植物基因表达调控与进化机制研究进展
|
|
王子韵, 吕燕文, 肖钰, 吴超, 胡新生
|
Advances in the Regulation and Evolutionary Mechanisms of Plant Gene Expression
|
|
Ziyun Wang, Yanwen Lü, Yu Xiao, Chao Wu, Xinsheng Hu
|
|
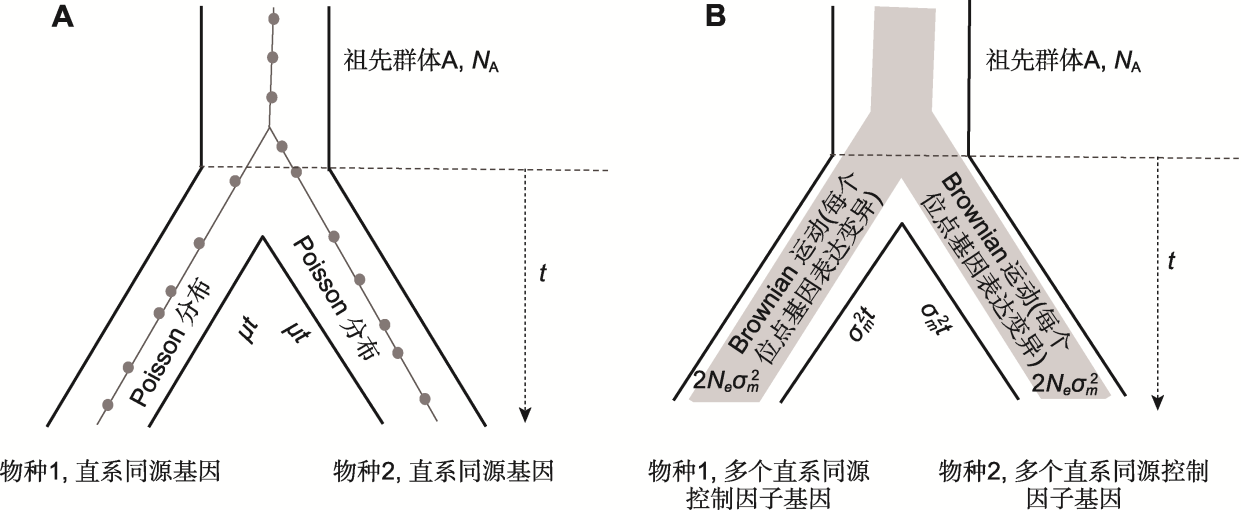
图1 直系同源基因序列进化与直系同源基因表达进化比较
(A) 一对直系同源基因序列进化: 在中性过程下, 物种内基因序列上的突变数用Poisson分布描述, 每个子代物种累积突变数为 为每个碱基的突变率, t为两物种分化时间。在突变-漂变作用平衡时, 两直系同源基因的总突变数 ; (B) 一对直系同源基因表达进化: 每个子代物种内, 1个基因表达受许多控制因子基因的影响, 在漂变过程中, 基因表达水平在物种内用Brownian运动分布表示, 在突变-漂变作用平衡时, 物种内基因表达的加性遗传方差为 为单世代突变产生的方差, 每个子代物种内积累的突变方差为 两子代物种间基因表达水平均值的加性方差为
|
Figure 1 Comparison of the gene sequence evolution versus the gene expression evolution in a pair of orthologous genes
(A) Gene sequence evolution of a pair of orthologous genes: under neutral processes, the number of mutations in a gene sequence within a species can be described by a Poisson distribution, the cumulative number of mutations in the gene sequence is approximated by where is the mutation rate per base and t is the divergence time between two species. When mutation- drift equilibrium is reached, the total number of mutations in two orthologous genes is (B) Gene expression evolution of a pair of orthologous genes: gene expression in each descendant species is controlled by multiple orthologous genes for regulatory elements, under the process of genetic drift, the distribution of gene expression levels within a species can be described by the Brownian motion distribution, under equilibrium between mutation and drift effects, the additive genetic variance of gene expression within a species is equal to where is the variance generated by mutations per generation, the cumulative mutation variance within each descendant species is and the additive genetic variance of the mean gene expression levels between two descendant species is
|
|
|
|
|
