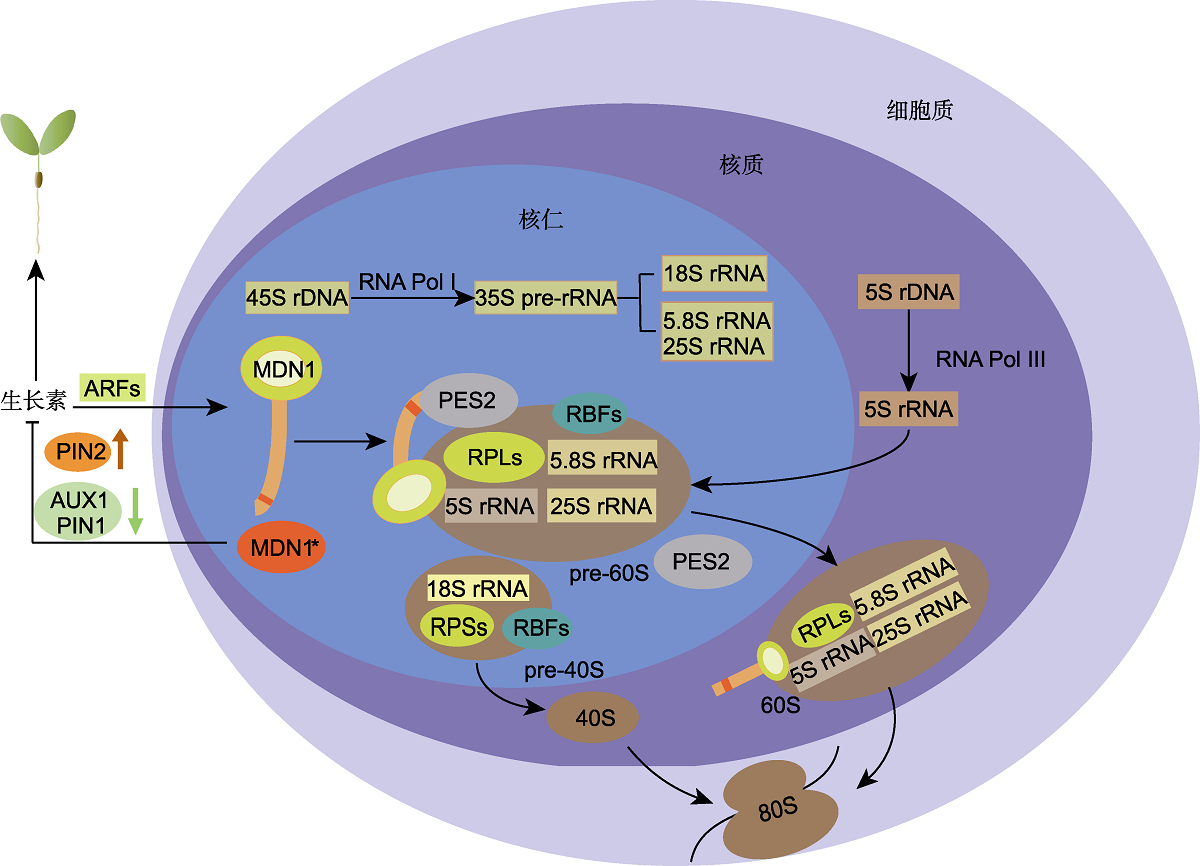
图2. 核糖体发生及MDN1相关功能
RNA Pol I: RNA聚合酶I; RPSs/RPLs: 核糖体小/大亚基蛋白; ARFs: 生长素响应因子; RBFs: 核糖体组装因子。在核糖体合成过程中, MDN1与PES2作为60S RBFs参与60S亚基的组装。MDN1的MIDAS结构域能够与PES2的UBL结构域相互作用, 在60S核糖体前体即将进入核质时, MDN1通过“机械力”使PES2从60S前体中解离; 当60S亚基出核进入胞质时, MDN1也从中解离。生长素与核糖体生物发生之间存在相互协调机制, 正常情况下, 生长素能通过ARF激活MDN1的表达; 当MDN1功能发生异常时(用红色MDN1*表示), 会造成PIN2蛋白积累量增加, AUX1和PIN1积累量降低, 进而改变生长素在植株中的稳态和分布。因此, 生长素系统可能通过参与核糖体应激响应来调控植物的生长发育。
Figure 2. Ribosome biogenesis and the related function of MDN1
RNA Pol I: RNA polymerase I; RPSs/RPLs: Ribosomal proteins of the small/large subunit; ARFs: Auxin response factors; RBFs: Ribosomes biogenetic factors. In the process of ribosome biogenesis, both MDN1 and PES2 participate in the assembly of 60S subunits as RBFs. The MIDAS domain of MDN1 can interact with the UBL domain of PES2. When the 60S ribosome precursor is about to enter the nucleoplasm, MDN1 uses ‘mechanical force' to dissociate PES2 from the 60S precursor; at the nuclear export checkpoint, MDN1 is also dissociated from the 60S ribosomal particle. There is a coordination mechanism between auxin and ribosome biogenesis. Under normal conditions, auxin activates the expression of MDN1 through ARFs. When MDN1 is dysfunction (indicated by the red MDN1*), the accumulation of PIN2 protein increases while that of AUX1 and PIN1 decreases, probably leading to changes in both homeostasis and distribution of auxin in plants. Therefore, the auxin system may participate in the ribosomal stress response to regulate plant growth and development.