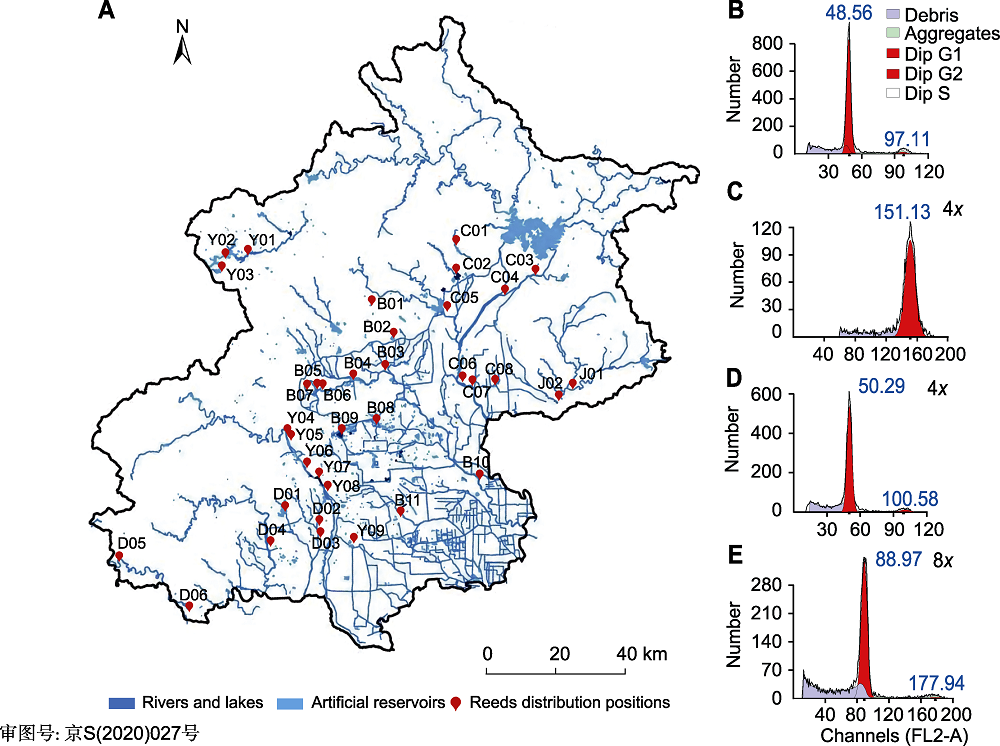
图1. 北京地区的芦苇分布和染色体倍性分析
(A) 北京地区芦苇分布(芦苇的主要分布区域以红点标注, 并依照水系进行编号: 永定河水系(Y)、潮白河水系(C)、北运河水系(B)、大运河水系(D)和蓟运河水系(J); 蓝色表示河流、湖泊或人造水库); (B)-(E) 用流式细胞术检测芦苇染色体倍性(横坐标为通道的荧光强度, 纵坐标为细胞核数目; G1和G2期分别用深红色和浅红色表示; 碎片和聚集体分别用灰紫色和绿色表示)。图(B)和(C)以水稻为内参, 检测四倍体芦苇; 图(D)和(E)以四倍体芦苇为内参, 检测八倍体芦苇。
Figure 1. Distribution and chromosome ploidy of Phragmites australis in Beijing
(A) Distribution of reeds in Beijing (The main distribution areas of reeds are marked by red dots and numbered according to the water system: Yongding River System (Y), Chaobai River System (C), North Canal System (B), Grand Canal System (D), Ji Canal System (J); Blue indicates rivers, lakes or artificial reservoirs); (B)-(E) Detection of reed chromosome ploidy by flow cytometry (The abscissa is the fluorescence intensity of the channel, and the ordinate is the number of nuclei; G1 and G2 phases are indicated by dark red and light red, respectively; fragments and aggregates are indicated by gray-purple and green, respectively). Figures (B) and (C) detected the tetraploid reeds using rice as the internal reference; Figures (D) and (E) detected the octaploid reeds using the tetraploid reeds as the internal reference.