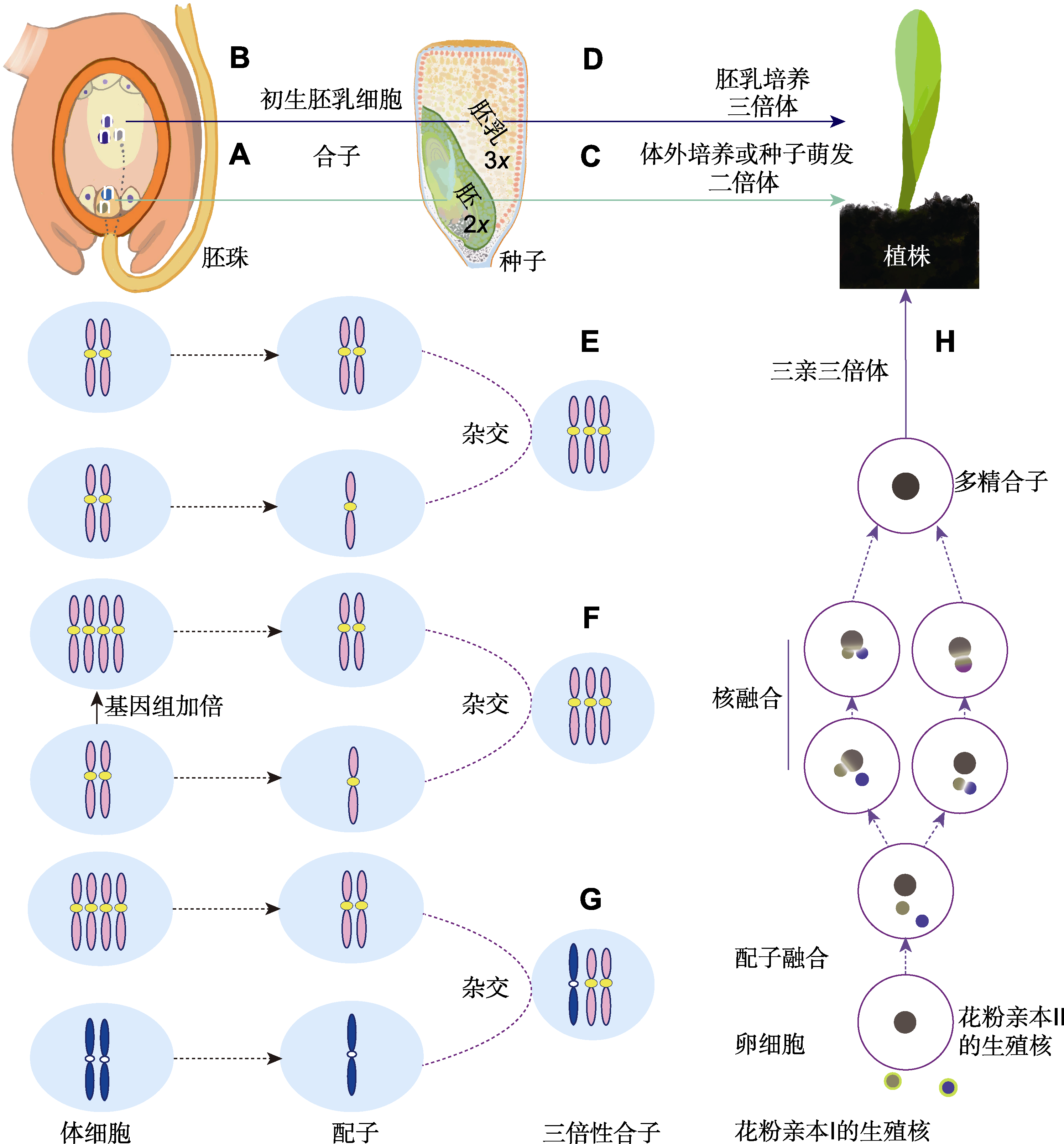
图1. 禾本科三倍体的形成途径
(A) 精细胞与卵细胞受精产生二倍性合子后发育成二倍体胚; (B) 精细胞与中央细胞受精产生三倍性初生胚乳细胞后发育成胚乳; (C) 通过离体培养胚或种子萌发发育成二倍体; (D) 通过胚乳组织培养形成三倍体; (E) 通过2n+n生殖方式形成三倍体; (F) 通过二倍体加倍后形成的同源四倍体(2n=4x=AAAA)与二倍体(2n=2x=AA)杂交合成同源三倍体; (G) 通过四倍体(2n=4x=AAAA)与二倍体(2n=2x=BB)杂交合成异源三倍体; (H) 通过多精受精形成三倍体
Figure 1. Pathways to triploidy formation in Poaceae
(A) A sperm fertilizes an egg cell to produce diploid zygote which subsequently grows into diploid embryo; (B) A sperm fertilizes a center cell to produce triploid primary endosperm cell which subsequently grows into endosperm; (C) The embryo develops into diploid plant through in vitro culture or seed germination; (D) The endosperm develops into triploid plant via culturing in vitro; (E) Triploid formation by a 2n+n mating; (F) The autotriploid hybrid produced by crossing tetraploid (2n=4x=AAAA) and diploid (2n=2x=AA); (G) The allotriploid hybrid produced by crossing tetraploid (2n=4x=AAAA) and diploid (2n=2x=BB); (H) Formation of triploid by polyspermy