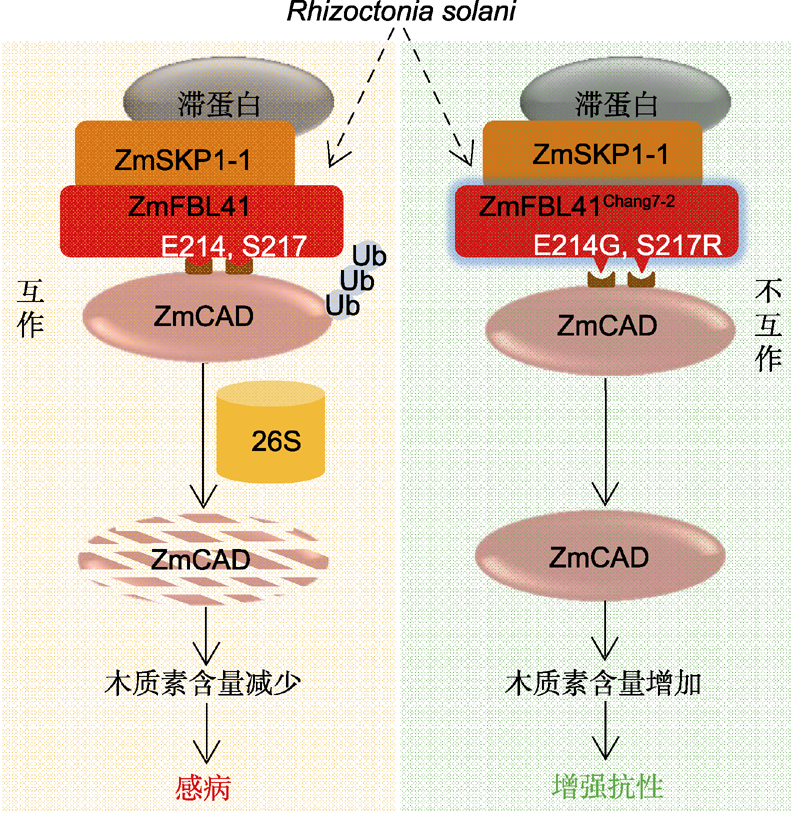
图1. ZmFBL41介导的纹枯病抗性
ZmFBL41与ZmSKP1-1互作形成SCF复合体, 通过26S蛋白酶体降解底物ZmCAD, 减少木质素的积累, 从而使玉米易感纹枯病。而ZmFBL41Chang7-2因其中2个关键氨基酸位点变异(E214G, S217R), 不能结合并降解底物ZmCAD, 从而引起木质素积累, 使玉米对纹枯病的抗性增强。
Figure 1. A model for ZmFBL41-mediated banded leaf and sheath blight (BLSB) resistance
ZmFBL41 interacts with ZmSKP1-1 to form the SCF complex, and recruits ZmCAD for 26S proteasome-mediated degradation, resulting in reduced lignin synthesis and increased susceptibility of maize to R. solani. However, in the natural maize resource Chang7-2, the protein ZmFBL41Chang7-2 with two amino acid variations (E214G and S217R) is not able to interact with ZmCAD, leading to failure in degradation of ZmCAD and resulting in accumulation of lignin, which consequently enhances resistance to R. solani.