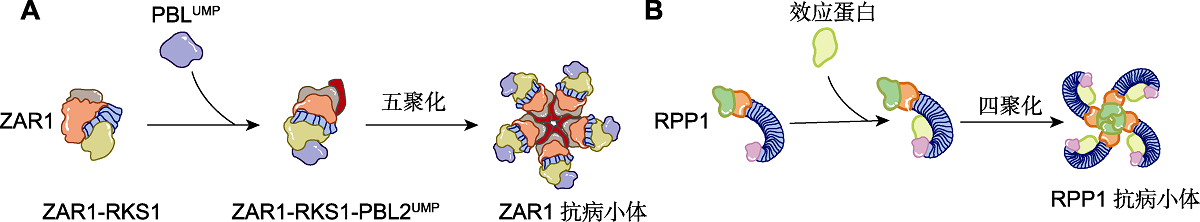
图2. 两类NLRs的激活方式(改自Duxbury et al.,
(A) CNL (ZAR1)抗病小体形成示意图。黄单胞菌效应蛋白AvrAC尿苷酸化拟南芥激酶PBL2。尿苷化的PBL2 (PBL2UMP)与胞内预先形成的ZAR1-RKS1二聚体结合, 导致ZAR1的构象发生变化, 并在ZAR1 NBD核苷酸结合位点以三磷酸腺苷或脱氧三磷酸腺苷((d)ATP)替换二磷酸腺苷(ADP)。最终, 5个ZAR1-RKS1-PBL2UMP单体形成1个五聚轮状ZAR1抗病小体。(B) TNL (RPP1)抗病小体形成示意图。胞内典型TIR-type NLR通过富亮氨酸重复序列(LRR)和羧基末端结构域(C-JID)直接识别病原体无病毒效应器, 形成具有烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸糖水解酶(NADase)活性的四聚体结构。
Figure 2. Activation modes of two NLRs (modified from Duxbury et al.,
(A) Schematic diagram of CNL (ZAR1) resistosome formation. The Xanthomonas effector AvrAC uridylates the Arabidopsis thaliana kinase PBL2. Uridylated PBL2 (PBL2UMP) associates with the intracellular pre-formed ZAR1-RKS1 dimer. This leads to a conformational change of ZAR1 and replacement of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) by adenosine triphosphate or deoxyadenosine triphosphate ((d)ATP) in the nucleotide-binding site of the NBD of ZAR1. Ultimately, this results in the formation of a pentameric wheel-like ZAR1 resistosome, which is composed of five ZAR1-RKS1-PBL2UMPprotomers. (B) Schematic diagram of TNL (RPP1) resistosome formation. Direct recognition of a pathogen avirulence effector by the leucine-rich repeat (LRR) and carboxy-terminal domains (C-JID) of a canonical Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing intracellular nucleotide- binding domain (NBD)-like receptor (TIR-type NLR) leads to the formation of a tetrameric structure with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide glycohydrolase (NADase) activity.