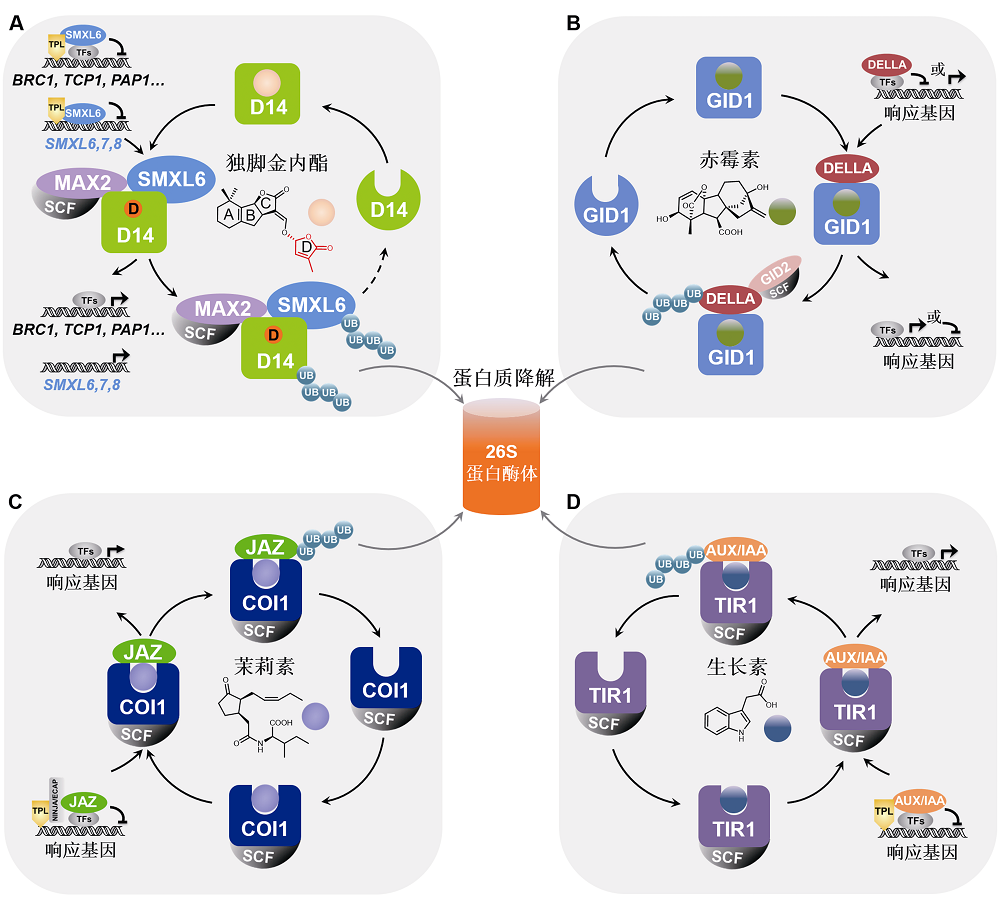
图2. 独脚金内酯、赤霉素、茉莉素及生长素信号途径中抑制子的功能比较
植物激素独脚金内酯(A)、赤霉素(B)、茉莉素(C)及生长素(D)信号传导途径中的抑制子DELLA、AUX/IAA、JAZ和D53/SMXL均通过结合下游信号蛋白(转录因子)调控其转录活性, 从而阻遏激素响应基因的表达。激素分子被相应的受体识别后激活其信号传导链,诱导抑制子通过泛素化-蛋白酶体途径降解, 促进响应基因表达并介导相应的生物学功能。独脚金内酯(SL)信号传导途径中的抑制子SMXL6,7,8同时还作为转录因子直接结合并抑制SMXL6,7,8基因的启动子; SL诱导SMXL6,7,8降解, 从而解除SMXL6,7,8对自身基因启动子的抑制, 激活SMXL6,7,8自身基因的表达, 形成维持SL通路稳态的负反馈调控体系(A)。
Figure 2. Comparison of the repressor proteins in strigolactone, gibberellin, jasmonate and auxin signaling pathways
The repressor proteins D53/SMXL, DELLA, JAZ, and AUX/IAA in the signaling pathways of strigolactone (A), gibberellin (B), jasmonate (C) and auxin (D) bind and inhibit downstream transcription factors, thereby suppressing the expression of hormone-responsive genes. Hormone molecule is recognized by corresponding receptor protein and activates the signal transduction chain to induce the degradation of the repressor protein via ubiquitination-proteasome pathway, then triggering response gene expression and related biological processes. Moreover, the repressor proteins SMXL6,7,8 in strigolactone (SL) signaling pathway can also directly bind and inhibit the promoter of SMXL6,7,8 gene as transcription factors. SL induces the degradation of SMXL6,7,8 to release its repression on the SMXL6,7,8 promoters to activate the expression of SMXL6,7,8 genes, forming a negative feedback regulation loop (A) essential for the homeostasis of SL pathway.