基因编辑技术在玉米中的研究进展
Research Progress of Gene Editing Technology in Maize
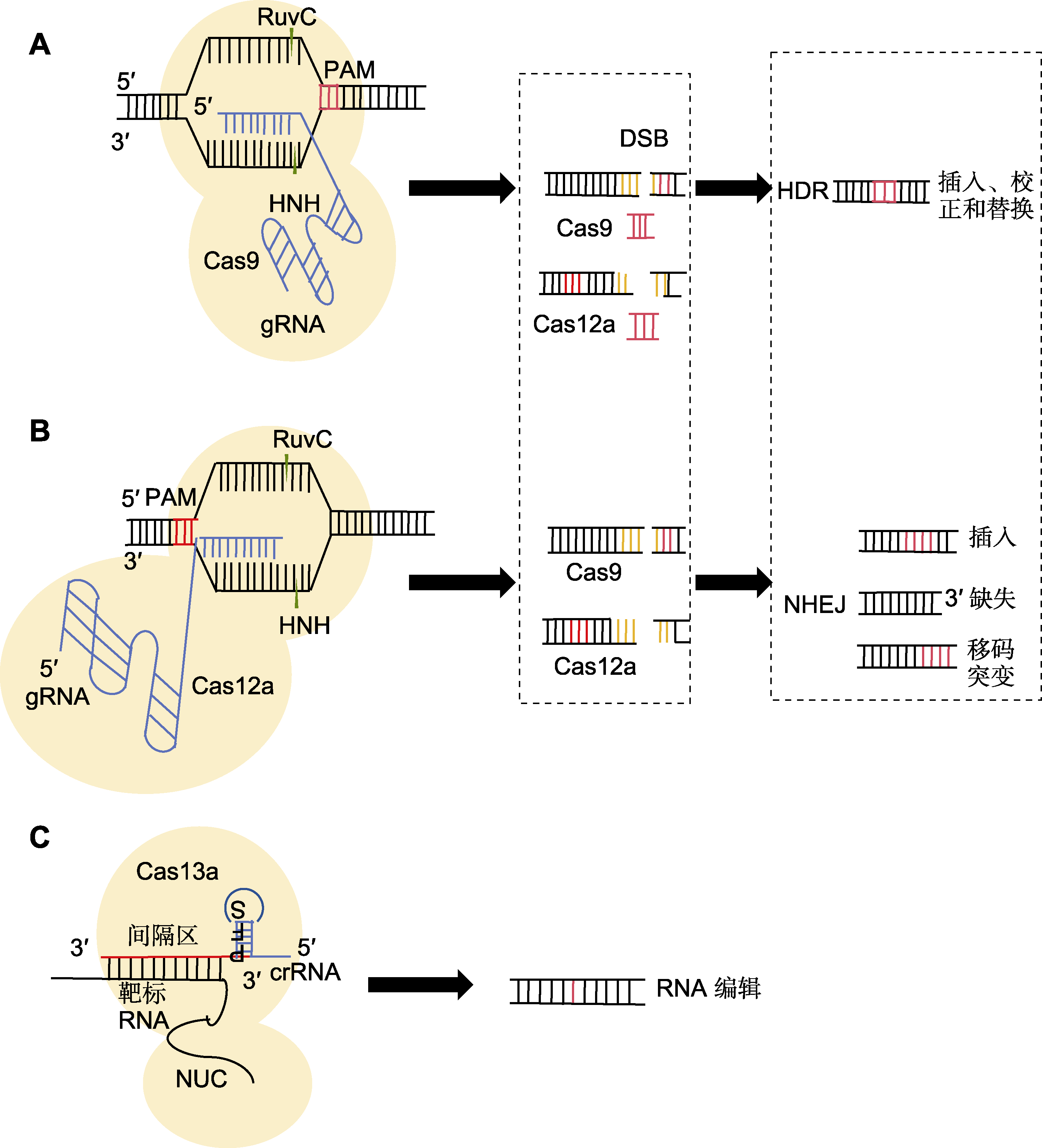
(A) Cas9蛋白利用结构域RuvC在原间隔区邻近基序(PAM)序列附近的特定单链DNA上切割, 随后, HNH的结构域与sgRNA配对的DNA另一条单链进行切割形成双链断裂(DSB), 最终进行同源定向修复(HDR)或非同源末端连接(NHEJ)修复成双链; (B) Cas12a通过crRNA介导识别5'-TTTN或5'-TTN的PAM序列; (C) 当crRNA与靶标RNA通过碱基互补配对结合后, 形成crRNA-Cas13复合物, 导致Cas13蛋白构象发生变化, 从而激活其RNA切割活性, 使其能够特异性识别并结合靶标RNA进行切割
(A) The Cas9 protein utilizes its RuvC domain to cleave a specific single-stranded DNA near the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence, subsequently, the HNH domain cleaves the other single strand of DNA paired with the sgRNA, resulting in the formation of a double-strand break (DSB), which is ultimately repaired by homology-directed repair (HDR) or non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) to form double-stranded DNA; (B) Cas12a mediates the recognition of the PAM sequence 5'-TTTN or 5'-TTN by crRNA; (C) When the crRNA pairs with the target RNA through base complementarity, a crRNA-Cas13 complex is formed, causing a conformational change in the Cas13 protein, thereby activating its RNA cleavage activity, enabling the target RNA to be specifically recognized, bound, and cleaved.