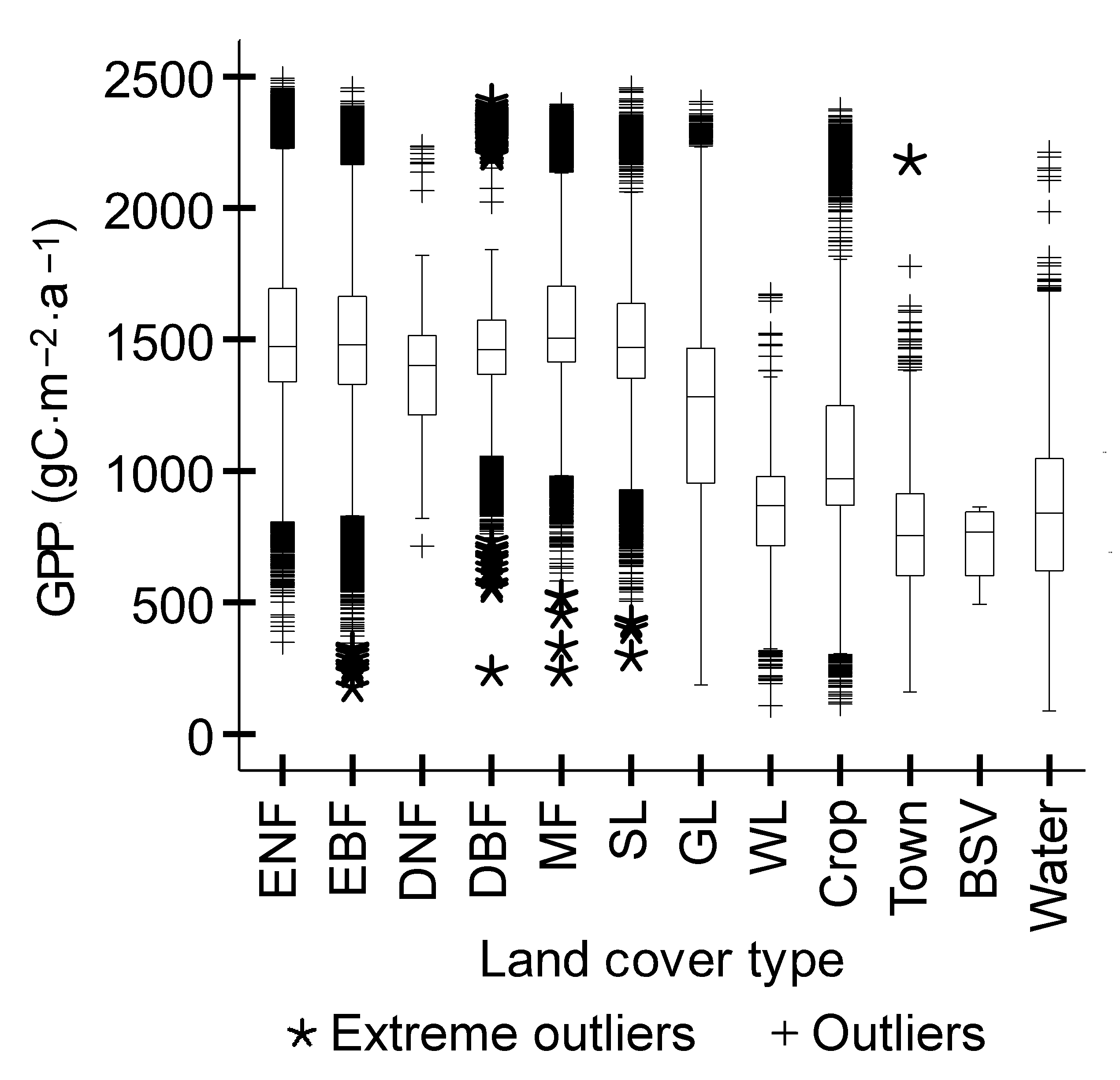
Figure 5 Comparison of GPP per unit area among different vegetation types in the Poyang Lake basin ENF, EBF, DNF, DBF, MF, SL, GL, WL and BSV see Figure 1.
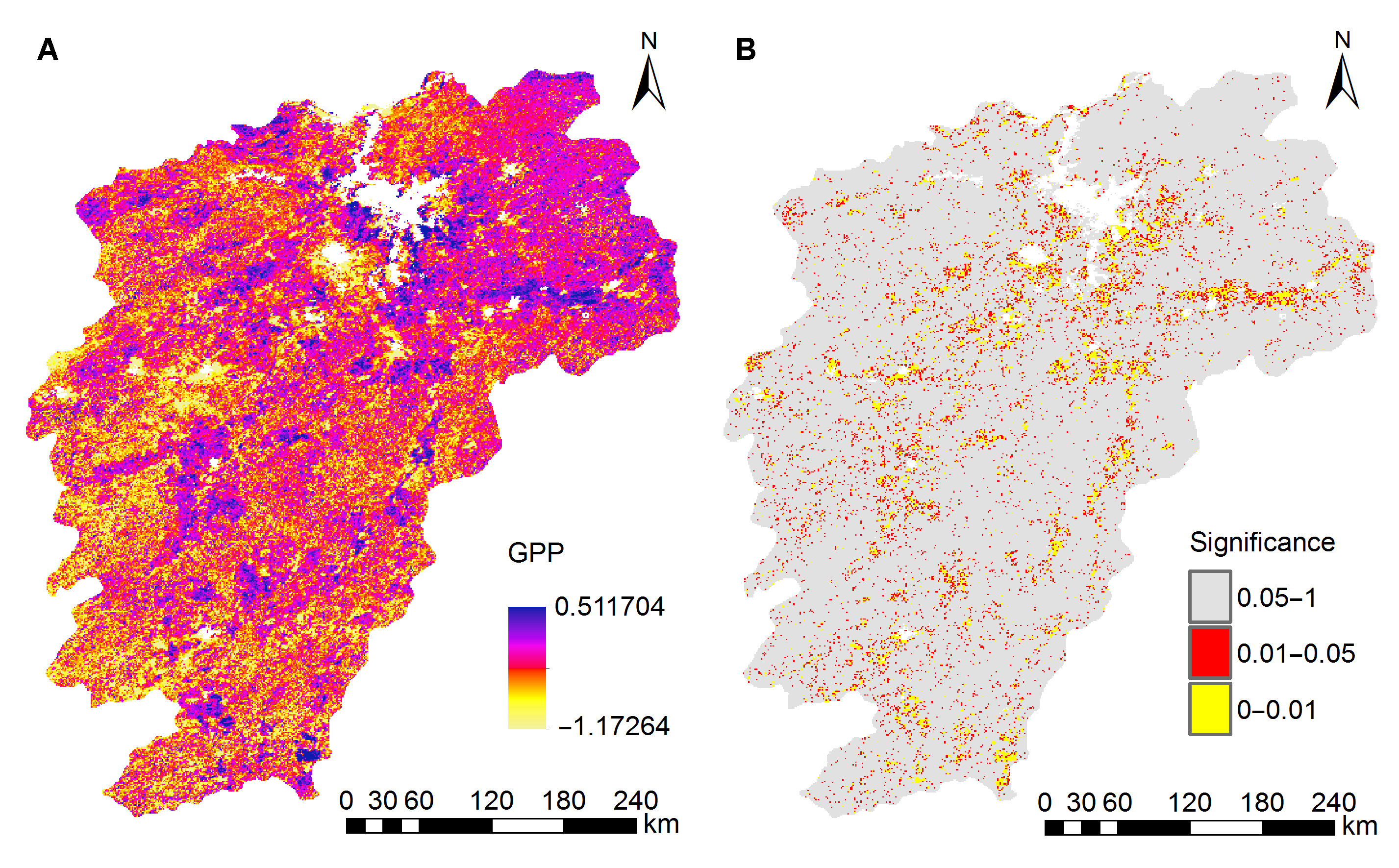
Figure 6 Spatial distribution of trends of GPP in the Poyang Lake basin from 2000 to 2013 (A) Spatial distribution of trends of GPP; (B) P-value from significance test
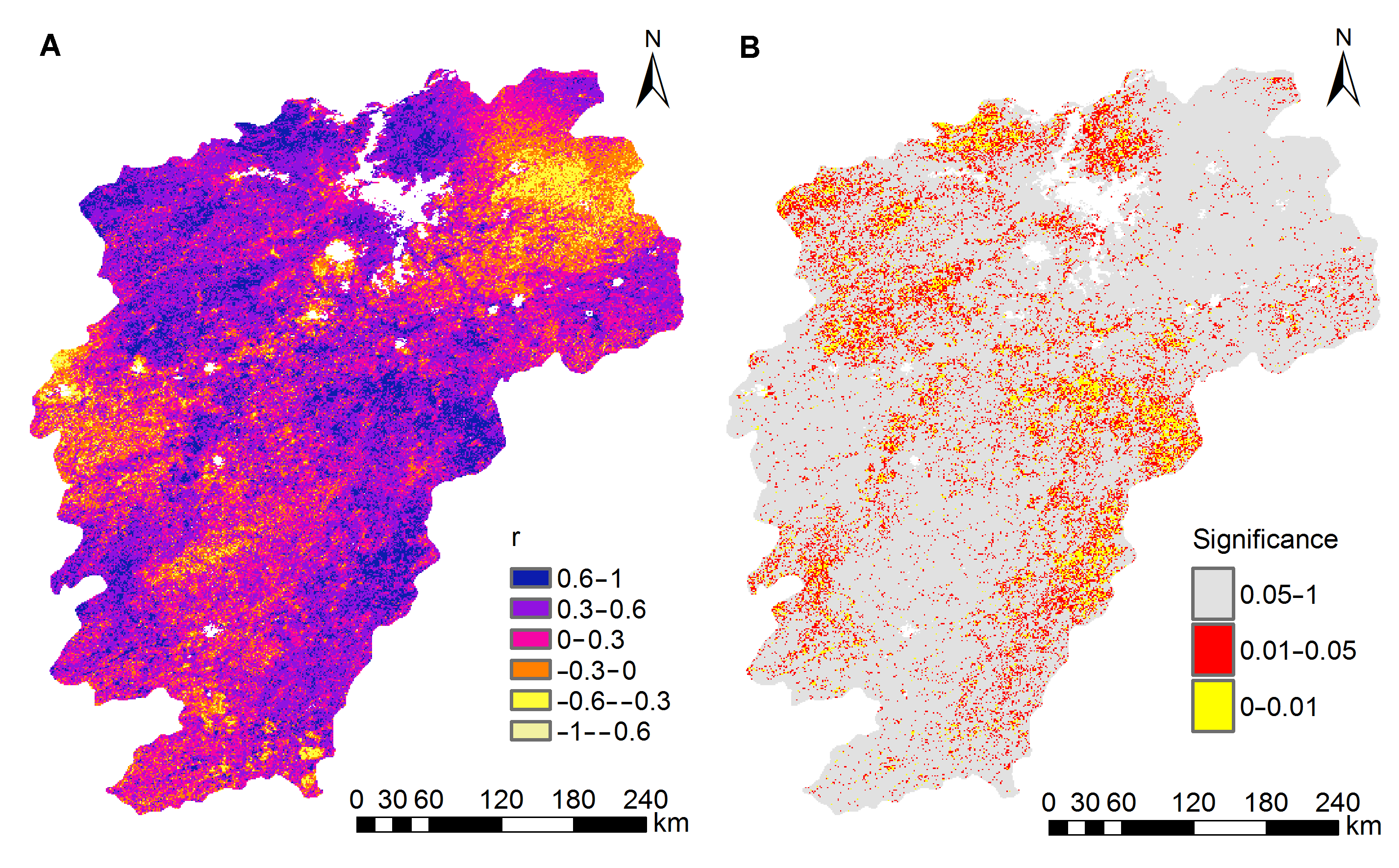
Figure 9 Spatial distribution of partial correlation coefficient of GPP and temperature in the Poyang Lake basin during 2000-2013 (A) Spatial distribution of partial correlation coefficient; (B) P-value from significance test
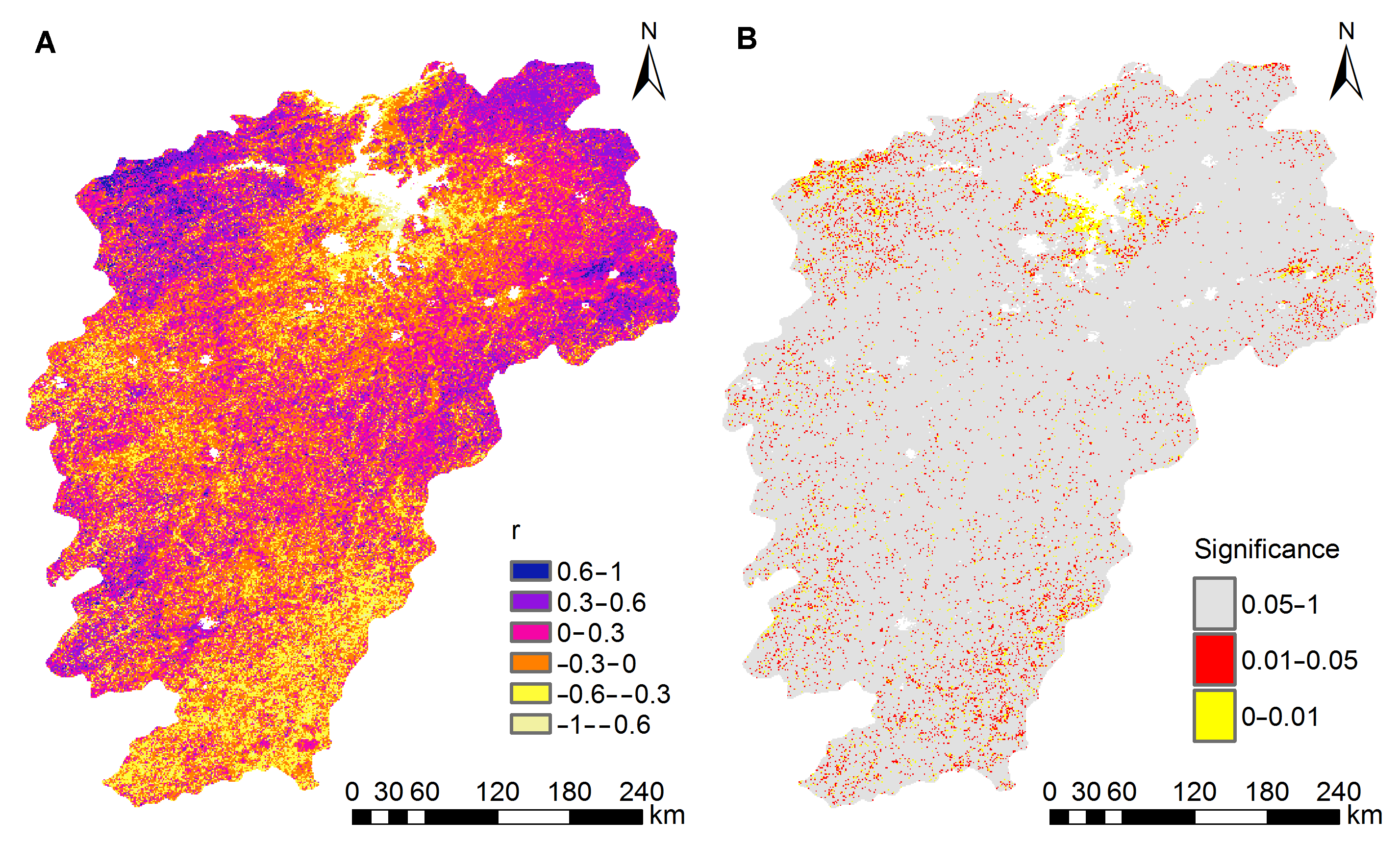
Figure 10 Spatial distribution of partial correlation coefficient of GPP and rainfall in the Poyang Lake basin during 2000-2013 (A) Spatial distribution of partial correlation coefficient; (B) P-value from significance test
| 1 | 蔡海生, 朱德海, 赵晓敏 (2005). 1998年前后鄱阳湖区土地利用变化分析. 中国农业大学学报 10(6), 88-93. |
| 2 | 陈全功 (2008). 中国草原监测的现状与发展. 草业科学 25(2), 29-38. |
| 3 | 陈佐忠, 汪诗平, 王艳芬 (2003). 内蒙古典型草原生态系统定位研究最新进展. 植物学通报 20, 423-429. |
| 4 | 戴星照, 方豫, 陈葵, 林联盛, 廖国朝, HAIKAI T (2003). 鄱阳湖流域综合规划与管理技术. 江西科学 21, 217-221. |
| 5 | 丁明军, 郑林, 李晓峰 (2009). 气候变化背景下鄱阳湖地区植被覆盖及生产力变化研究. 安徽农业科学 37, 3641-3644. |
| 6 | 顾婷婷, 周锁铨, 邵步粉, 李强 (2009). 鄱阳湖区域植被覆盖变化与降水相互响应关系. 生态学杂志 28, 1060-1066. |
| 7 | 何勇, 董文杰, 郭晓寅, 丹利 (2007). 基于MODIS的中国陆地植被生长及其与气候的关系. 生态学报 27, 5086-5092. |
| 8 | 金斌松, 聂明, 李琴, 陈家宽, 周文斌 (2012). 鄱阳湖流域基本特征面临挑战和关键科学问题. 长江流域资源与环境 21, 268-275. |
| 9 | 李迪强, 孙成永, 张新时 (1998). 中国潜在植被生产力的分布与模拟. 植物学报 40, 560-566. |
| 10 | 李相虎, 张奇, 邵敏 (2012). 鄱阳湖流域叶面积指数时空变化特征及其与气候因子的关系. 长江流域资源与环境 21, 296-301. |
| 11 | 李月臣, 宫鹏, 刘春霞, 陈晋, 于德永 (2006). 北方13省1982年-1999年植被变化及其与气候因子的关系. 资源科学28(2), 109-117. |
| 12 | 邵步粉, 周锁铨, 顾婷婷, 李强 (2010). 鄱阳湖流域NDVI时空变化及其与地表径流的关系. 中国农业气象 31, 288-294. |
| 13 | 孙红雨, 王长耀, 牛铮, 布和敖斯尔, 李兵 (1998). 中国地表植被覆盖变化及其与气候因子关系——基于NOAA时间序列数据. 遥感学报 2, 204-210. |
| 14 | 汪权方, 李家永 (2008). 基于时序NDVI数据的鄱阳湖流域常绿覆被季节性变化特征. 长江流域资源与环境 17, 866-871. |
| 15 | 吴桂平, 刘元波, 赵晓松, 叶春 (2013). 基于MOD16产品的鄱阳湖流域地表蒸散量时空分布特征. 地理研究 32, 617-627. |
| 16 | 徐婷婷, 刘跃进 (2010). 粮食大省江西的生态转型. 中国经济周刊 (3), 46-47. |
| 17 | 张福庆, 陈文波 (2007). 鄱阳湖区土地利用的生态效应. 生态学杂志 26, 1058-1062. |
| 18 | 赵晓松, 刘元波, 吴桂平 (2013). 基于遥感的2000-2009年鄱阳湖流域蒸散特征及影响因子研究. 长江流域资源与环境 22, 369-378. |
| 19 | 周广胜, 张新时 (1996). 全球气候变化的中国自然植被的净第一性生产力研究. 植物生态学报 1, 11-19. |
| 20 | 朱凤凤, 程巧贞 (2012). 鄱阳湖流域NDVI的时空变化及其与气候的关系. 江西农业学报 2(3), 98-102. |
| 21 | Beer C, Reichstein M, Ciais P, Farquhar GD, Papale D (2007). Mean annual GPP of Europe derived from its water balance.Geophys Res Lett 34, 306-316. |
| 22 | Behrenfeld MJ, Randerson JT, Mcclain CR, Feldman GC, Los SO, Tucker CJ, Falkowski PG, Field CB, Frouin R, Esaias WE (2001). Biospheric primary production during an ENSO transition.Science 291, 2594-2597. |
| 23 | Buys P, Deichmann U, Meisner CM, Ton-That T, Wheeler D (2009). Country stakes in climate change negotiations: two dimensions of vulnerability.Climate Policy 9, 288-305. |
| 24 | Falge E, Baldocchi D, Tenhunen J, Aubinet M, Bakwin P, Berbigier P, Bernhofer C, Burba G, Clement R, Davis KJ, Elbers JA, Goldstein AH, Grelle A, Granier A, Guðmundsson J, Hollinger D, Kowalski AS, Katul G, Law BE, Malhi Y, Meyers T, Monson RK, Munger WJ, Oechel W, Paw UKT, Pilegaard K, Rannik Ü, Rebmann C, Suyker A, Valentini R, Wilson K, Wofsy S (2002a). Seasonality of ecosystem respiration and gross primary production as derived from FLUXNET measurements.Agric For Meteorol 113, 53-74. |
| 25 | Falge E, Tenhunen J, Baldocchi D, Aubinet M, Bakwin P, Berbigier P, Bernhofer C, Bonnefond JM, Burba G, Clement R, Davis KJ, Elbers JA, Falk M, Goldstein AH, Grelle A, Granier A, Grünwald T, Guðmundsson J, Hollinger D, Janssens IA, Keronen P, Kowalski AS, Katul G, Law BE, Malhi Y, Meyers T, Monson RK, Moors E, Munger JW, Oechel W, Paw UKT, Pilegaard K, Rannik Ü, Rebmann C, Suyker A, Thorgeirsson H, Tirone G, Turnipseed A, Wilson K, Wofsy S (2002b). Phase and amplitude of ecosystem carbon release and uptake potentials as derived from FLUXNET measurements.Agric For Meteorol 113, 75-95. |
| 26 | Farquhar GD, Caemmerer SV, Berry JA (1980). A biochemical model of photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in leaves of C3 species.Planta 149, 78-90. |
| 27 | Gitelson AA, Viña A, Verma SB, Rundquist DC, Arkebauer TJ, Keydan G, Leavitt B, Ciganda V, Burba GG, Suyker AE (2006). Relationship between gross primary production and chlorophyll content in crops: implications for the synoptic monitoring of vegetation productivity.J Geophys Res Atmos 111, 854-871. |
| 28 | Heinsch FA, Reeves M, Votava P, Kang S, Milesi C, Zhao M, Glassy J, Jolly WM, Loehman R, Bowker CF, Kimball JS, Nemani RR, Running SW (2003). User’s Guide: GPP and NPP (MOD17A2/A3) Products, NASA MODIS Land Algorithm. Missoula, MT: Univ. Montana. pp. 17. |
| 29 | Heinsch FA, Zhao MS, Running SW, Kimball JS, Nemani RR, Davis KJ, Bolstad PV, Cook BD, Desai AR, Ricciuto DM, Law BE, Oechel WC, Kwon H, Luo H, Wofsy SC, Dunn AL, Munger JW, Baldocchi DD, Xu L, Hollinger DY, Richardson AD, Stoy PC, Siqueira MBS, Monson RK, Burns SP, Flanagan LB (2006). Evaluation of remote sensing based terrestrial productivity from MODIS using regional tower eddy flux network observations.IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 44, 1908-1925. |
| 30 | Lipford JW, Yandle B (2010). Environmental Kuznets curves, carbon emissions, and public choice.Environ Dev Econ 15, 417-438. |
| 31 | MaM G, Dong LX, Wang XM (2003). Study on the dynamically monitoring and simulating the vegetation cover in northwest China in the past 21 years.J Glaciol Geocryol 25, 232-236. |
| 32 | Maselli F, Papale D, Puletti N, Chirici G, Corona P (2009). Combining remote sensing and ancillary data to monitor the gross productivity of water-limited forest ecosystems.Remote Sens Environ 113, 657-667. |
| 33 | Monteith JL (1972). Solar-radiation and productivity in tropical ecosystem.J Appl Ecol 9, 747-766. |
| 34 | Monteith JL (1977). Climate and the efficiency of crop production in Britain.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 281, 277-294. |
| 35 | Prince SD (1991). A model of regional primary production for use with coarse resolution satellite data.Int J Remote Sens 12, 1313-1330. |
| 36 | Running SW, Nemani RR, Heinsch FA, Zhao MS, Reeves M, Hashimoto H (2004). A continuous satellite-derived measure of global terrestrial primary production.Bioscience 54, 547-560. |
| 37 | Running SW, Thornton PE, Nemani R, Glassy JM (2000). Global terrestrial gross and net primary productivity from the Earth Observing System. In: Sala OE, Jackson RB, Mooney HA, Howarth RW, eds. Methods in Ecosystem Science. New York: Springer New York. pp. 44-57. |
| 38 | Wu CY, Niu Z, Tang Q, Huang WJ, Rivard B, Feng JL (2009). Feng remote estimation of gross primary production in wheat using chlorophyll-related vegetation indices.Agric For Meteorol 149, 1015-1021. |
| 39 | Xiao JF, Zhuang QL, Law BE, Chen JQ, Baldocchi DD, Cook DR, Oren R, Richardson AD, Wharton S, Ma SY, Martin TA, Verma SB, Suyker AE, Scott RL, Monson RK, Litvak M, Hollinger DY, Sun G, Davis KJ, Bolstad PV, Burns SP, Curtis PS, Drake BG, Falk M, Fischer ML, Foster DR, Gu LH, Hadley JL, Katul GG, Roser Y, McNulty S, Meyers TP, Munger JW, Noormets A, Oechel WC, Paw KT, Schmid HP, Starr G, Torn MS, Wofsy SC (2010). A continuous measure of gross primary production for the conterminous United States derived from MODIS and AmeriFlux data.Remote Sens Environ 114, 576-591. |
| 40 | Xiao XM, Zhang QY, Hollinger D, Aber J, Moore B (2005). Modeling gross primary production of an evergreen need- leleaf forest using modis and climate data.Ecol Appl 15, 954-969. |
| 41 | Yu GR, Zhang LM, Sun XM, Fu YL, Li ZQ (2005). Advances in carbon flux observation and research in Asia.Sci China Ser D 48, 1-16. |
| 42 | Zhang Q, Cheng YB, Lyapustin AI, Wang Y, Xiao X, Suyker A, Verma S, Tan B, Middleton EM (2014). Estimation of crop gross primary production (GPP): impact of MODIS observation footprint and impact of vegetation BRDF characteristics.Agric For Meteorol 191, 51-63. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||