高温胁迫对植物光合作用的影响研究进展
Research Advances on the Effect of High Temperature Stress on Plant Photosynthesis
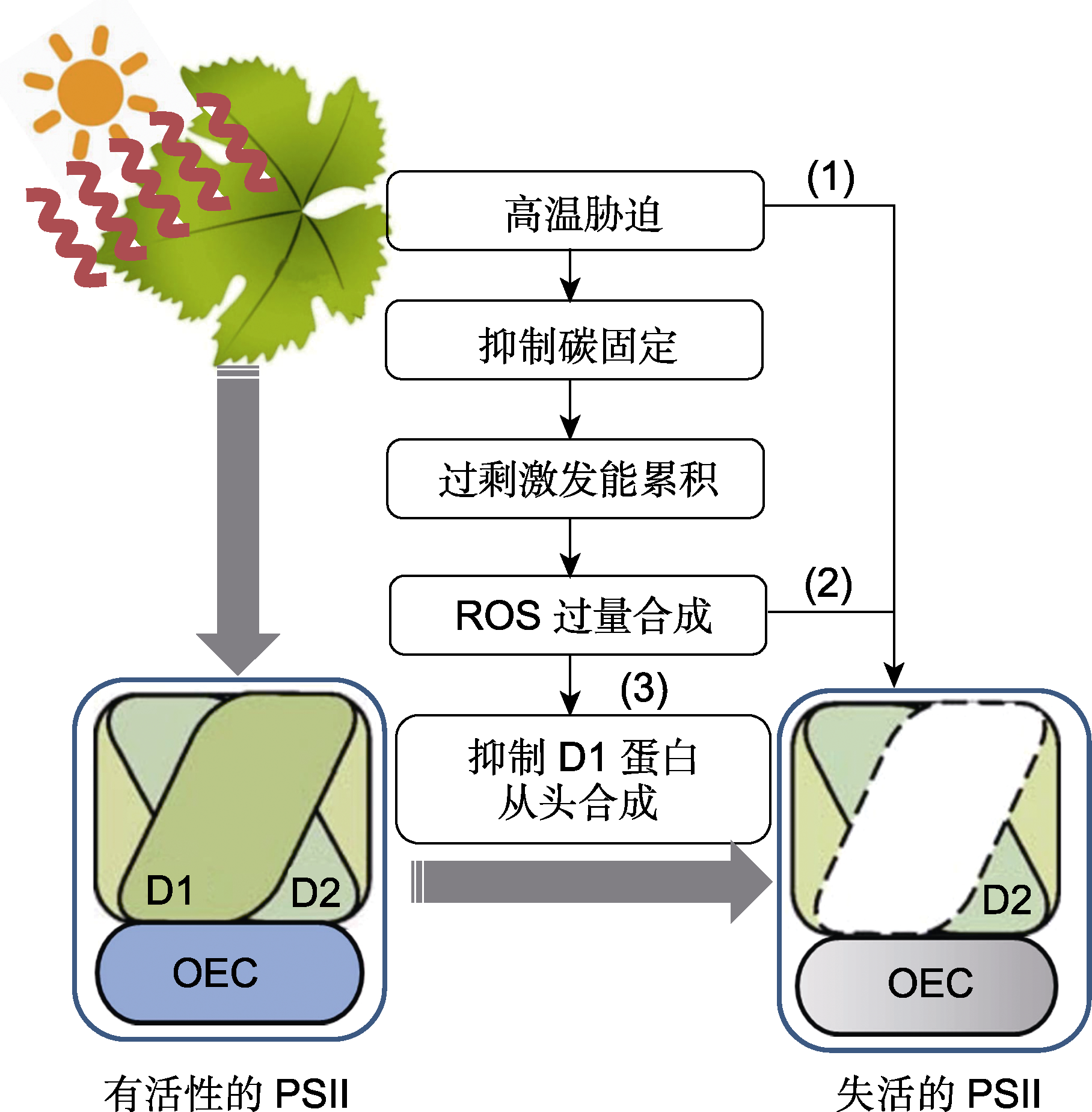
高温胁迫导致PSII处的放氧复合体及光合电子传递链失活(1), 或者通过抑制碳固定, 使过剩激发能引发ROS大量积累, ROS一方面直接损伤光合机构组分(2), 另一方面通过抑制D1蛋白的从头合成, 导致D1蛋白的净损失(3), 引起PSII光抑制。D1: D1蛋白; D2: D2蛋白; OEC: 放氧复合体; PSII: 光系统II; ROS: 活性氧
High temperature stress can lead to the inactivation of oxygen evolving complex and photosynthetic electron transport chain at PSII (1), It can also result in excess excitation and accumulation by inhibiting the process of carbon fixation, resulting in excess excitation and accumulation, resulting in a large amount of ROS accumulation. On the one hand, ROS directly damage the photosynthetic apparatus components (2), on the other hand, ROS cause the net loss of the D1 protein by inhibiting its de novo synthesis (3), thereby inducing PSII photoinhibition. D1: D1 protein; D2: D2 protein; OEC: Oxygen evolving complex; PSII: Photosystem II; ROS: Reactive oxygen species