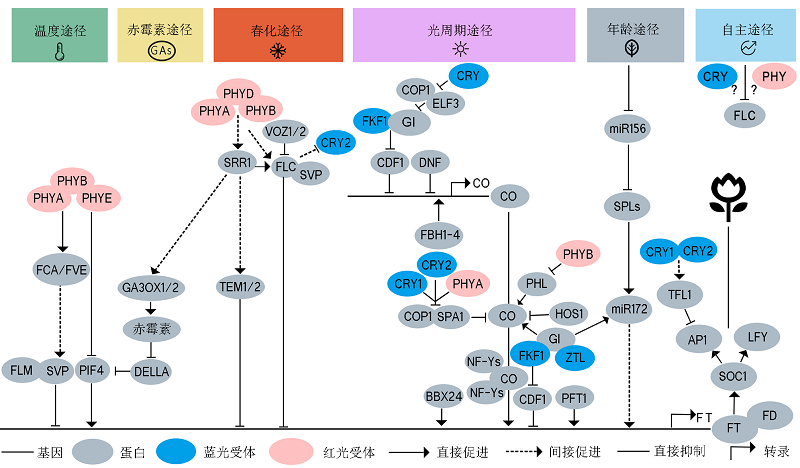
图2. 光受体介导环境信号调控拟南芥开花示意图
植物中已探明至少有6种开花调控途径: 光周期途径、春化途径、温度途径、自主途径、赤霉素途径和年龄途径。在叶片中, 光敏色素、隐花色素和ZTL/FKF1/LKP2等光受体介导光信号并将信号传递给昼夜节律钟, 经过多种开花途径的信号整合, 最终直接或间接调控CO、FT和FLC的表达和蛋白稳定性。温度途径中光敏色素通过FCA/FVE间接调控FLM、SVP和PIF4进而调控FT的转录; 赤霉素途径和春化途径由SRR1进行信号整合, 通过GA生物合成途径GA3OX1/2以及DELLA蛋白调控FT的转录, 春化途径通过VOZ1/2和光敏色素调控FLC、SVP和TEM1/2进而调控FT的表达; 自主途径通过抑制开花阻遏物和春化途径关键基因FLC促进开花; 光受体在光周期途径中发挥重要作用, GI、CDF1、DNF、FBH1-4、COP1、SPA1、HOS1和NF-Ys等蛋白直接或间接与光受体互作, 对CO转录、转录后水平以及FT的转录水平等关键调控节点进行调控。年龄途径通过miR156/172和SPLs调控FT的表达。不同的开花途径之间存在信号整合机制, 最终开花信号被整合到FT、SOC1和LFY, 激活AP1和LFY, 进而完成开花起始。实线箭头表示直接促进, 虚线箭头表示间接促进, 钝化线表示直接抑制, 红色表示红光/远红光受体, 蓝色表示蓝光受体, 灰色表示信号蛋白。
Figure 2. A schematic diagram of flowering time regulation by photoreceptor-mediated environmental signaling in Arabidopsis
Six flowering regulatory pathways have been identified in plants, including photoperiodic pathway, vernalization pathway, temperature pathway, autonomous pathway, gibberellin pathway, and age pathway. Phytochromes, cryptochromes, and ZTL/FKF1/ LKP2 perceive light signals in leaves, and transmit the signals to the circadian clock. After signaling integration through multiple flowering pathways, the photoreceptors eventually directly or indirectly regulate CO, FT and FLC expression and protein stability. In the ambient temperature pathway, the phytochromes indirectly regulate the transcription of FT by FLM, SVP and PIF4 through FCA/FVE. SRR1 integrates signals from the gibberellin pathway and vernalization pathway and regulate FT transcription through GA3OX1/2 and DELLA proteins in the GA pathway. In the vernalization pathway, VOZ1/2 and phytochromes regulates FT expression through FLC, SVP, and TEM1/2. The autonomous pathway promotes flowering by repressing FLC. Photoreceptors play an important role in the photoperiodic pathway. GI, CDF1, DNF, FBH1-4, COP1, SPA1, HOS1, and NF-Ys directly or indirectly interact with photoreceptors to regulate CO transcription, CO stability, and FT transcription. The age pathway regulates FT expression through miR156/172 and SPLs. There are signal integration mechanisms between different flowering pathways. The signals are integrated into FT, SOC1, and LFY, leading to the activation of AP1 and LFY and eventually the initiation of flowering. Solid arrows indicate direct promotion; dotted arrows indicate indirect promotion; blunted lines indicate direct inhibition; red ovals indicate red/far-red light photoreceptors; blue ovals indicate blue light photoreceptors, and gray ovals indicates signaling intermediate proteins.