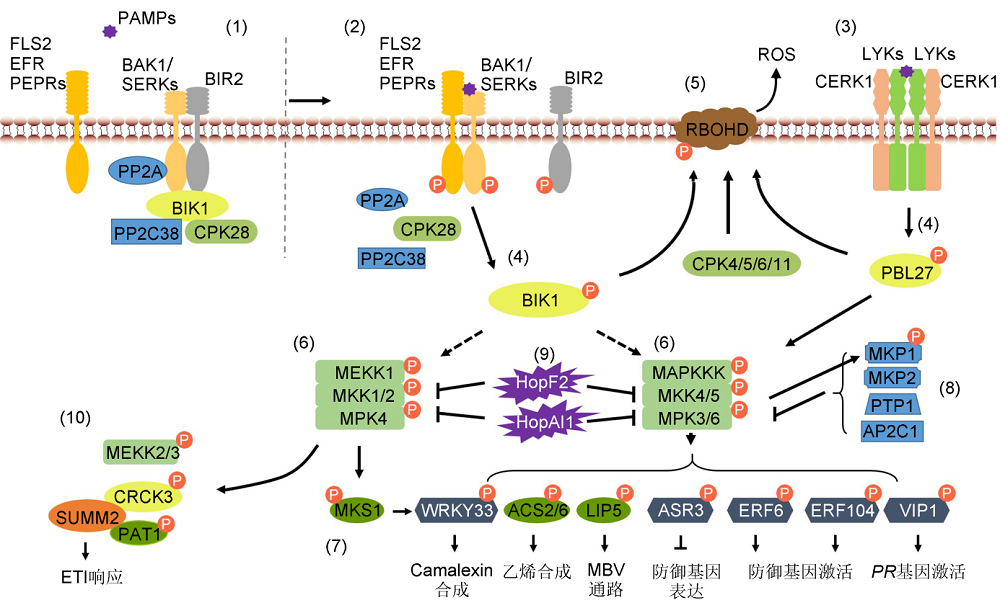
图2. 植物中防御相关蛋白的磷酸化修饰调控免疫信号途径
(1) 拟南芥中, 未接受病原信号时, PP2A负调控BAK1的激活, 同时BIK1的活性受到PP2C38和CPK28的共同抑制。(2), (3) 病原菌侵染时, LRR类PRRs识别PAMPs, 结合BAK1后被磷酸化激活, LysM类受体激酶CERK1结合LYKs激活免疫信号。(4) 激活的PRRs磷酸化激活胞质内受体激酶(BIK1和PBL27)等。(5) BIK1与CPKs共同磷酸化激活RBOHD, 促进ROS的产生。(6), (7) 激活的RLCKs将信号传递至MAPK信号级联, 导致MAPK激酶被激活。激活的MAPK磷酸化修饰不同的下游底物, 调控不同的防御应答。(8) MKP1、MKP2、PTP1以及AP2C1等磷酸酶负调控MAPKs的活性。(9) 病原菌分泌的效应蛋白HopF2和HopAI1抑制MAPK信号级联途径。(10) 抗病蛋白SUMM2通过监测MPK4对底物MEKK2、CRCK3以及PAT1的磷酸化修饰, 适时地激活ETI途径。
Figure 2. Phosphorylation of defense related proteins in plant immune signaling pathway
(1) In Arabidopsis, PP2A negatively regulates the activation of BAK1, meanwhile PP2C38 and CPK28 negatively regulate the phosphorylation of BIK1 without pathogen infection. (2), (3) LRR-type PRRs combine with BAK1 and LysM-type RLK CERK1 combine with LYKs to activate immune signaling after perception of pathogen attack. (4) Activated PRRs phosphorylate BIK1 or PBL27. (5) BIK1 and CPKs phosphorylate RBOHD to promote ROS generation. (6), (7) MAPK cascades are activated and then phosphorylate different substrates to regulate different defense responses. (8) MKP1, MKP2, PTP1 and AP2C1 negatively regulate the activity of MAPKs. (9) Bacterial pathogens inject effector proteins HopF2 and HopAI1 to inhibit the activation of MAPK cascades. (10) Resistance protein SUMM2 activate ETI pathway in time by monitoring the phosphorylation statue of MEKK2, CRCK3 and PAT1, the substrates of MPK4.