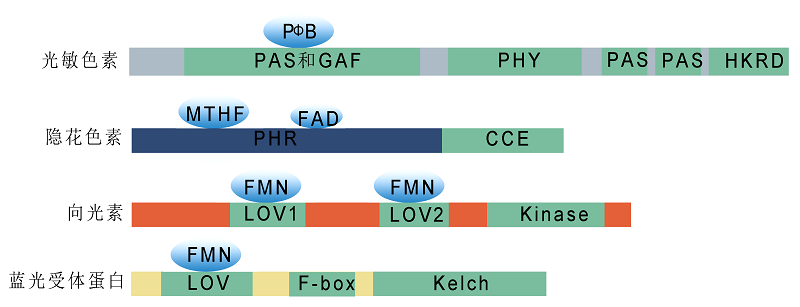
图1. 植物光受体结构示意图
光敏色素N端为可共价结合生色团的光感受结构域, 包括PAS、GAF和PHY等亚功能域; C端为光调节结构域, 主要参与光敏色素二聚体的形成及下游的信号转导过程, 包括PAS和HKRD两个亚功能域。隐花色素N端为非共价结合生色团黄素(FAD)和叶酸(MTHF)的光裂解酶相关PHR结构域, C端是对蛋白互作和信号转导十分重要的CCE结构域。向光素通过2个N端的LOV结构域(LOV1和LOV2)结合生色团黄素单核苷酸FMN来感知光照信号, 并通过LOV结构域与辅因子结合或与其它蛋白发生互作。蓝光受体蛋白ZTLs含有3个重要的功能保守结构域: N端的LOV结构域、中间的F-box基序和C端的Kelch重复序列。ZTLs以LOV结构域结合生色团黄素单核苷酸FMN, Kelch结构域则与蛋白质的相互作用相关。
Figure 1. Schematic structural diagrams of plant photoreceptors
The N-terminus of phytochromes is a photosensory region (containing PAS, GAF, and PHY), which covalently binds chromophores. The C-terminal light regulatory domains, including PAS and HKRD, are involved in phytochrome dimer formation and downstream signaling transduction. The N-terminus of cryptochromes is a PHR domain, which non-covalently binds FAD and MTHF, and the C-terminal CCE domain is important for protein-protein interactions and signaling transduction. The two N-terminal LOV domains (LOV1 and LOV2) of phototropins bind FMN to perceive light signals and are required for interaction with other proteins. ZTL proteins contain three important functional conserved domains: the N-terminal LOV domain, the intermediate F-box motif, and the C-terminal Kelch repeat region. The LOV domain binds to FMN, and the Kelch domain mediates protein-protein interactions.