|
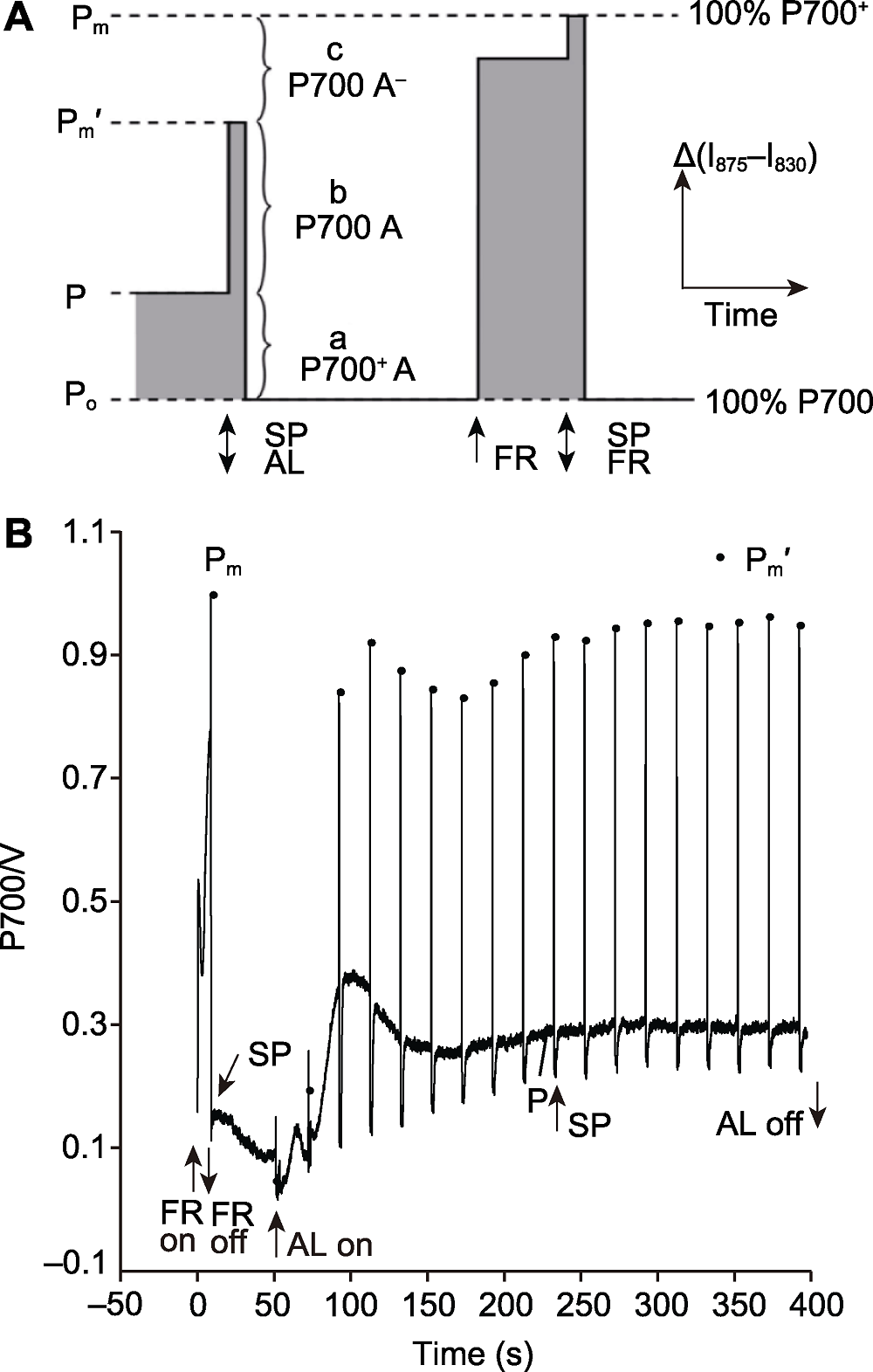
图3. 利用饱和脉冲法计算PSI能量转化
(A)利用饱和脉冲法计算PSI能量转化的原理示意图(改自Klughammer and Schreiber, 2008); (B) 利用饱和脉冲法计算PSI能量转化的测量曲线。AL: 活化光; SP: 饱和脉冲(10000 μmol·m-2·s-1); FR: 远红光(720 nm); Po: 远红光和饱和脉冲关闭后, 全部PSI反应中心处于完全还原状态, 此时P700信号是0; P: 活化光照光过程中, 部分PSI反应中心被氧化的P700信号; Pm': 活化光关闭, 具有开放、有活性的PSI反应中心被饱和脉冲完全氧化的P700信号; Pm: 远红光关闭, 全部PSI反应中心被饱和脉冲完全氧化的P700信号; a P700+ A: 由于PSI电子供体侧限制导致的关闭的PSI反应中心; A: PSI的下游电子受体; b P700 A: 开放的PSI反应中心; c P700 A-: 由于PSI电子受体侧限制导致的关闭的PSI反应中心; a、b、c是PSI反应中心的3个部分, b是开放的、有活性的, 其光化学量子产量定义为1, 而a和c是关闭的、没有活性的, 其光化学量子产量定义为0。
|
|
Figure 3. The saturation pulse method for determination of efficiency of energy conversion in PSI
(A) Principle of saturation pulse method for determination of efficiency of energy conversion in PSI (modified from Klughammer and Schreiber, 2008); (B) Curve of saturation pulse method for determination of efficiency of energy conversion in PSI. AL: Actinic light; SP: Saturation pulse (10000 μmol·m-2·s-1); FR: Far-red light (720 nm); Po: Complete reduction is induced after the cessation of SP and far-red light with the zero P700 signal; P: In the presence of AL, a part of the PSI centers are oxidized by the AL resulting in an intermediate P700 signal; Pm': A part of the PSI centers are oxidized completely by the SP with the maximal P700 signal after the AL is turned off; Pm: All the PSI centers are oxidized completely by the SP with the maximal P700 signal after FR pre-illumination; a P700+ A: Donor-side limited closed centers; A: The effective ensemble of PSI acceptors, the same as below; b P700 A: Open centers P700A; c P700 A-: Acceptor-side limited closed centers. a, b, c are the three parts of all PSI centers, b is open and active, and the photochemical quantum yield is unity, while a and c are closed and inactive, and the photochemical quantum yield is 0.
|