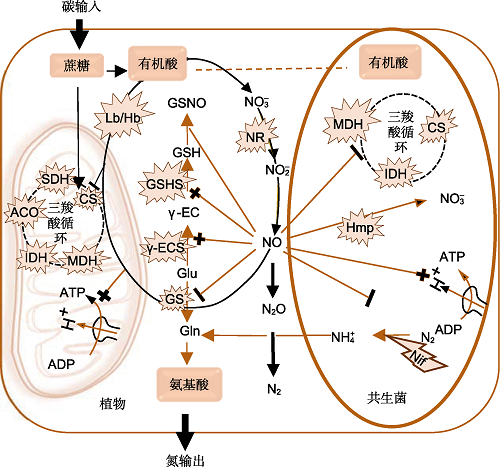
图2. NO在共生固氮中的作用示意图(改自
一方面, NO抑制固氮和C、N代谢; 另一方面, NO调控细胞氧化还原和保持低氧水平下的能量状态。带+的细线表示NO的活化、诱导和保持效果; 带有-的细线表示NO的抑制作用。椭圆形粗线箭头表示NO主要的代谢途径。爆炸型图示指来自植物和菌共生体的酶, 闪电型图示表示根瘤菌内的基因。ACO: 乌头酸; CS: 柠檬酸合酶; Gln: 谷氨酰胺; Glu: 谷氨酸; GS: 谷氨酰胺合成酶; GSH: 谷胱甘肽; GSHS: 谷胱甘肽合成酶; GSNO: S-亚硝基谷胱甘肽; Hb: 血红蛋白; IDH: 异柠檬酸脱氢酶; MDH: 苹果酸脱氢酶; NH4+: 铵根离子; Nif: 固氮酶; SDH: 琥珀酸脱氢酶; γ-EC: γ-谷氨酰半胱氨酸; γ-ECS: γ-谷氨酰半胱氨酸合成酶
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the role of NO in symbiotic nitrogen fixation (modified from
On the one hand, NO inhibits nitrogen fixation and carbon and nitrogen metabolism; on the other hand, it regulates cellular redox status and maintains the energy state under low oxygen levels. A thin line with + indicate the activation, induction, and retention effects of NO; a thin line with - indicate the inhibition of NO. The oval thick line arrows indicate the main metabolic pathways of NO. Explosive type diagrams refer to enzymes from plants and bacterial symbionts, and lightning type diagram represents genes within rhizobium. ACO: Aconitic acid; CS: Citrate synthase; Gln: Glutamine; Glu: Glutamic acid; GS: Glutamine synthetase; GSH: Glutathione; GSHS: Glutathione synthetase; GSNO: S-nitrosoglu- tathione; Hb: Hemoglobin; IDH: Isocitrate dehydrogenase; MDH: Malate dehydrogenase; NH4+: Ammonium ion; Nif: Nitrogenase; SDH: Succinate dehydrogenase; γ-EC: γ-glu- tamylcysteine; γ-ECS: γ-glutamyl cysteine synthetase