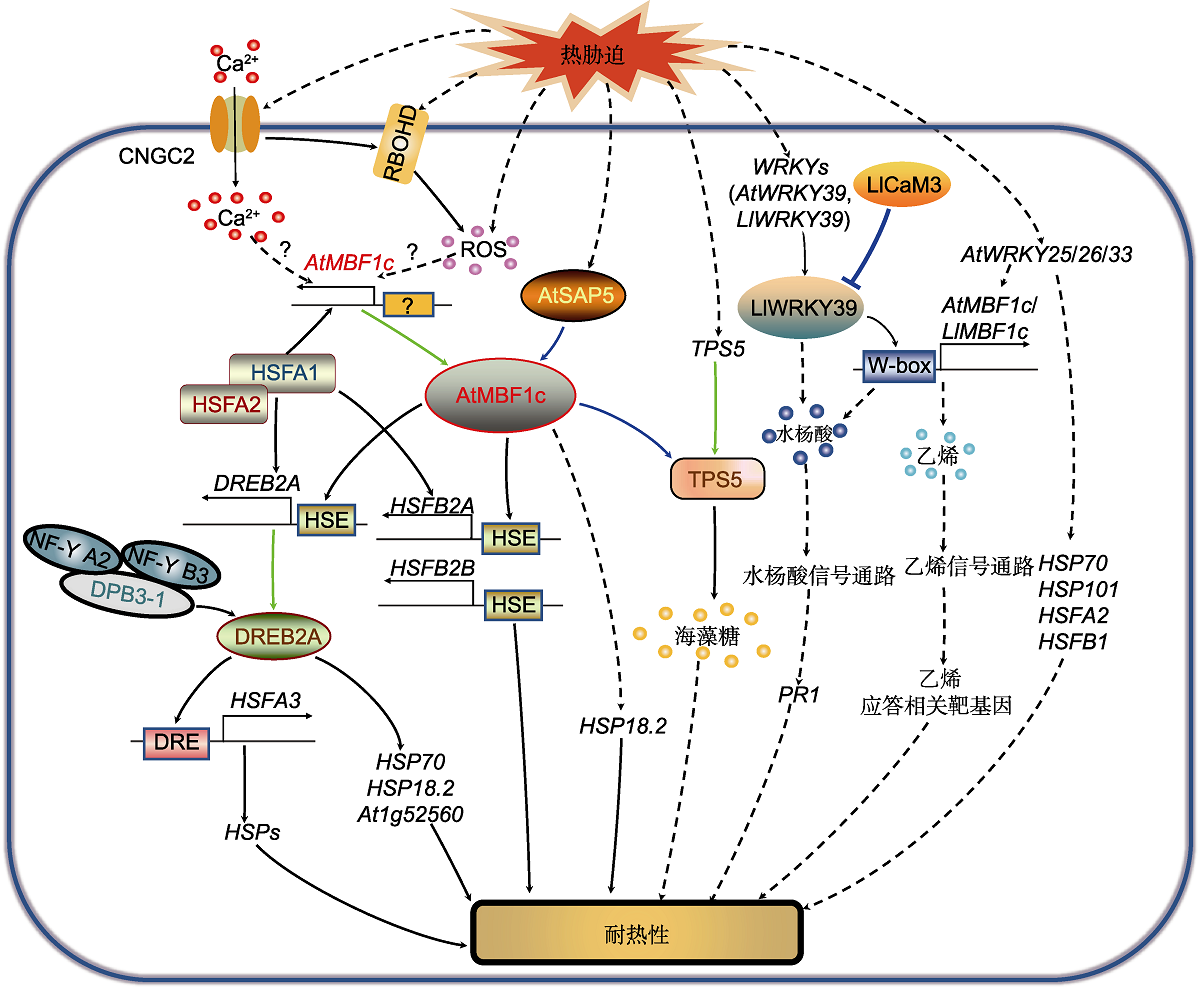
图3. MBF1调控热胁迫应答信号通路
热胁迫通过激活质膜CNGC2引起Ca2+内流, 通过激活质膜结合的RBOHD导致ROS积累。而Ca2+信号和ROS信号通过未知途径激活AtMBF1c及其下游靶基因调节的热胁迫应答。热激转录因子HSFA1与HSFA2相互作用, 直接调控AtMBF1c、HSFA2、HSFBs和DREB2A的表达。同时, AtMBF1c通过与DREB2A、HSFB2A和HSFB2B的启动子HSE元件结合, 调控其基因表达, 提高热胁迫耐受性。DREB2A与DPB3-1、NF-Y A2和NF-Y B3形成的三聚体共激活复合物互作, 增强其对下游靶基因HSFA3的转录激活, 提高植物的耐热性。DREB2A也促进HSP70、HSP18.2和At1g52560的表达, 增强植株耐热性。AtSAP5作为上游调控因子与AtMBF1c发生互作并激活AtMBF1c, 调节细胞核中HSP18.2的表达, 提高植物耐热性。热胁迫诱导TPS5的表达, AtMBF1c与TPS5互作, 通过促进海藻糖的合成和积累提高耐热性。热胁迫诱导AtWRKY39、AtWRKY25、AtWRKY26和AtWRKY33的表达。AtWRKY39通过AtMBF1c调节水杨酸(SA)信号通路下游PR1基因表达, 提高耐热性。AtWRKY25、AtWRKY26和AtWRKY33通过AtMBF1c调节乙烯信号通路下游基因的表达提高耐热性, 同时通过促进HSP70、HSP101、HSFA2和HSFB1的表达提高耐热性。CNGC2: 环核苷酸门控离子通道2; DPB3-1 (NF-YC10): DNA聚合酶II亚基B3-1; DRE: 脱水应答元件; DREB2A: 干旱应答元件结合蛋白2A; HSE: 热休克响应元件; HSFA1/2/3: 热激转录因子A1/2/3; HSFB2A/B: 热激转录因子B2A/B; HSP18.2/70/101: 热激蛋白18.2/70/101; MBF1c: 多蛋白桥梁因子1c; NF-Y A2/B3: 核因子-Y A2/B3; PR1: 病程相关因子1; RBOHD: 呼吸爆发氧化同源蛋白D; ROS: 活性氧; SAP5: 胁迫相关蛋白5; TPS5: 海藻糖磷酸合成酶5。蓝色实线箭头表示蛋白互作; 绿色实线箭头表示基因编码蛋白; 黑色实线箭头表示直接转录激活; 黑色虚线箭头表示间接转录激活。
Figure 3. Signaling pathway of MBF1 regulating heat stress response
Heat stress causes Ca2+ influx by activating the plasma membrane-localized protein CNGC2, and leads to the accumulation of ROS by activating the plasma membrane-bound RBOHD. The Ca2+ signal and ROS signal activate the heat stress response by regulating AtMBF1c and its downstream target genes through unknown pathways. The heat stress transcription factor HSFA1 interacts with HSFA2 and directly regulates the expression of AtMBF1c, HSFA2, HSFBs and DREB2A. At the same time, AtMBF1c binds to the HSE elements of DREB2A, HSFB2A and HSFB2B promoters to regulate their gene expression and improve heat stress tolerance. DREB2A interacts with the trimeric co-activation complex formed by DPB3-1, NF-Y A2 and NF-Y B3 to enhance the transcriptional activation of the downstream target gene HSFA3 and improve plant heat tolerance. DREB2A also promotes the expression of HSP70, HSP18.2 and At1g52560 to enhance plant heat tolerance. As the upstream regulator, AtSAP5 interacts with and activates AtMBF1c in the nucleus, regulating the expression of HSP18.2 and improving plant heat tolerance. Heat stress induces the expression of TPS5. AtMBF1c interacts with TPS5 to improve heat tolerance by promoting the synthesis and accumulation of trehalose. Heat stress induces the expression of AtWRKY39, AtWRKY25, AtWRKY26 and AtWRKY33. AtWRKY39 regulates the expression of the downstream gene of salicylic acid (SA) signaling pathway PR1 through AtMBF1c to improve heat tolerance. AtWRKY25, AtWRKY26 and AtWRKY33 regulate the expression of downstream genes in the ethylene (ET) signaling pathway through AtMBF1c to improve heat resistance, and at the same time promote the expression of HSP70, HSP101, HSFA2, and HSFB1. CNGC2: Cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 2; DPB3-1 (NF-YC10): DNA polymerase II subunit B3-1; DRE: Dehydration-responsive element; DREB2A: Dehydration responsive element-binding protein 2A; HSE: Heat shock elements; HSFA1/2/3: Heat stress transcription factor A1/2/3; HSFB2A/B: Heat stress transcription factor B2A/B; HSP18.2/ 70/101: Heat shock protein 18.2/70/101; MBF1c: Multiprotein bridging factor 1c; NF-Y A2/B3: Nuclear factor Y A2/B3; PR1: Pathogenesis-related factor 1; RBOHD: Respiratory burst oxidase homologue D; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SAP5: Stress-associated protein 5; TPS5: Trehalose phosphate synthetase 5. The blue solid arrow indicates protein interaction; the green solid arrow indicates gene encoding protein; the black solid arrow indicates direct transcription activation; the black dashed arrow indicates indirect transcription activation.