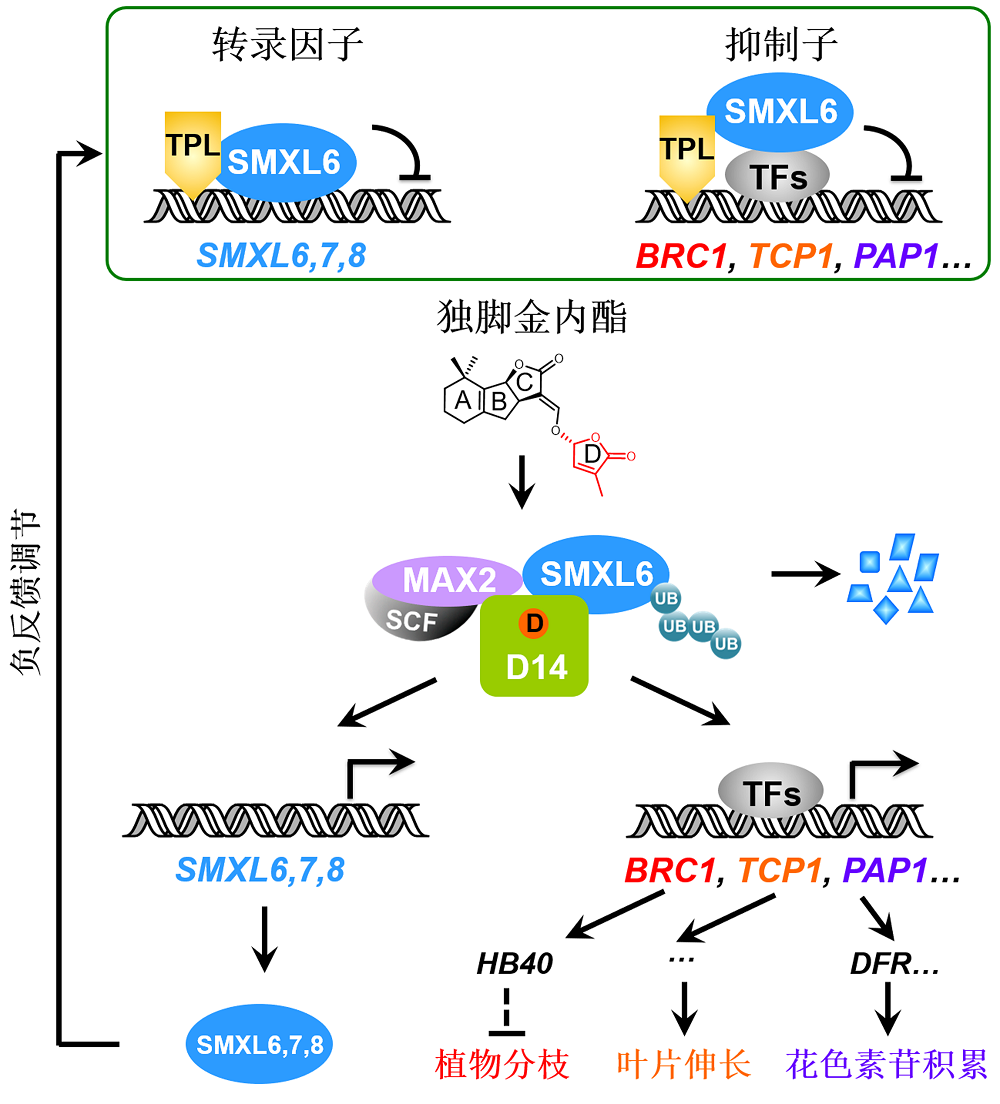
图1. 独脚金内酯信号通路中抑制子SMXL6,7,8的双重功能工作模型
独脚金内酯信号通路中的SMXL6,7,8是具有双重功能的新型抑制子: SMXL6,7,8作为抑制子招募TPL共抑制子并直接结合下游转录因子抑制其转录活性, 从而阻遏独脚金内酯(SL)响应基因的表达; 同时SMXL6,7,8又作为转录因子直接结合并抑制SMXL6,7,8基因的启动子。SL被D14感知, 诱导SMXL6,7, 8-D14-MAX2复合体形成, 导致SMXL6,7,8通过泛素化-蛋白酶体途径降解, 从而解除SMXL6,7,8对下游转录因子以及自身基因启动子的抑制, 一方面激活BRC1、TCP1和PAP1等响应基因的转录, 最终调控植物分枝、叶片伸长和花色素苷积累等生物学过程; 另一方面解除对SMXL6,7,8启动子的抑制, 激活SMXL6,7,8自身基因的表达, 形成维持SL通路稳态的负反馈调控体系。SCF: Skp1-Cullin-F-box; UB: 泛素
Figure 1. Working model for the dual-function repressors SMXL6,7,8 in strigolactone signaling
SMXL6,7,8 in the strigolactone signaling pathway act as novel repressors with dual functions: SMXL6,7,8 act as repressors that recruit TPL co-repressor proteins and bind transcription factors to inhibit their transcriptional activity, thereby suppressing expression of strigolactone (SL)-responsive genes; meanwhile, SMXL6,7,8 also serve as transcription factors that directly bind and inhibit the promoters of SMXL6,7,8 genes. SL is perceived by D14 to trigger formation of SMXL6,7,8-D14-MAX2 complex and further induce SMXL6,7,8 degradation via the ubiquitination-proteasome pathway. The SL-induced SMXL6,7,8 degradation releases transcription factors to activate expression of the SL-responsive genes such as BRC1, TCP1 and PAP1 essential for plant branching, leaf elongation, and anthocyanin biosynthesis, respectively. Such SMXL6,7,8 degradation also de- represses the SMXL6,7,8 suppression on the SMXL6,7,8 promoters to activate the expression of SMXL6,7,8 genes, which forms a negative feedback regulation loop that maintains the homeostasis of SL pathway. SCF: Skp1-Cullin-F- box; UB: Ubiquitin