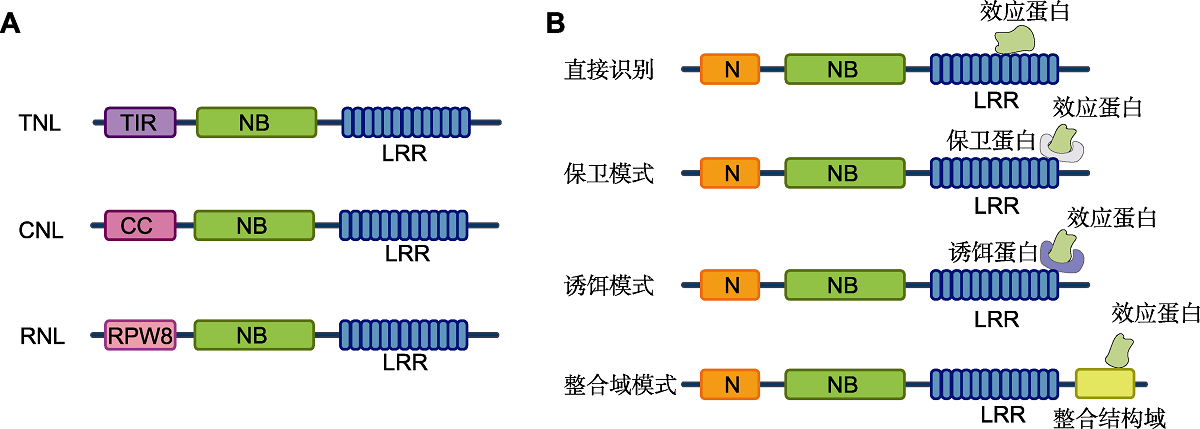
图1. NLRs的结构组成及与效应蛋白的识别模式(改自Duxbury et al.,
(A) 植物NLRs的结构域分为3类, 包括中间部位的核苷酸结合域(NBD)和C端的富含亮氨酸重复序列(LRR)结构域以及N端的TIR、CC或类RPW8的CC结构域; (B) 植物NLRs识别效应蛋白的不同模式: 一些植物NLR直接与相应的效应蛋白结合, 或通过保卫蛋白或诱饵蛋白间接检测病原体效应蛋白; 此外, 一些植物NLRs具有特异的整合结构域(ID), 介导效应蛋白的识别。
Figure 1. Structural composition of NLRs and its recognition pattern to effector proteins (modified from Duxbury et al.,
(A) The domains of plant NLRs are divided into three categories, including a central nucleotide-binding (NB) domain, a C-terminal leucine-rich repeats (LRR) region and N-terminal TIR, CC, or RPW8-like CC domain; (B) Different patterns of effector recognition by plant NLRs: Some plant NLRs directly bind to the corresponding effector proteins or indirectly detect the pathogen effector through the guardee or decoy proteins; Some plant NLRs have special integrated domains (ID) to mediate effector recognition.