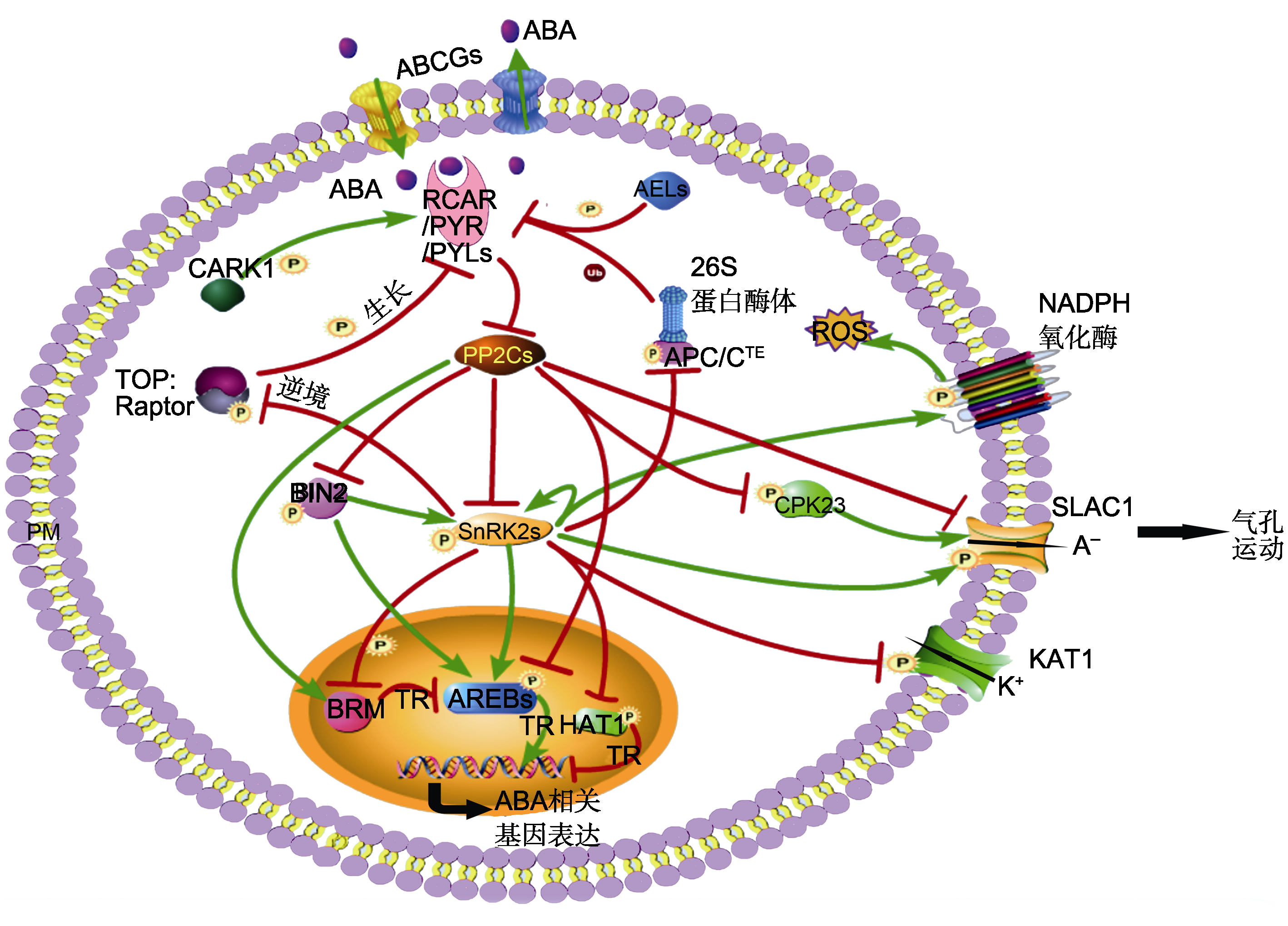
图1. 磷酸化修饰在ABA信号中的作用
ABA的转运由运输载体如AtABCGs完成, 其转导途径由受体RCAR/PYR/PYLs、磷酸酶PP2Cs、激酶SnRK2s以及SnRK2s的底物等组成。转录因子(AREBs和HAT1)、膜蛋白(SLAC1、KAT1和NADPH氧化酶)、DNA解旋酶BRM、TOR激酶复合体和APC/C泛素复合体被SnRK2s磷酸化, 其中AREBs、BRM和SLAC1被PP2Cs去磷酸化。激酶BIN2是整合BR信号通路和ABA信号通路的关键因子。TOR激酶复合体与ABA信号相互拮抗调节植物生长与逆境响应。钙调激酶CPK23独立于SnRK2s参与气孔运动。激酶CARK1和AEL1磷酸化ABA受体PYR1的不同位点引起相反结果。绿色箭头表示促进作用; 红色T型线表示抑制作用。PM: 细胞膜; P: 磷酸化; Ub: 泛素化; A-: 阴离子; ROS: 活性氧; TR: 转录调控
Figure 1. The regulatory roles of protein phosphorylation in core
ABA signaling ABA transport is performed by transporters, such as AtABCGs. The core ABA signaling pathway is composed of RCAR/PYR/PYLs, PP2Cs, SnRK2s, and the substrates of SnRK2s. The substrates of SnRK2s include AREBs, HAT1, SLAC1, KAT1, NADPH oxidases, BRM, TOR complex, and APC/C complex. AREBs, BRM and SLAC1 can be dephosphorylated by PP2Cs. BIN2 is a key factor that integrates BR and ABA signaling pathway. The TOR complex and ABA signaling antagonistically regulates plant growth and stress response. CPK23 is independent of SnRK2s in stomatal movement. Different phosphorylation sites of ABA receptor PYR1 by CARK1 and AEL1 give opposite results. Green arrows represent promotion; Red T-shaped bars represent repression. PM: Plasma membrane; P: Phosphorylation; Ub: Ubiquitination; A-: Negative ions; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TR: Transcriptional regulation