植物响应镉胁迫的生理生化机制研究进展
Research Advances in Plant Physiological and Biochemical Mechanisms in Response to Cadmium Stress
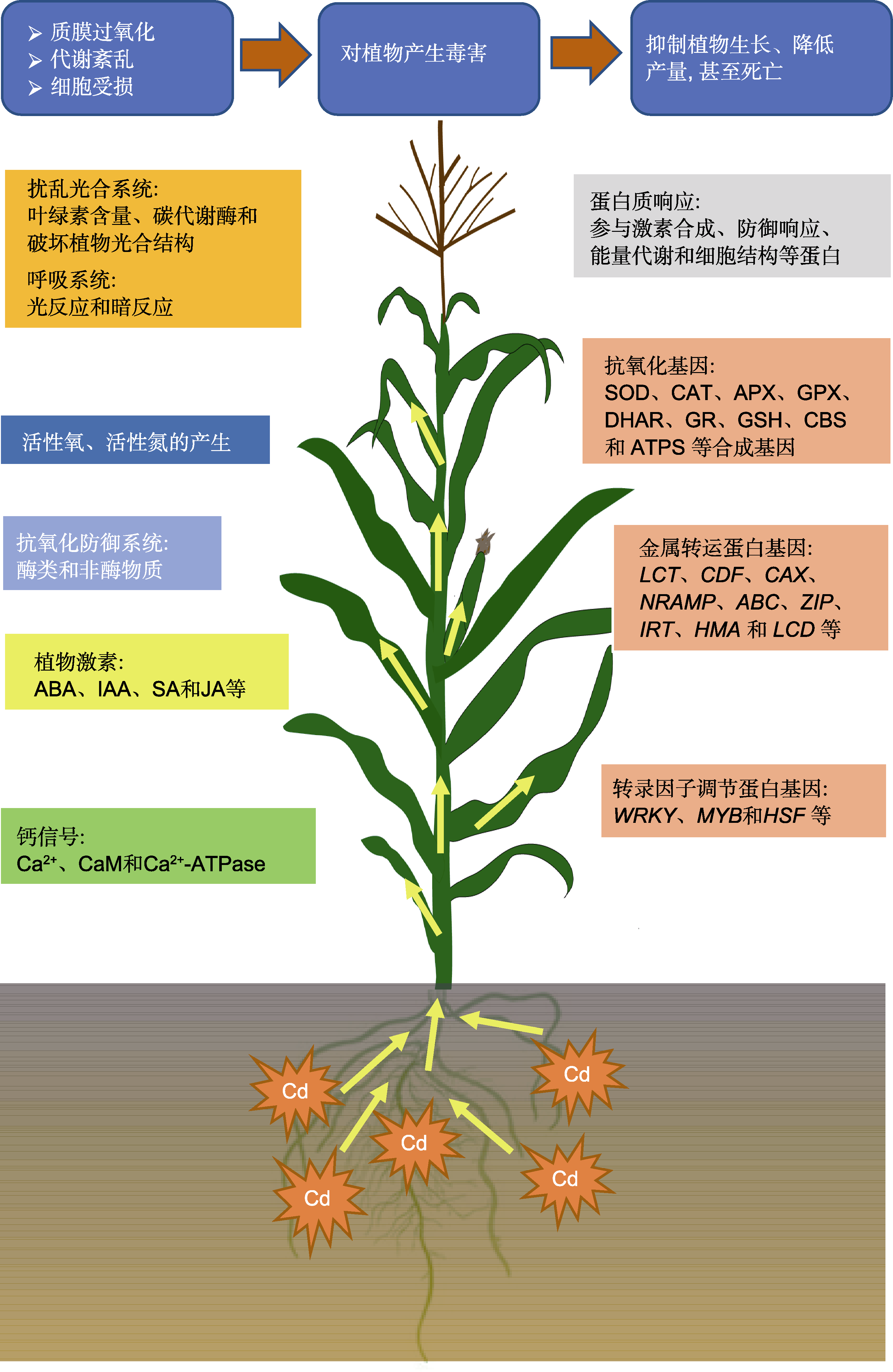
图1. Cd胁迫下植物体内主要生理生化代谢的响应机制
ABA: 脱落酸; IAA: 吲哚乙酸; SA: 水杨酸; JA: 茉莉酸; SOD: 超氧化物歧化酶; CAT: 过氧化氢酶; APX: 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶; GPX: 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶; DHAR: 脱氢抗坏血酸还原酶; GR: 谷胱甘肽还原酶; GSH: 谷胱甘肽; CBS: 胱硫醚β-合酶; ATPS: ATP硫酸化酶
Figure 1. Response mechanism of physiological and biochemical metabolism in plants under Cd stress
ABA: Abscisic acid; IAA: Indole-3-acetic acid; SA: Salicylic acid; JA: Jasmonic acid; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; CAT: Catalase; APX: Ascorbateperoxidase; GPX: Glutathione peroxidase; DHAR: Dehydroascorbate reductase; GR: Glutathione reductase; GSH: Glutathione; CBS: Cystatohinine β-synthetase; ATPS: ATP sulfatase