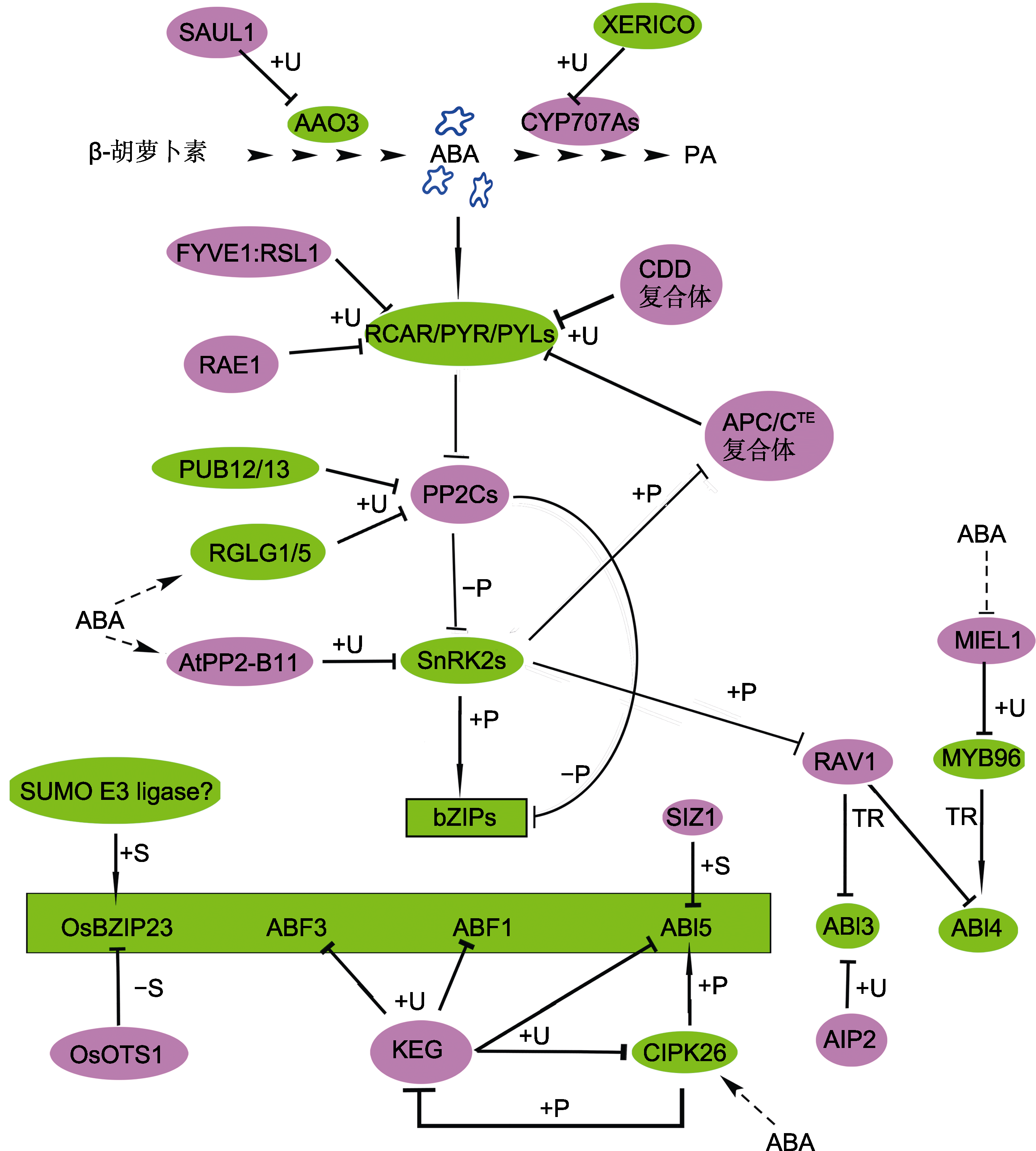
图2. 蛋白泛素化和SUMO化修饰调节ABA合成代谢、识别、转导和响应
AAO3和CYP707A分别是ABA的合成酶和氧化酶。ABA中心转导途径由RCAR/PYR/PYLs-PP2Cs-SnRK2s-bZIPs组成。图中bZIPs代表OsBZIP23、ABF3、ABF1和ABI5 (绿色背景方框内)。红色背景中蛋白是ABA信号的负调节因子; 绿色背景中蛋白是ABA信号的正调节因子。箭头表示促进作用; T型线表示抑制作用; 实线表示有直接的互作关系; 虚线和?表示具体过程未知。+/-P: 磷酸化/去磷酸化; +U: 泛素化; +/-S: SUMO/去SUMO化; TR: 转录调控
Figure 2. Protein ubiquitination and sumoylation regulate ABA biosynthesis and catabolism, ABA perception, signal transduction and responses
AAO3 and CYP707A are ABA synthase and oxidase enzyme, respectively. The core ABA signaling pathway is composed of RCAR/PYR/PYLs-PP2Cs-SnRK2s-bZIPs. In this figure, bZIPs represent OsBZIP23, ABF3, ABF1 and ABI5 (inside the box on the green background). The proteins in the red (green) background are negative (positive) factors in ABA signaling. Arrows represent promotion; T-shaped bars represent repression; The solid line indicates direct interaction; Dotted lines and ? represent uncon?rmed. +/-P: Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation; +U: Ubiquitination; +/-S: SUMOylation/de-SUMOylation; TR: Transcriptional regulation