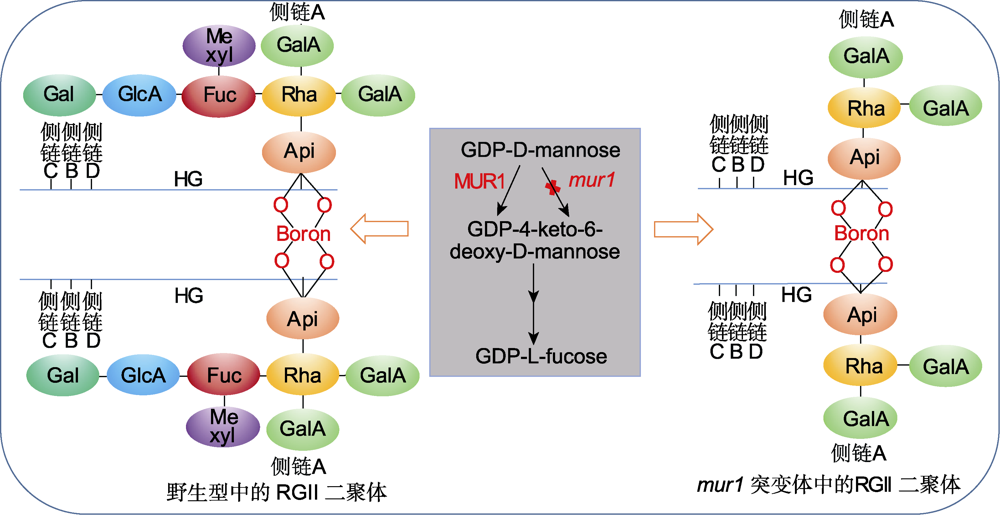
图2. 拟南芥野生型和mur1突变体中的鼠李半乳糖醛酸聚糖II (RGII)二聚体(改自O’Neill et al.
野生型植株中的鼠李半乳糖醛酸聚糖II二聚体由侧链A的芹菜糖残基通过硼酸二酯键共价交联而成。MUR1催化GDP-L-岩藻糖从头合成的第一步, MUR1功能缺失导致GDP-L-岩藻糖合成受阻。因此, mur1突变体中的鼠李半乳糖醛酸聚糖II侧链A被截断, 这一缺陷导致鼠李半乳糖醛酸聚糖II二聚体的形成减少。HG: 同型半乳糖醛酸聚糖; Api: 芹菜糖; Rha: L-鼠李糖; Fuc: L-岩藻糖; GlcA: D-葡萄糖醛酸; Gal: L-半乳糖; GalA: D-半乳糖醛酸; Me xyl: 2-O-甲基-D-木糖
Figure 2. Rhamngalacturonan II (RGII) dimer in Arabidopsis wild-type and mur1 mutants (modified from O’Neill et al.
In wild-type plants, RGII dimers are formed between Apiosyl residue of side chain A which are cross-linked covalently by the diester borate bonds. MUR1 catalyzes the first step in the de novo synthesis of GDP-L-fucose. The loss of MUR1 function leads to the block of GDP-L-fucose synthesis. Therefore, the RGII side chain A was truncated in mur1 mutants which resulted in reduced formation of RG-II dimers. HG: Homogalacturonan; Api: D-apiosyl; Rha: L-rhamnose; Fuc: L-fucose; GlcA: D-glucuronic acid; Gal: L-galactose; GalA: D-galacturonic acid; Me xyl: 2-O-methyl-D-xylose