植物ESCRT复合体的功能研究进展
Research Advances of the Plant ESCRT Machinery
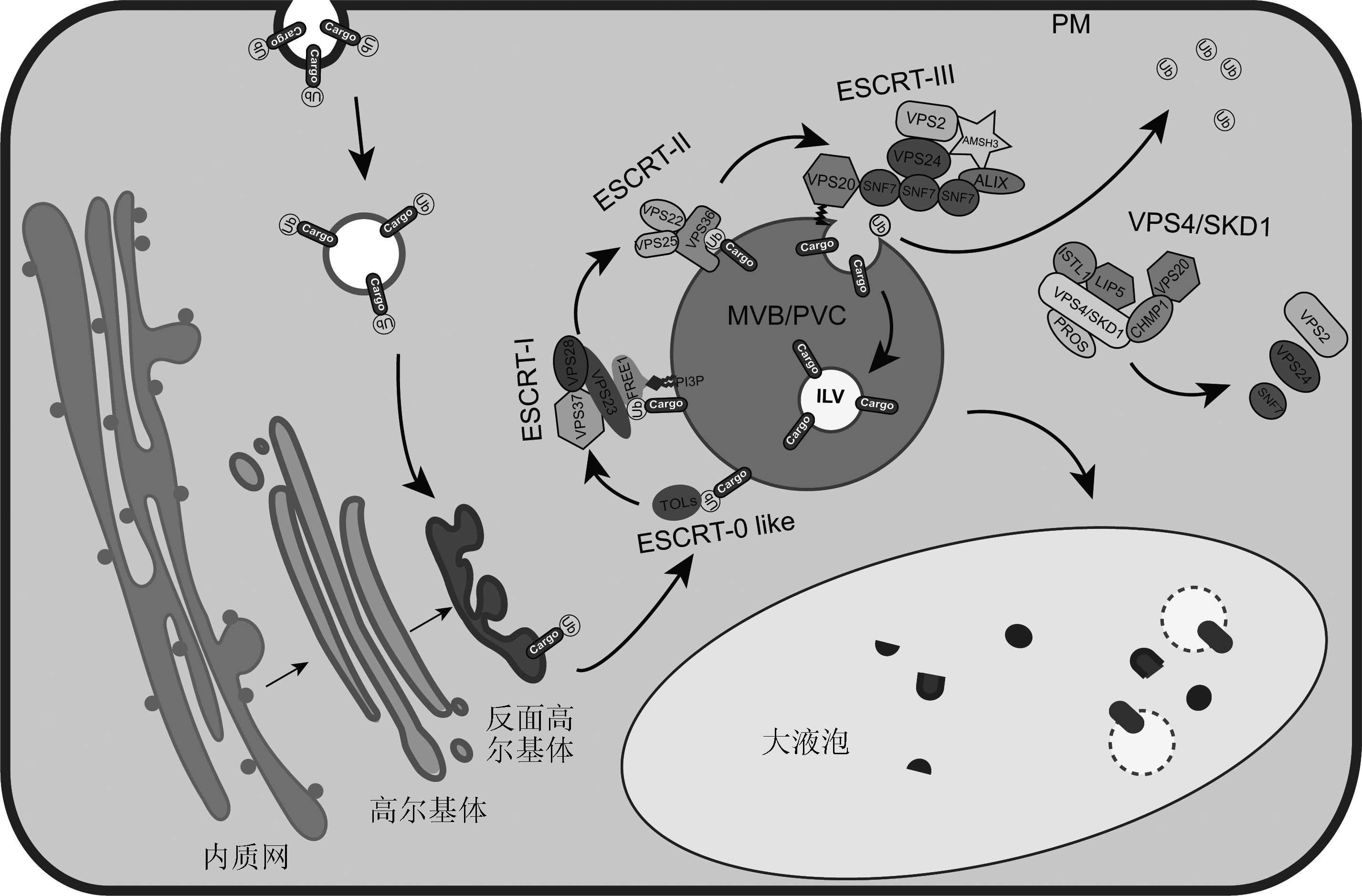
胞外蛋白和营养物质及新合成的蛋白分别通过蛋白内吞和分泌途径进入反面高尔基体(TGN)。经泛素化修饰的膜蛋白被ESCRT复合物识别, 并以依赖ESCRT的作用机制通过内腔泡(ILVs)进入MVB/PVC内腔, MVB/PVC与液泡融合, 最终使货物蛋白进入液泡中降解, 与此同时ESCRT-III复合体在VPS4/SKD1 ATP水解酶的作用下解离, 进入下一个循环。PM: 质膜; MVB/PVC: 多囊泡体/液泡前体
Extracellular proteins, materials and newly synthesized proteins are transported to trans Golgi network (TGN) via the endocytic or the secretory pathway, respectively. The ubiquitinated membrane proteins are then recognized by ESCRT machinery and be transported into the lumen of MVB/PVC via intraluminal vesicles (ILVs). After membrane fusion of MVB/PVC and vacuole, the cargo proteins are then transported to vacuole for degradation.The ESCRT-III complex is finally released from MVB/PVC membrane and the components are disassembled from each other by the activation of VPS4/SKD1 ATPase and recycled. PM: Plasma membrane; MVB/PVC: Multivesicular body/prevacuolar compartment