Advances on the Executor Resistance Genes in Plants
- College of Life Sciences, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua 321004, China
Received date: 2024-01-03
Accepted date: 2024-05-15
Online published: 2024-06-06
Abstract
The survive of plants is mainly attributed to their complex and sophisticated immune defense system that has evolved through the process of battles against pathogens. The cloning and functional research of disease resistance (R) genes have greatly facilitated people’s understanding of plant immune defense systems. Executor (E) genes, as a new type of plant disease resistance genes, has unique disease resistance characteristics and is also an important resource for disease resistance genes, making it a research hotspot in the field of plant immunity. In recent years, significant progress has been made in the cloning and functional mechanism research of E genes, however, there is no Chinese review about them. This article comprehensively summarizes the protein sequence characteristics, interaction mechanisms with pathogens, biological functions and breeding applications of the E genes, aiming to provide important references for understanding the molecular mechanisms of plant-pathogen interactions and disease-resistant breeding of crops.
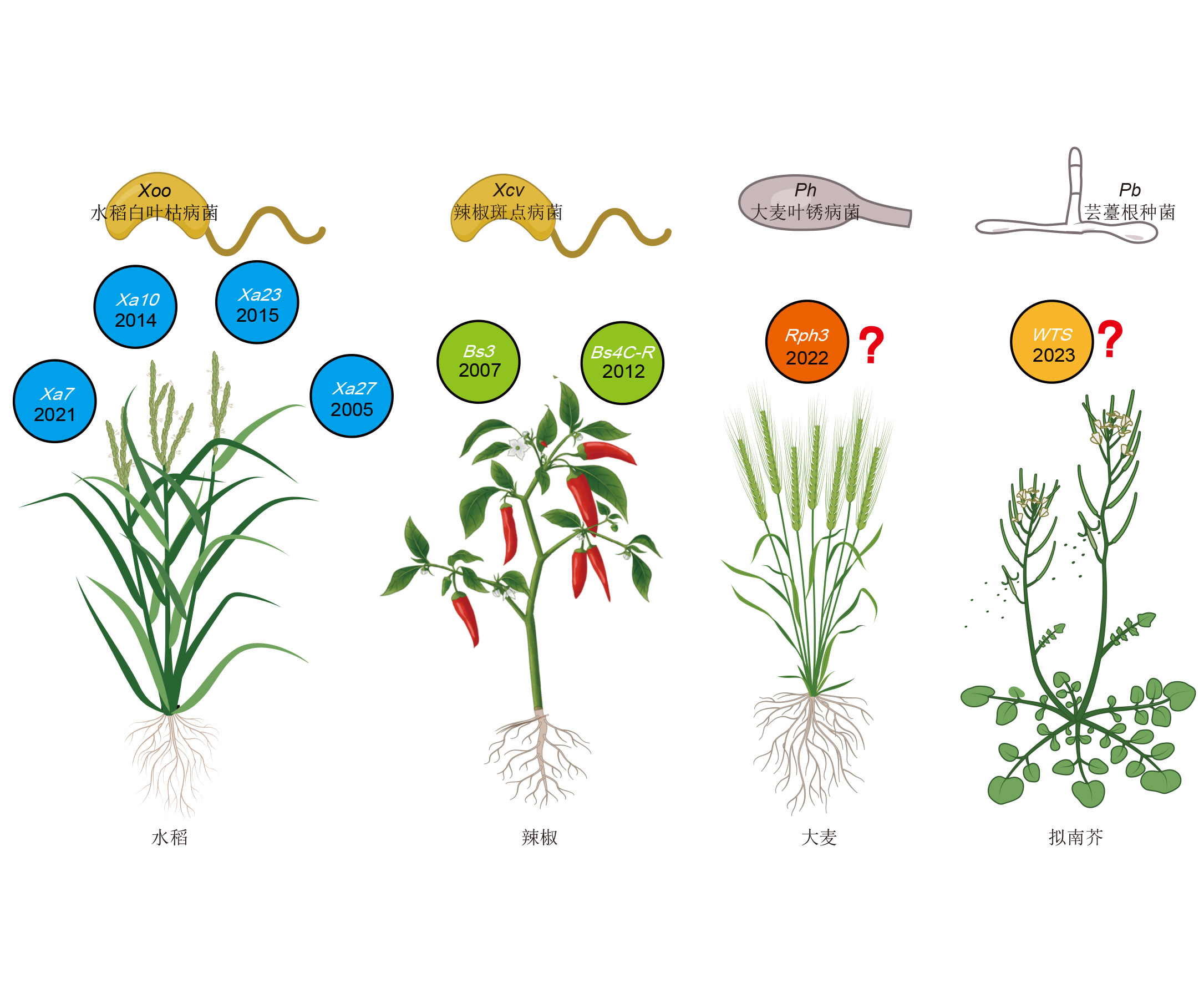
Cite this article
Lumei He , Bojun Ma , Xifeng Chen . Advances on the Executor Resistance Genes in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024 , 59(4) : 671 -680 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB24002
References
| [1] | Antony G, Zhou JH, Huang S, Li T, Liu B, White F, Yang B (2010). Rice xa13 recessive resistance to bacterial blight is defeated by induction of the disease susceptibility gene Os-11N3. Plant Cell 22, 3864-3876. |
| [2] | Bi GZ, Su M, Li N, Liang Y, Dang S, Xu JC, Hu MJ, Wang JZ, Zou MX, Deng YN, Li QY, Huang SJ, Li JJ, Chai JJ, He KM, Chen YH, Zhou JM (2021). The ZAR1 resistosome is a calcium-permeable channel triggering plant immune signaling. Cell 184, 3528-3541. |
| [3] | Boch J, Scholze H, Schornack S, Landgraf A, Hahn S, Kay S, Lahaye T, Nickstadt A, Bonas U (2009). Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL-type III effectors. Science 326, 1509-1512. |
| [4] | Bogdanove AJ, Schornack S, Lahaye T (2010). TAL effectors: finding plant genes for disease and defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13, 394-401. |
| [5] | Chen LQ, Hou BH, Lalonde S, Takanaga H, Hartung ML, Qu XQ, Guo WJ, Kim JG, Underwood W, Chaudhuri B, Chermak D, Antony G, White FF, Somerville SC, Mudgett MB, Frommer WB (2010). Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange and nutrition of pathogens. Nature 468, 527-532. |
| [6] | Chen XF, Liu PC, Mei L, He XL, Chen L, Liu H, Shen SR, Ji ZD, Zheng XX, Zhang YC, Gao ZY, Zeng DL, Qian Q, Ma BJ (2021). Xa7, a new executor R gene that confers durable and broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice. Plant Commun 2, 100143. |
| [7] | Cruz CMV, Bai JF, O?a I, Leung H, Nelson RJ, Mew TW, Leach JE (2000). Predicting durability of a disease resistance gene based on an assessment of the fitness loss and epidemiological consequences of avirulence gene mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 13500-13505. |
| [8] | de Lange O, Schreiber T, Schandry N, Radeck J, Braun KH, Koszinowski J, Heuer H, Strau? A, Lahaye T (2013). Breaking the DNA-binding code of Ralstonia solanacearum TAL effectors provides new possibilities to generate plant resistance genes against bacterial wilt disease. New Phytol 199, 773-786. |
| [9] | Dinh HX, Singh D, de la Cruz DG, Hensel G, Kumlehn J, Mascher M, Stein N, Perovic D, Ayliffe M, Moscou MJ, Park RF, Pourkheirandish M (2022). The barley leaf rust resistance gene Rph3 encodes a predicted membrane protein and is induced upon infection by avirulent pathotypes of Puccinia hordei. Nat Commun 13, 2386. |
| [10] | Doyle EL, Booher NJ, Standage DS, Voytas DF, Brendel VP, Vandyk JK, Bogdanove AJ (2012). TAL effector- nucleotide targeter (TALE-NT) 2.0: tools for TAL effector design and target prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 40, W117- W122. |
| [11] | F?rderer A, Li ET, Lawson AW, Deng YN, Sun Y, Logemann E, Zhang XX, Wen J, Han ZF, Chang JB, Chen YH, Schulze-Lefert P, Chai JJ (2022). A wheat resistosome defines common principles of immune receptor channels. Nature 610, 532-539. |
| [12] | Gu KY, Yang B, Tian DS, Wu LF, Wang DJ, Sreekala C, Yang F, Chu ZQ, Wang GL, White FF, Yin ZC (2005). R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature 435, 1122-1125. |
| [13] | Gupta A, Liu B, Chen QJ, Yang B (2023). High-efficiency prime editing enables new strategies for broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight of rice. Plant Biotechnol J 21, 1454-1464. |
| [14] | Gupta A, Liu B, Raza S, Chen QJ, Yang B (2024). Modularly assembled multiplex prime editors for simultaneous editing of agronomically important genes in rice. Plant Com- mun 5, 100741. |
| [15] | He LM, Liu PC, Mei L, Luo HC, Ban TX, Chen XF, Ma BJ (2024). Disease resistance features of the executor R gene Xa7reveal novel insights into the interaction between rice and Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Front Plant Sci 15, 1365989. |
| [16] | Huang S, Antony G, Li T, Liu B, Obasa K, Yang B, White FF (2016). The broadly effective recessive resistance gene xa5 of rice is a virulence effector-dependent quantitative trait for bacterial blight. Plant J 86, 186-194. |
| [17] | Hui SG, Shi YR, Tian JJ, Wang L, Li YY, Wang SP, Yuan M (2019). TALE-carrying bacterial pathogens trap host nuclear import receptors for facilitation of infection of rice. Mol Plant Pathol 20, 519-532. |
| [18] | Hummel AW, Doyle EL, Bogdanove AJ (2012). Addition of transcription activator-like effector binding sites to a pathogen strain-specific rice bacterial blight resistance gene makes it effective against additional strains and against bacterial leaf streak. New Phytol 195, 883-893. |
| [19] | Ji CH, Ji ZY, Liu B, Cheng H, Liu H, Liu SZ, Yang B, Chen GY (2020). Xa1 allelic R genes activate rice blight resistance suppressed by interfering TAL effectors. Plant Commun 1, 100087. |
| [20] | Ji ZY, Guo W, Chen XF, Wang CL, Zhao KJ (2022). Plant executor genes. Int J Mol Sci 23, 1524. |
| [21] | Kay S, Hahn S, Marois E, Hause G, Bonas U (2007). A bacterial effector acts as a plant transcription factor and induces a cell size regulator. Science 318, 648-651. |
| [22] | Kourelis J, van der Hoorn RAL (2018). Defended to the nines: 25 years of resistance gene cloning identifies nine me- chanisms for R protein function. Plant Cell 30, 285-299. |
| [23] | Kr?nauer C, Kilian J, Strau? T, Stahl M, Lahaye T (2019). Cell death triggered by the YUCCA-like Bs3 protein coincides with accumulation of salicylic acid and pipecolic acid but not of indole-3-acetic acid. Plant Physiol 180, 1647-1659. |
| [24] | Kr?nauer C, Lahaye T (2021). The flavin monooxygenase Bs3 triggers cell death in plants, impairs growth in yeast and produces H2O2 in vitro. PLoS One 16, e0256217. |
| [25] | Liu PC, Mei L, He LM, Xu YL, Zhang YT, Zeng DL, Zhang XM, Qian Q, Chen XF, Ma BJ (2021). Development of markers for identification and maker-assisted breeding of Xa7gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 217, 134. |
| [26] | Liu YD, Ren DT, Pike S, Pallardy S, Gassmann W, Zhang SQ (2007). Chloroplast-generated reactive oxygen species are involved in hypersensitive response-like cell death mediated by a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Plant J 51, 941-954. |
| [27] | Luo DP, Huguet-Tapia JC, Raborn RT, White FF, Brendel VP, Yang B (2021). The Xa7resistance gene guards the rice susceptibility gene SWEET14 against exploitation by the bacterial blight pathogen. Plant Commun 2, 100164. |
| [28] | Nowack MK, Holmes DR, Lahaye T (2022). TALE-induced cell death executors: an origin outside immunity? Trends Plant Sci 27, 536-548. |
| [29] | Oliva R, Ji CH, Atienza-Grande G, Huguet-Tapia JC, Perez-Quintero A, Li T, Eom JS, Li CH, Nguyen H, Liu B, Auguy F, Sciallano C, Luu VT, Dossa GS, Cunnac S, Schmidt SM, Slamet-Loedin IH, Cruz CV, Szurek B, Frommer WB, White FF, Yang B (2019). Broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice using genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 37, 1344-1350. |
| [30] | R?mer P, Hahn S, Jordan T, Strauss T, Bonas U, Lahaye T (2007). Plant pathogen recognition mediated by promoter activation of the pepper Bs3 resistance gene. Science 318, 645-648. |
| [31] | R?mer P, Jordan T, Lahaye T (2010). Identification and application of a DNA-based marker that is diagnostic for the pepper (Capsicum annuum) bacterial spot resistance gene Bs3. Plant Breed 129, 737-740. |
| [32] | Schornack S, Minsavage GV, Stall RE, Jones JB, Lahaye T (2008). Characterization of AvrHah1, a novel AvrBs3-like effector from Xanthomonas gardneri with virulence and avirulence activity. New Phytol 179, 546- 556. |
| [33] | Schwartz AR, Morbitzer R, Lahaye T, Staskawicz BJ (2017). TALE-induced bHLH transcription factors that activate a pectate lyase contribute to water soaking in bacterial spot of tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, E897-E903. |
| [34] | Siddens LK, Krueger SK, Henderson MC, Williams DE (2014). Mammalian flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO) as a source of hydrogen peroxide. Biochem Pharmacol 89, 141-147. |
| [35] | Strau? T, Strau? A, R?mer P, Minsavage GV, Singh S, Wolf C, Strau? A, Kim S, Lee HA, Yeom SI, Parniske M, Stall RE, Jones JB, Choi D, Prins M, Lahaye T (2012). RNA-seq pinpoints a Xanthomonas TAL-effector activated resistance gene in a large-crop genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 19480- 19485. |
| [36] | Szurek B, Marois E, Bonas U, Van den Ackerveken G (2001). Eukaryotic features of the Xanthomonas type III effector AvrBs3: protein domains involved in transcriptional activation and the interaction with nuclear import receptors from pepper. Plant J 26, 523-534. |
| [37] | Tariq R, Wang CL, Qin TF, Xu FF, Tang YC, Gao Y, Ji ZY, Zhao KJ (2018). Comparative transcriptome profiling of rice near-isogenic line carrying Xa23 under infection of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Int J Mol Sci 19, 717. |
| [38] | Thomas V (2010). Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Mol Plant 3, 2-20. |
| [39] | Tian CY, Fang YL, Shen Q, Wang HJ, Chen XF, Guo W, Zhao KJ, Wang CL, Ji ZY (2023). Genotypic diversity and pathogenisity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae isolated from southern China in 2019-2021. Chin Bull Bot 58, 743-749. (in Chinese) |
| 田传玉, 方妍力, 沈晴, 王宏杰, 陈析丰, 郭威, 赵开军, 王春连, 纪志远 (2023). 2019-2021年我国南方稻区白叶枯病菌的毒力与遗传多样性调查研究. 植物学报 58, 743-749. | |
| [40] | Tian DS, Wang JX, Zeng X, Gu KY, Qiu CX, Yang XB, Zhou ZY, Goh M, Luo YC, Murata-Hori M, White FF, Yin ZC (2014). The rice TAL effector-dependent resistance protein XA10 triggers cell death and calcium depletion in the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Cell 26, 497- 515. |
| [41] | Timilsina S, Potnis N, Newberry EA, Liyanapathiranage P, Iruegas-Bocardo F, White FF, Goss EM, Jones JB (2020). Xanthomonas diversity, virulence and plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 18, 415-427. |
| [42] | van Berkel WJH, Kamerbeek NM, Fraaije MW (2006). Flavoprotein monooxygenases, a diverse class of oxidative biocatalysts. J Biotechnol 124, 670-689. |
| [43] | Wang CL, Zhang XP, Fan YL, Gao Y, Zhu QL, Zheng CK, Qin TF, Li YQ, Che JY, Zhang MW, Yang B, Liu YG, Zhao KJ (2015). XA23 is an executor R protein and confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Mol Plant 8, 290-302. |
| [44] | Wang CY, Chen S, Feng AQ, Su J, Wang WJ, Feng JQ, Chen B, Zhang MY, Yang JY, Zeng LX, Zhu XY (2021). Xa7, a small orphan gene harboring promoter trap for AvrXa7, leads to the durable resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Rice 14, 48. |
| [45] | Wang J, Tian DS, Gu KY, Yang XB, Wang LL, Zeng X, Yin ZC (2017). Induction of Xa10-like genes in rice cultivar Nipponbare confers disease resistance to rice bacterial blight. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 30, 466-477. |
| [46] | Wang J, Zeng X, Tian DS, Yang XB, Wang LL, Yin ZC (2018). The pepper Bs4C proteins are localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane and confer disease resistance to bacterial blight in transgenic rice. Mol Plant Pathol 19, 2025-2035. |
| [47] | Wang MX, Li SF, Li HY, Song CF, Xie WY, Zuo SM, Zhou XP, Zhou CY, Ji ZY, Zhou HB (2024). Genome editing of a dominant resistance gene for broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial diseases in rice without growth penalty. Plant Biotechnol J 22, 529-531. |
| [48] | Wang W, Qin L, Zhang WJ, Tang LH, Zhang C, Dong XJ, Miao P, Shen M, Du HL, Cheng HY, Wang K, Zhang XY, Su M, Lu HW, Li C, Gao Q, Zhang XJ, Huang Y, Liang CZ, Zhou JM, Chen YH (2023). WeiTsing, a pericycle- expressed ion channel, safeguards the stele to confer clubroot resistance. Cell 186, 2656-2671. |
| [49] | Wei Z, Abdelrahman M, Gao Y, Ji ZY, Mishra R, Sun HD, Sui Y, Wu CY, Wang CL, Zhao KJ (2021). Engineering broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight by CRISPR- Cas9-mediated precise homology directed repair in rice. Mol Plant 14, 1215-1218. |
| [50] | Wu DS, von Roepenack-Lahaye E, Buntru M, de Lange O, Schandry N, Pérez-Quintero AL, Weinberg Z, Lowe-Power TM, Szurek B, Michael AJ, Allen C, Schillberg S, Lahaye T (2019). A plant pathogen type III effector protein subverts translational regulation to boost host polyamine levels. Cell Host Microbe 26, 638-649. |
| [51] | Wu LF, Goh ML, Sreekala C, Yin ZC (2008). XA27 depends on an amino-terminal signal-anchor-like sequence to localize to the apoplast for resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae. Plant Physiol 148, 1497-1509. |
| [52] | Xia ZH, Han F, Gao LF, Yuan QH, Zhai WX, Liu D, Luo YH (2009). Application of functional marker to identify genes for bacterial blight resistance in Oryza rufipogon. Chin J Rice Sci 23, 653-656. (in Chinese) |
| 夏志辉, 韩飞, 高利芬, 袁潜华, 翟文学, 刘迪, 罗越华 (2009). 利用功能标记鉴定普通野生稻中的白叶枯病抗性基因. 中国水稻科学 23, 653-656. | |
| [53] | Xiang X, Chen LL, Zhang DD, Zhai WX, Xia ZH (2019). Physical mapping and functional markers of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice. Mol Plant Breed 17, 509- 516. (in Chinese) |
| 向贤, 陈露露, 张丹丹, 翟文学, 夏志辉 (2019). 水稻白叶枯病抗性基因物理图谱定位与功能标记. 分子植物育种 17, 509-516. | |
| [54] | Yang B, White FF (2004). Diverse members of the AvrBs3/ PthA family of type III effectors are major virulence determinants in bacterial blight disease of rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17, 1192-1200. |
| [55] | Zeng X, Tian DS, Gu KY, Zhou ZY, Yang XB, Luo YC, White FF, Yin ZC (2015). Genetic engineering of the Xa10 promoter for broad-spectrum and durable resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Biotechnol J 13, 993-1001. |
| [56] | Zhang JL, Yin ZC, White F (2015). TAL effectors and the executor R genes. Front Plant Sci 6, 641. |
| [57] | Zhao KJ, Zhang Q (2021). A climate-resilient R gene in rice traps two pathogen effectors for broad and durable resistance to bacterial blight. Mol Plant 14, 366-368. |
| [58] | Zhao Q, Dixon RA (2011). Transcriptional networks for lignin biosynthesis: more complex than we thought? Trends Plant Sci 16, 227-233. |