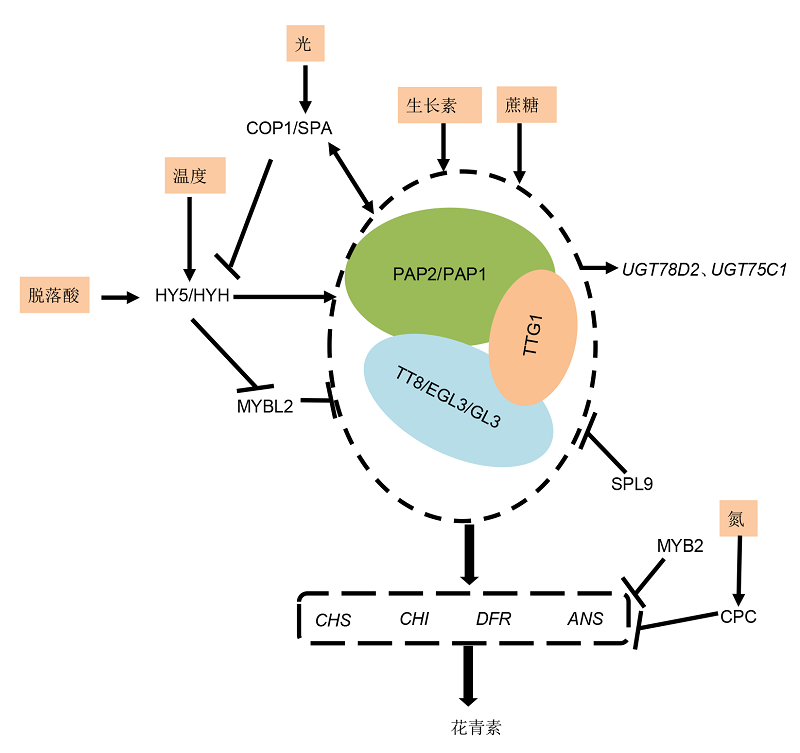
图2. 拟南芥MBW转录复合体参与花青素的代谢调控网络
拟南芥PAP1/PAP2、TT8/EGL3/GL3和TTG1组成的MBW复合体主要激活CHS、CHI、DFR和ANS的表达进而调控花青素的积累。MBW复合体的功能不仅受环境因子的影响, 还受负调控因子的调控。外源施加生长素和蔗糖直接影响花青素的积累。光信号直接作用于COP1/SPA受体, 温度和脱落酸通过诱导HY5/HYH基因的表达, 进而间接作用于MBW复合体中的MYB型转录因子。负调控因子MYBL2、SPL9、MYB2和CPC则通过负调控MBW复合体或者结构基因的表达, 进而抑制花青素的积累。
Figure 2. Summary of MBW transcription complex in the regulation of anthocyanins in Arabidopsis
The MBW complex composes of PAP1/PAP2, TT8/EGL3/GL3 and TTG1, which mainly regulates anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana by the regulation of the expression levels of key structural genes, including CHS, CHI, DFR and ANS. The function of the MBW complex is not only affected by environmental factors, but also by negative regulators. The application of auxin and sucrose can directly affect the accumulation of anthocyanins. The light signal directly acts on COP1/SPA receptor, and temperature and ABA induce the expression of HY5/HYH gene, which in turn affect the MYB transcription factor in the MBW complex. The negative regulatory factors such as MYBL2, SPL9, MYB2 and CPC, negatively regulate the expression levels of MBW complex or structural genes, and then reduce the accumulation of anthocyanins.