

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2016, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 16-23.DOI: 10.11983/CBB15007 cstr: 32102.14.CBB15007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Lin Qi1, Xinfu Bai1*, Weihao Niu1, Zhenhua Zhang2
Received:2015-01-12
Accepted:2015-03-30
Online:2016-01-01
Published:2016-02-01
Contact:
Bai Xinfu
About author:? These authors contributed equally to this paper
Lin Qi, Xinfu Bai, Weihao Niu, Zhenhua Zhang. Effect of Rhizosphere Ventilation on Growth of Cotton Seedlings Under Salt Stress[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(1): 16-23.
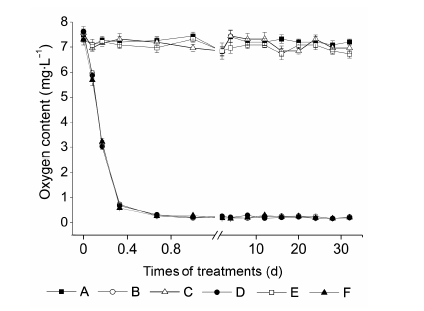
Figure 1 Changes in O2 content in culture solutions of different treatmentsA: Aeration+0 mmol·L-1 NaCl; B: No aeration+0 mmol·L-1 NaCl; C: Aeration+100 mmol·L-1 NaCl; D: No aeration+100 mmol·L-1 NaCl; E: Aeration+200 mmol·L-1 NaCl; F: No aeration+200 mmol·L-1 NaCl
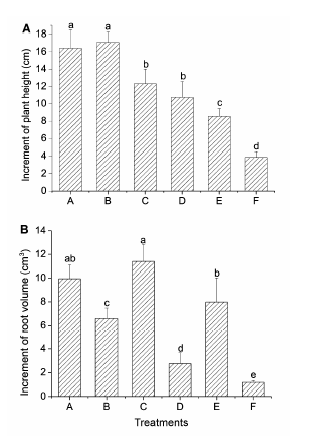
Figure 2 Comparison of the increments in plant height (A) and root volume (B) in different treatmentsA-F see Figure 1. Significant differences (P<0.05) were indicated with different lowercase letters.
| Sources of variation | Plant height | Root volume | Single leaf area | Specific leaf area | Total biomass | Root biomass | Root-shoot ratio | Ash content | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salt concention | F value | 174.56 | 43.42 | 91.43 | 2.56 | 106.84 | 61.75 | 24.40 | 89.03 |
| P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.943 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Ventilation | F value | 16.63 | 360.63 | 416.34 | 16.33 | 67.76 | 236.02 | 349.23 | 724.15 |
| P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Interaction | F value | 11.47 | 22.15 | 2.99 | 5.73 | 4.48 | 9.02 | 13.69 | 10.50 |
| P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.065 | 0.008 | 0.020 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
Table 1 Analysis of the variance of the physiological indices in cotton seedlings under salt stress and ventilation
| Sources of variation | Plant height | Root volume | Single leaf area | Specific leaf area | Total biomass | Root biomass | Root-shoot ratio | Ash content | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salt concention | F value | 174.56 | 43.42 | 91.43 | 2.56 | 106.84 | 61.75 | 24.40 | 89.03 |
| P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.943 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Ventilation | F value | 16.63 | 360.63 | 416.34 | 16.33 | 67.76 | 236.02 | 349.23 | 724.15 |
| P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| Interaction | F value | 11.47 | 22.15 | 2.99 | 5.73 | 4.48 | 9.02 | 13.69 | 10.50 |
| P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.065 | 0.008 | 0.020 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
Parameters | Aeration | No aeration | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum value | Minimum value | Coefficient of variability | Maximum value | Minimum value | Coefficient of variability | ||
| Plant height (cm) | 16.40±2.09 | 8.56±0.89 | 31.57 | 17.06±1.20 | 3.84±0.67 | 62.66 | |
| Root volume (cm3·plantlet-1) | 11.40±1.45 | 7.98±2.05 | 17.54 | 6.60±0.87 | 1.18±0.15 | 79.39 | |
| Single leaf area (cm2) | 137.78±6.18 | 109.39±10.22 | 11.52 | 101.73±6.26 | 60.93±5.46 | 24.90 | |
| Specific leaf area (cm2·g-1) | 342.82±20.83 | 332.69±24.60 | 1.56 | 337.02±24.02 | 279.85±16.62 | 9.95 | |
| Total biomass (g·plantlet-1) | 4.91±0.35 | 3.28±0.24 | 15.14 | 4.47±0.34 | 2.28±0.18 | 22.13 | |
| Root biomass (g·plantlet-1) | 1.11±0.11 | 0.85±0.04 | 11.25 | 0.86±0.05 | 0.46±0.04 | 21.94 | |
| Root-shoot ratio | 0.35±0.01 | 0.29±0.02 | 7.07 | 0.25±0.01 | 0.23±0.01 | 2.85 | |
| Ash content (%) | 13.18±0.27 | 11.41±0.14 | 7.23 | 10.55±0.24 | 9.69±0.24 | 4.31 | |
Table 2 The salt stress resulted variance of the indices in cotton seedlings under different ventilation
Parameters | Aeration | No aeration | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum value | Minimum value | Coefficient of variability | Maximum value | Minimum value | Coefficient of variability | ||
| Plant height (cm) | 16.40±2.09 | 8.56±0.89 | 31.57 | 17.06±1.20 | 3.84±0.67 | 62.66 | |
| Root volume (cm3·plantlet-1) | 11.40±1.45 | 7.98±2.05 | 17.54 | 6.60±0.87 | 1.18±0.15 | 79.39 | |
| Single leaf area (cm2) | 137.78±6.18 | 109.39±10.22 | 11.52 | 101.73±6.26 | 60.93±5.46 | 24.90 | |
| Specific leaf area (cm2·g-1) | 342.82±20.83 | 332.69±24.60 | 1.56 | 337.02±24.02 | 279.85±16.62 | 9.95 | |
| Total biomass (g·plantlet-1) | 4.91±0.35 | 3.28±0.24 | 15.14 | 4.47±0.34 | 2.28±0.18 | 22.13 | |
| Root biomass (g·plantlet-1) | 1.11±0.11 | 0.85±0.04 | 11.25 | 0.86±0.05 | 0.46±0.04 | 21.94 | |
| Root-shoot ratio | 0.35±0.01 | 0.29±0.02 | 7.07 | 0.25±0.01 | 0.23±0.01 | 2.85 | |
| Ash content (%) | 13.18±0.27 | 11.41±0.14 | 7.23 | 10.55±0.24 | 9.69±0.24 | 4.31 | |
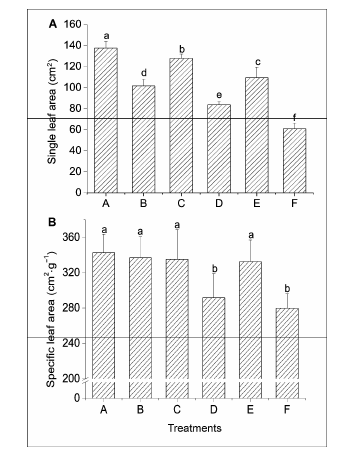
Figure 3 Comparison of the increments in single leaf area (A) and specific leaf area (B) in different treatmentsA-F see Figure 1. Significant differences (P<0.05) were indicated with different lowercase letters.

Figure 4 Comparison of shoot/root/total biomass (A) and root-shoot ratio (B) in different treatments A-F see Figure 1. Significant differences (P<0.05) were indicated with different lowercase letters.
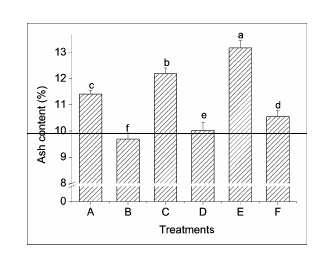
Figure 5 Comparison of the increments in ash content in different treatments A-F see Figure 1. Significant differences (P<0.05) were indicated with different lowercase letters.
| 1 | 白团辉, 马锋旺, 李翠英, 束怀瑞, 韩明玉, 王昆 (2008). 苹果砧木幼苗对根际低氧胁迫的生理响应及耐性分析. 中国农业科学 41, 4140-4148. |
| 2 | 柏新富, 卜庆梅, 谭永芹, 朱建军, 刘林德 (2012). NaCl对渗透胁迫下三角叶滨藜光合作用和水分状况的调节. 植物学报 47, 500-507. |
| 3 | 陈庆彬, 雷凯健, 赵航, 郭莉, 安国勇 (2014). 一种适于营养胁迫研究的拟南芥水培方法. 植物学报 49, 462-468. |
| 4 | 代建龙, 卢合全, 李振怀, 段留生, 董合忠 (2013). 盐胁迫下施肥对棉花生长及氮素利用的影响. 应用生态学报 24, 3453-3458. |
| 5 | 郭超, 牛文全 (2010). 根际通气对盆栽玉米生长与根系活力的影响. 中国生态农业学报 18, 1194-1198. |
| 6 | 李奕林 (2012). 水稻根系通气组织与根系泌氧及根际硝化作用的关系. 生态学报 32, 2066-2074. |
| 7 | 刘义玲, 孙周平, 李天来 (2013). 根际低氧胁迫对网纹甜瓜果期根系氮代谢的影响. 生态学杂志 32, 2332-2338. |
| 8 | 娄成后, 白克智, 宋茂山 (1964). 高等植物幼苗茎叶向根系运输氧气的研究——I. 茎叶向根系运氧的数量. 科学通报 6, 537-541. |
| 9 | 潘澜, 薛立 (2012). 植物淹水胁迫的生理学机制研究进展. 生态学杂志 31, 2662-2672. |
| 10 | 生利霞, 冯立国, 束怀瑞 (2011). 低氧胁迫下钙对樱桃根系功能及氮代谢的影响. 生态学杂志 30, 2209-2213. |
| 11 | 孙运朋, 陈小兵, 张振华, 吴从稳, 颜坤, 张立华 (2013). 滨海棉田土壤盐分时空分布特征研究. 土壤学报 50, 891-899. |
| 12 | 王汝镛, 武志杰, 曹承绵, 刘永恩, 张素君, 张岫岚, 王春裕, 田林杰 (2011). 近代黄河三角洲东营农业综合试验区的滨海盐渍土及其改良利用的研究. I. 土壤类型与性质. 土壤通报 32, 3-7. |
| 13 | 王树凤, 胡韵雪, 孙海菁, 施翔, 潘红伟, 陈益泰 (2014). 盐胁迫对2种栎树苗期生长和根系生长发育的影响. 生态学报34, 1021-1029. |
| 14 | 杨鹏, 胥晓 (2012). 淹水胁迫对青杨雌雄幼苗生理特性和生长的影响. 植物生态学报 36, 81-87. |
| 15 | 弋良朋, 王祖伟 (2011). 盐胁迫下3种滨海盐生植物的根系生长和分布. 生态学报 31, 1195-1202. |
| 16 | 曾小平, 蔡锡安, 赵平, 饶兴权 (2009). 广东鹤山人工林群落主要优势植物的热值和灰分含量. 应用生态学报 20, 485-492. |
| 17 | 中国农业科学院棉花研究所 (2013). 中国棉花栽培学. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社. pp.101-114. |
| 18 | Bernstein N, Meiri A, Zilberstaine M (2004). Root growth of avocado is more sensitive to salinity than shoot growth.J Am Soc Hortic Sci 129, 188-192. |
| 19 | Grichko VP, Glick BR (2001). Ethylene and flooding stress in plants.Plant Physiol Bioch 39, 1-9. |
| 20 | Grzesiaka S, Grzesiaka MT, Huraa T, Marcińskaa I, Rzepka A (2013). Changes in root system structure, leaf water potential and gas exchange of maize and triticale seedlings affected by soil compaction.Environ Exp Bot 88, 2-10. |
| 21 | Horchani F, Khayati H, Raymond P, Brouquisse R, Aschi-Smiti S (2009). Contrasted effects of prolonged root hypoxia on tomato root and fruit (Solanum lycopersicum) metabolism.J Agron Crop Sci 195, 313-318. |
| 22 | Jackson MB (2008). Ethylene-promoted elongation: an adaptation to submergence stress.Ann Bot 101, 229-248. |
| 23 | Link KHR, Weng CC, Lo HF, Chen JT (2004). Study of the root antioxidative system of tomatoes and eggplants under waterlogged conditions.Plant Sci 167, 355-365. |
| 24 | Mano Y, Omori F (2013). Relationship between constitutive root aerenchyma formation and flooding tolerance in Zea nicaraguensis.Plant Soil 370, 447-460. |
| 25 | Maryam A, Nasreen S (2012). A review: water logging effects on morphological, anatomical, physiological and biochemical attributes of food and cash crops.Int J Water Resour Environ Sci 1, 113-120. |
| 26 | Mi YF, Ma XW, Chen SC (2013). Resistant evaluation of kiwifruit rootstocks to root zone hypoxia stress.Am J Plant Sci 4, 945-954. |
| 27 | Nakano Y (2007). Response of tomato root systems to environmental stress under soilless culture.Jpn Agri Res Q 41, 7-15. |
| 28 | Niu WQ, Jia ZX, Zhang X, Shao HB (2012). Effects of soil rhizosphere aeration on the root growth and water absorption of tomato.Clean-Soil Air Water 40, 1364-1371. |
| 29 | Pushpalatha G, Subrahmanyam D, Sreenu K, Ram T, Subbarao LV, Parmar B, Giri A, Sarla N, Rai V (2013). Effect of salt stress on seedling growth and antioxidant enzymes in two contrasting rice introgression lines.Indian J Plant Physiol 18, 360-366. |
| 30 | Shimamura S, Yamamoto R, Nakamura T, Shimada S, Komatsu S (2010). Stem hypertrophic lenticels and secondary aerenchyma enable oxygen transport to roots of soybean in flooded soil.Ann Bot 106, 277-284. |
| 31 | Voesenek LACJ, Sasidharan R (2013). Ethylene-and oxygen signaling-drive plant survival during flooding.Plant Biol 15, 426-435. |
| [1] | PING Xiao-Yan, DU Yi-Qian, LAI Shi-Rong, KONG Meng-Qiao, YU Guo-Jie. Research progress of plant chemical defense strategies in response to herbivory [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(5): 667-680. |
| [2] | LI Xin-Yi, ZHANG Li-Fang, WU You-Gui, GUO Jing, LAN Rong-Guang, LÜ Hong-Fei, YU Ming-Jian. Growth characteristics of Abies beshanzuensis seedlings at different altitudes and the influencing factors [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(4): 610-623. |
| [3] | Haobin Zhang, Lu Xiao, Yanjie Liu. Effects of artificial light at night on the diversity and growth of invasive alien and native plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [4] | OUYANG Zi-Long, JIA Xiang-Lu, SHI Jing-Zhong, TENG Wei-Chao, LIU Xiu. Effects of growth regulators on photosynthetic characteristics of Rhizophora stylosa seedlings under low temperature stress and re-warming [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(4): 638-652. |
| [5] | Xu Tiantian, Yang Peijian, Zhou Xiaoxi, Cao Yi, Chen Yanhong, Liu Guoyuan, Zhang Jian, Wei Hui. Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics and Expression Characteristics of Lagerstroemia indica GolS Family Genes [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 393-406. |
| [6] | TIAN Ao, LI Wei-Jie, CAO Yang, JIA Zhen-Zhen, ZENG Song. Growth response of Rhododendron delavayi seedlings to the soil water stress and its physiological mechanism [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(3): 488-501. |
| [7] | CHEN Wen-Yi, WANG Zhi-Yong, ZHOU Meng-Yan, MA Wen-Jun, WANG Jun-Hui, LUO Zhi-Bin, ZHOU Jing. Biomass allocation and allometric growth model of young Catalpa bungei [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(2): 356-366. |
| [8] | LI Si-Yu, YANG Feng-Ting, WANG Hui-Min, DAI Xiao-Qin, MENG Sheng-Wang. Seasonal dynamics of xylem formation in Cunninghamia lanceolata and Schima superba and its response to environmental factors [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(2): 295-307. |
| [9] | HAN Da-Yong, LI Hai-Yan, ZHANG Wei, YANG Yun-Fei. Superior growth process of creeping ramets of Phragmites australis and its physiological mechanisms in an alkaline meadow in Northeast China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(2): 320-330. |
| [10] | Qingyang Li, Cui Liu, Li He, Shan Peng, Jiayin Ma, Ziyi Hu, Hongbo Liu. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the BnaA02.CPSF6 Gene from Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 62-73. |
| [11] | WANG Lin, LI Xue, WANG Yu, WANG Xin, HU Xiao-Wen, YANG Mei, ZHU Jian-Xiao. Effects of different coating agents on seed growth and planting of native grasses in alpine grassland [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(1): 118-128. |
| [12] | Yaping Wang, Wenquan Bao, Yu’e Bai. Advances in the Application of Single-cell Transcriptomics in Plant Growth, Development and Stress Response [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [13] | XIA Min-Chang, LI Qian-Qian, QIAN Qing-Qing, REN Shu-Jun, LIANG Ying-Chong, CHEN Ting-Ying, LI Ying-Jia, MOU Zong-Min, CHEN Sui-Yun. Effect of dry mycelium of Penicillium chrysogenum on the growth and physiological performance of Trifolium repens and Lolium perenne [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(1): 189-198. |
| [14] | ZHANG Peng, JIAO Liang, XUE Ru-Hong, WEI Meng-Yuan, DU Da-Shi, WU Xuan, WANG Xu-Ge, LI Qian. Drought intensity affected the growth recovery of Picea crassifolia across different altitudes in western Qilian Mountains [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2024, 48(8): 977-987. |
| [15] | DONG Yun-Tao, JIA Heng-Feng, YANG Jing, LI Pei-Xuan, FANG Ou-Ya. Reconstruction of disturbance history on Juniperus przewalskii forests in middle Qilian Mountains [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2024, 48(8): 967-976. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||