生物钟与光温环境信号互作网络研究进展
- 1中国科学院植物研究所, 饲草种质高效设计与利用全国重点实验室, 北京 100093
2中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3 国家植物园, 北京 100093
†共同第一作者
收稿日期: 2024-11-18
录用日期: 2024-12-26
网络出版日期: 2024-12-27
基金资助
国家自然科学基金青年基金(32300294);国家自然科学基金(32370307);中国博士后第73批面上项目(2023M733729)
Advances of Plant Circadian Clock Response to Light and Temperature Signals
- 1State Key Laboratory of Forage Breeding-by-Design and Utilization, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100093, China
2University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 China National Botanical Garden, Beijing 100093, China
†These authors contributed equally to this work
Received date: 2024-11-18
Accepted date: 2024-12-26
Online published: 2024-12-27
摘要
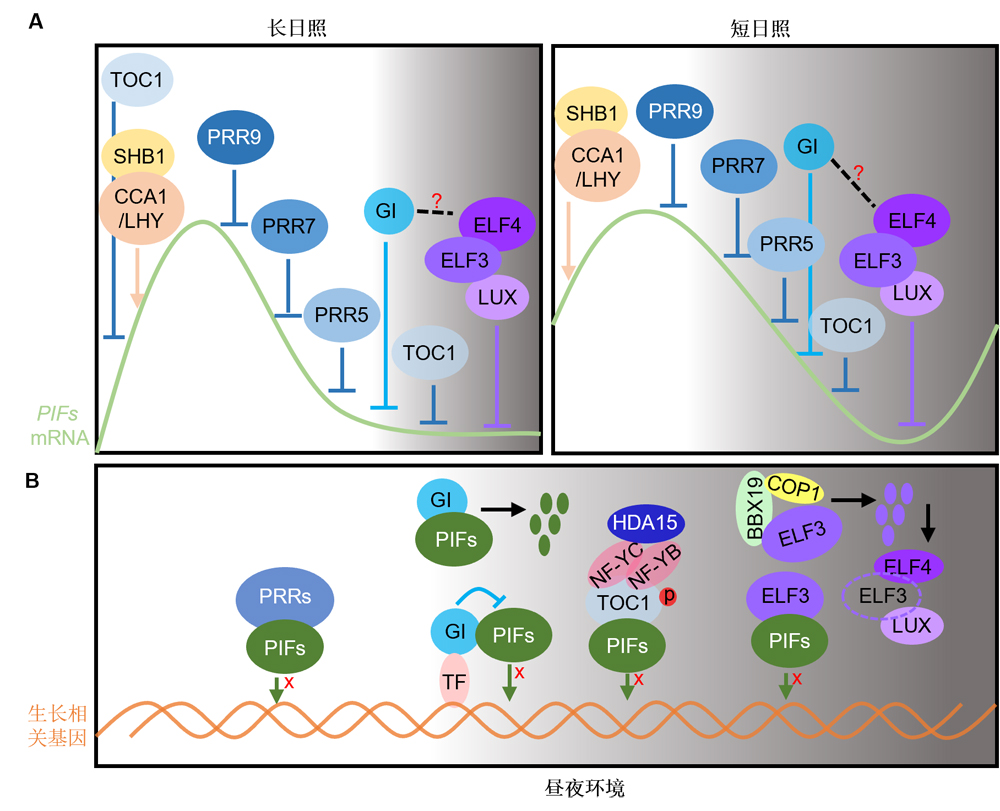
随着全球气候的急剧变化, 植物生长发育所处的生态环境日益恶劣, 生物钟与光、温受体互作协同传递环境信号并调控下游生长发育的应答机制开始受到科研人员的广泛关注。生物钟作为植物内源计时器, 其核心由多个耦联的转录-翻译反馈环(TTFL)组成, 在转录、转录后、翻译、翻译后和表观遗传层面受到多层级精细调控。这些精密的调控机制保证了生物钟能不断被外界环境信号驯化和重置, 使内源节律与外界环境相匹配, 从而赋予植物优化资源利用和趋向最适生长的能力, 对于指导农作物遗传改良和引种驯化具有重要意义。该综述总结了生物钟核心振荡器的多层级调控机制以及生物钟同源基因在农作物中的分子功能, 详述了生物钟与光、温环境信号通路间的互作网络, 展望了以此为基础的作物分子育种, 为提高农作物的环境适应性和优化改良农艺性状提供了新思路。
本文引用格式
苏晨 , 牛钰凡 , 徐航 , 王希岭 , 于英俊 , 何雨晴 , 王雷 . 生物钟与光温环境信号互作网络研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025 , 60(3) : 315 -341 . DOI: 10.11983/CBB24174
Abstract
With the sharp change of the global climate, the ecological environment for plant is becoming increasingly harsh, therefore the molecular mechanisms underlying how circadian synergistically interacts with light or temperature receptors to transmit environmental signals and rhythmically regulate various growth and development process received widespread attention. As an endogenous timer of plants, the core oscillator of circadian clock is composed of multiple coupled transcriptional-translational feedback loops (TTFL), and it is modified from transcription, post-transcription, translation, post-translation to epigenetic levels. These multi-precise regulatory mechanisms ensure that the circadian clock can be synchronized and reset by external signals, so that the endogenous rhythm matches with external cycles, thereby endowing plants with the ability to optimize resource utilization and tend towards the optimal growth, which also has an important significance for guiding the genetic improvement and domestication of crops. In this review, we summarized the multi-level of regulatory mechanisms of core oscillator as well as the molecular function of circadian homologous genes in crops, thoroughly described the interaction network between the circadian clock and the light and temperature signal pathways and give prospects for molecular breeding based on the opinion, which provides new ideas for expanding the environmental adaptability and optimizing agronomic traits of crops.

参考文献
| [1] | Adams S, Grundy J, Veflingstad SR, Dyer NP, Hannah MA, Ott S, Carré IA (2018). Circadian control of abscisic acid biosynthesis and signaling pathways revealed by genome-wide analysis of LHY binding targets. New Phytol 220, 893-907. |
| [2] | Anwer MU, Davis A, Davis SJ, Quint M (2020). Photoperiod sensing of the circadian clock is controlled by EARLY FLOWERING 3 and GIGANTEA. Plant J 101, 1397-1410. |
| [3] | Aschoff J (1979). Circadian rhythms: influences of internal and external factors on the period measured in constant conditions. Z Tierpsychol 49, 225-249. |
| [4] | Avello PA, Davis SJ, Ronald J, Pitchford JW (2019). Heat the clock: entrainment and compensation in Arabidopsis circadian rhythms. J Circadian Rhythms 17, 5. |
| [5] | Bendix C, Mendoza JM, Stanley DN, Meeley R, Harmon FG (2013). The circadian clock-associated gene gigantea1 affects maize developmental transitions. Plant Cell Environ 36, 1379-1390. |
| [6] | Bu TT, Lu SJ, Wang K, Dong LD, Li SL, Xie QG, Xu XD, Cheng Q, Chen LY, Fang C, Li HY, Liu BH, Weller JL, Kong FJ (2021). A critical role of the soybean evening complex in the control of photoperiod sensitivity and adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118, e2010241118. |
| [7] | Buhr ED, Yoo SH, Takahashi JS (2010). Temperature as a universal resetting cue for mammalian circadian oscillators. Science 330, 379-385. |
| [8] | Cha JY, Kim J, Kim TS, Zeng QN, Wang L, Lee SY, Kim WY, Somers DE (2017). GIGANTEA is a co-chaperone which facilitates maturation of ZEITLUPE in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Nat Commun 8, 3. |
| [9] | Chen A, Li CX, Hu W, Lau MY, Lin HQ, Rockwell NC, Martin SS, Jernstedt JA, Lagarias JC, Dubcovsky J (2014). Phytochrome C plays a major role in the acceleration of wheat flowering under long-day photoperiod. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 10037-10044. |
| [10] | Chen CQ, Tian XY, Li J, Bai S, Zhang ZY, Li Y, Cao HR, Chen ZC (2022). Two central circadian oscillators OsPRR59 and OsPRR95 modulate magnesium homeostasis and carbon fixation in rice. Mol Plant 15, 1602-1614. |
| [11] | Chen WW, Takahashi N, Hirata Y, Ronald J, Porco S, Davis SJ, Nusinow DA, Kay SA, Mas P (2020). A mobile ELF4 delivers circadian temperature information from shoots to roots. Nat Plants 6, 416-426. |
| [12] | Cheng Q, Gan ZR, Wang YP, Lu SJ, Hou ZH, Li HY, Xiang HT, Liu BH, Kong FJ, Dong LD (2020). The soybean gene J contributes to salt stress tolerance by up-regulating salt-responsive genes. Front Plant Sci 11, 272. |
| [13] | Choudhary MK, Nomura Y, Wang L, Nakagami H, Somers DE (2015). Quantitative circadian phosphoproteomic analysis of Arabidopsis reveals extensive clock control of key components in physiological, metabolic, and signaling pathways. Mol Cell Proteomics 14, 2243-2260. |
| [14] | Chung BYW, Balcerowicz M, Di Antonio M, Jaeger KE, Geng F, Franaszek K, Marriott P, Brierley I, Firth AE, Wigge PA (2020). An RNA thermoswitch regulates daytime growth in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 6, 522-532. |
| [15] | Cortijo S, Charoensawan V, Brestovitsky A, Buning R, Ravarani C, Rhodes D, van Noort J, Jaeger KE, Wigge PA (2017). Transcriptional regulation of the ambient temperature response by H2A.Z nucleosomes and HSF 1transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 10, 1258-1273. |
| [16] | Dai SH, Wei XP, Pei LP, Thompson RL, Liu Y, Heard JE, Ruff TG, Beachy RN (2011). BROTHER OF LUX ARRHYTHMO is a component of the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 23, 961-972. |
| [17] | Daniel X, Sugano S, Tobin EM (2004). CK2 phosphorylation of CCA1 is necessary for its circadian oscillator function in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 3292-3297. |
| [18] | Devlin PF, Kay SA (2000). Cryptochromes are required for phytochrome signaling to the circadian clock but not for rhythmicity. Plant Cell 12, 2499-2510. |
| [19] | Dong KQ, Wang LL, Liu QQ, Zhang YL, Wang CL (2023). Cloning and expression analysis of circadian gene ZmPRR1-2 in maize. Acta Bot Boreal Occident Sin 43, 21-28. (in Chinese) |
| 董柯清, 王雷立, 刘青青, 张严玲, 王翠玲 (2023). 玉米生物钟基因ZmPRR1-2的克隆及表达分析. 西北植物学报 43, 21-28. | |
| [20] | Dong LD, Fang C, Cheng Q, Su T, Kou K, Kong LP, Zhang CB, Li HY, Hou ZH, Zhang YH, Chen LY, Yue L, Wang LS, Wang K, Li YL, Gan ZR, Yuan XH, Weller JL, Lu SJ, Kong FJ, Liu BH (2021). Genetic basis and adaptation trajectory of soybean from its temperate origin to tropics. Nat Commun 12, 5445. |
| [21] | Dong LD, Hou ZH, Li HY, Li ZB, Fang C, Kong LP, Li YL, Du H, Li T, Wang LS, He ML, Zhao XH, Cheng Q, Kong FJ, Liu BH (2022). Agronomical selection on loss-of- function of GIGANTEA simultaneously facilitates soybean salt tolerance and early maturity. J Integr Plant Biol 64, 1866-1882. |
| [22] | Dong MA, Farré EM, Thomashow MF (2011). Circadian clock-associated 1 and late elongated hypocotyl regulate expression of the C-repeat binding factor (CBF) pathway in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 7241-7246. |
| [23] | Edwards KD, Anderson PE, Hall A, Salathia NS, Locke JCW, Lynn JR, Straume M, Smith JQ, Millar AJ (2006). FLOWERING LOCUS C mediates natural variation in the high-temperature response of the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 18, 639-650. |
| [24] | Edwards KD, Lynn JR, Gyula P, Nagy F, Millar AJ (2005). Natural allelic variation in the temperature-compensation mechanisms of the Arabidopsis thaliana circadian clock. Genetics 170, 387-400. |
| [25] | Ezer D, Jung JH, Lan H, Biswas S, Gregoire L, Box MS, Charoensawan V, Cortijo S, Lai XL, St?ckle D, Zubieta C, Jaeger KE, Wigge PA (2017). The evening complex coordinates environmental and endogenous signals in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 3, 17087. |
| [26] | Farinas B, Mas P (2011). Functional implication of the MYB transcription factor RVE8/LCL5 in the circadian control of histone acetylation. Plant J 66, 318-329. |
| [27] | Farré EM, Harmer SL, Harmon FG, Yanovsky MJ, Kay SA (2005). Overlapping and distinct roles of PRR7 and PRR9 in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Curr Biol 15, 47-54. |
| [28] | Fehér B, Kozma-Bognár L, Kevei é, Hajdu A, Binkert M, Davis SJ, Sch?fer E, Ulm R, Nagy F (2011). Functional interaction of the circadian clock and UV RESISTANCE LOCUS 8-controlled UV-B signaling pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 67, 37-48. |
| [29] | Filichkin SA, Cumbie JS, Dharmawardhana P, Jaiswal P, Chang J, Palusa S, Reddy ASN, Megraw M, Mockler T (2015). Environmental stresses modulate abundance and timing of alternatively spliced circadian transcripts in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 8, 207-227. |
| [30] | Fornara F, Panigrahi KCS, Gissot L, Sauerbrunn N, Rühl M, Jarillo JA, Coupland G (2009). Arabidopsis DOF transcription factors act redundantly to reduce CONSTANS expression and are essential for a photoperiodic flowering response. Dev Cell 17, 75-86. |
| [31] | Fraser DP, Panter PE, Sharma A, Sharma B, Dodd AN, Franklin KA (2021). Phytochrome A elevates plant circadian-clock components to suppress shade avoidance in deep-canopy shade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118, e2108176118. |
| [32] | Fujiwara S, Wang L, Han LQ, Suh SS, Salomé PA, Mcclung CR, Somers DE (2008). Post-translational regula- a)tion of the Arabidopsis circadian clock through selective proteolysis and phosphorylation of pseudo-response regulator proteins. J Biol Chem 283, 23073-23083. |
| [33] | Fustin JM, Doi M, Yamaguchi Y, Hida H, Nishimura S, Yoshida M, Isagawa T, Morioka M, Kakeya H, Manabe I, Okamura H,(2013). RNA-methylation-dependent RNA processing controls the speed of the circadian clock. Cell 155, 793-806. |
| [34] | Gan ES, Xu YF, Wong JY, Goh JG, Sun B, Wee WY, Huang JB, Ito T (2014) Jumonji demethylases moderate precocious flowering at elevated temperature via regula-tion of FLC in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun |
| [35] | Gendron JM, Pruneda-Paz JL, Doherty CJ, Gross AM, Kang SE, Kay SA (2012). Arabidopsis circadian clock protein, TOC1, is a DNA-binding transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 3167-3172. |
| [36] | Gil KE, Kim WY, Lee HJ, Faisal M, Saquib Q, Alatar AA, Park CM (2017). ZEITLUPE contributes to a thermoresponsive protein quality control system in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 29, 2882-2894. |
| [37] | Goralogia GS, Liu TK, Zhao L, Panipinto PM, Groover ED, Bains YS, Imaizumi T (2017). CYCLING DOF FACTOR 1 represses transcription through the TOPLESS co- repressor to control photoperiodic flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant J 92, 244-262. |
| [38] | Gould PD, Locke JCW, Larue C, Southern MM, Davis SJ, Hanano S, Moyle R, Milich R, Putterill J, Millar AJ, Hall A (2006). The molecular basis of temperature compensation in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 18, 1177-1187. |
| [39] | Hajdu A, Dobos O, Domijan M, Bálint B, Nagy I, Nagy F, Kozma-bognár L (2018). ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 5 mediates blue light signaling to the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant J 96, 1242-1254. |
| [40] | Hansen LL, van den Burg HA, van Ooijen G (2017). SUMOylation contributes to timekeeping and temperature compensation of the plant circadian clock. J Biol Rhythms 32, 560-569. |
| [41] | Harmer SL (2009). The circadian system in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60, 357-377. |
| [42] | Hayama R, Sarid-Krebs L, Richter R, Fernández V, Jang S, Coupland G (2017). PSEUDO RESPONSE REGULATORs stabilize CONSTANS protein to promote flowering in response to day length. EMBO J 36, 904-918. |
| [43] | He YQ, Yu YJ, Wang XL, Qin YM, Su C, Wang L (2022). Aschoff's rule on circadian rhythms orchestrated by blue light sensor CRY2 and clock component PRR9. Nat Commun 13, 5869. |
| [44] | Helfer A, Nusinow DA, Chow BY, Gehrke AR, Bulyk ML, Kay SA (2011). LUX ARRHYTHMO encodes a nighttime repressor of circadian gene expression in the Arabidopsis core clock. Curr Biol 21, 126-133. |
| [45] | Hemmes H, Henriques R, Jang IC, Kim S, Chua NH (2012). Circadian clock regulates dynamic chromatin modifications associated with Arabidopsis CCA1/LHY and TOC1 transcriptional rhythms. Plant Cell Physiol 53, 2016-2029. |
| [46] | Hernando CE, Romanowski A, Yanovsky MJ (2017). Transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of the plant circadian gene regulatory network. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1860, 84-94. |
| [47] | Himanen K, Woloszynska M, Boccardi TM, De Groeve S, Nelissen H, Bruno L, Vuylsteke M, Van Lijsebettens M (2012). Histone H2B monoubiquitination is required to reach maximal transcript levels of circadian clock genes in Arabidopsis. Plant J 72, 249-260. |
| [48] | Hsu PY, Devisetty UK, Harmer SL (2013). Accurate timekeeping is controlled by a cycling activator in Arabidopsis. eLife 2, e00473. |
| [49] | Hu Y, Zhou X, Zhang B, Li SL, Fan XW, Zhao H, Zhang J, Liu HY, He Q, Li QP, Ayaad M, You AQ, Xing YZ (2021). OsPRR37 alternatively promotes heading date through suppressing the expression of Ghd7 in the Japonica variety Zhonghua 11 under natural long-day conditions. Rice 14, 20. |
| [50] | Huang H, Alvarez S, Bindbeutel R, Shen ZX, Naldrett MJ, Evans BS, Briggs SP, Hicks LM, Kay SA, Nusinow DA (2016). Identification of evening complex associated proteins in Arabidopsis by affinity purification and mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 15, 201-217. |
| [51] | Huang H, Nusinow DA (2016). Into the evening: complex interactions in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Trends Genet 32, 674-686. |
| [52] | Huang W, Pérez-García P, Pokhilko A, Millar AJ, Antoshechkin I, Riechmann JL, Mas P (2012). Mapping the core of the Arabidopsis circadian clock defines the network structure of the oscillator. Science 336, 75-79. |
| [53] | Hung FY, Chen FF, Li CL, Chen C, Chen JH, Cui YH, Wu KQ (2019). The LDL1/2-HDA6 histone modification complex interacts with TOC1 and regulates the core circadian clock components in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 10, 233. |
| [54] | Hung FY, Chen FF, Li CL, Chen C, Lai YC, Chen JH, Cui YH, Wu KQ (2018). The Arabidopsis LDL1/2-HDA6 histone modification complex is functionally associated with CCA1/LHY in regulation of circadian clock genes. Nucleic Acids Res 46, 10669-10681. |
| [55] | Hwang DY, Park S, Lee S, Lee SS, Imaizumi T, Song YH (2019). GIGANTEA regulates the timing stabilization of CONSTANS by altering the interaction between FKF1 and ZEITLUPE. Mol Cells 42, 693-701. |
| [56] | Izawa T, Mihara M, Suzuki Y, Gupta M, Itoh H, Nagano AJ, Motoyama R, Sawada Y, Yano M, Hirai MY, Makino A, Nagamura Y (2011). Os-GIGANTEA confers robust diurnal rhythms on the global transcriptome of rice in the field. Plant Cell 23, 1741-1755. |
| [57] | James AB, Calixto CPG, Tzioutziou NA, Guo WB, Zhang RX, Simpson CG, Jiang WY, Nimmo GA, Brown JWS, Nimmo HG (2018). How does temperature affect splicing events? Isoform switching of splicing factors regulates splicing of LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL(LHY). Plant Cell Environ 41, 1539-1550. |
| [58] | Jiang YP, Yang CW, Huang S, Xie FM, Xu YT, Liu C, Li L (2019). The ELF3-PIF7 interaction mediates the circadian gating of the shade response in Arabidopsis. iScience 22, 288-298. |
| [59] | Jones MA, Covington MF, DiTacchio L, Vollmers C, Panda S, Harmer SL (2010). Jumonji domain protein JMJD5 functions in both the plant and human circadian systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 21623-21628. |
| [60] | Jones MA, Morohashi K, Grotewold E, Harmer SL (2019). Arabidopsis JMJD5/JMJ30 acts independently of LUX ARRHYTHMO within the plant circadian clock to enable temperature compensation. Front Plant Sci 10, 57. |
| [61] | Jones MA, Williams BA, McNicol J, Simpson CG, Brown IWS, Harmer SL (2012). Mutation of Arabidopsis SPLICEOSOMAL TIMEKEEPER LOCUS1 causes circadian clock defects. Plant Cell 24, 4066-4082. |
| [62] | Jung JH, Barbosa AD, Hutin S, Kumita JR, Gao MJ, Derwort D, Silva CS, Lai XL, Pierre E, Geng F, Kim SB, Baek S, Zubieta C, Jaeger KE, Wigge PA (2020). A prion-like domain in ELF3functions as a thermosensor in Arabidopsis. Nature 585, 256-260. |
| [63] | Jung JH, Domijan M, Klose C, Biswas S, Ezer D, Gao MJ, Khattak AK, Box MS, Charoensawan V, Cortijo S, Kumar M, Grant A, Locke JCW, Sch?fer E, Jaeger KE, Wigge PA (2016). Phytochromes function as thermosensors in Arabidopsis. Science 354, 886-889. |
| [64] | Kamioka M, Takao S, Suzuki T, Taki K, Higashiyama T, Kinoshita T, Nakamichi N (2016). Direct repression of evening genes by CIRCADIAN CLOCK-ASSOCIATED1 in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 28, 696-711. |
| [65] | Kiba T, Henriques R, Sakakibara H, Chua NH (2007). Targeted degradation of PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR5 by an SCFZTL complex regulates clock function and photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 19, 2516-2530. |
| [66] | Kidokoro S, Hayashi K, Haraguchi H, Ishikawa T, Soma F, Konoura I, Toda S, Mizoi J, Suzuki T, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2021). Posttranslational regulation of multiple clock-related transcription factors triggers cold-inducible gene expression in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118, e2021048118. |
| [67] | Kim J, Geng RS, Gallenstein RA, Somers DE (2013). The F-box protein ZEITLUPE controls stability and nucleocytoplasmic partitioning of GIGANTEA. Development 140, 4060-4069. |
| [68] | Kim J, Kim Y, Yeom M, Kim JH, Nam HG (2008). FIONA1 is essential for regulating period length in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 20, 307-319. |
| [69] | Kim TS, Kim WY, Fujiwara S, Kim J, Cha JY, Park JH, Lee SY, Somers DE (2011). HSP90 functions in the circadian clock through stabilization of the client F-box protein ZEITLUPE. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108, 16843-16848. |
| [70] | Kim TS, Wang L, Kim YJ, Somers DE (2020). Compensatory mutations in GI and ZTL may modulate temperature compensation in the circadian clock. Plant Physiol 182, 1130-1141. |
| [71] | Kim WY, Fujiwara S, Suh SS, Kim J, Kim Y, Han LQ, David K, Putterill J, Nam HG, Somers DE (2007). ZEITLUPE is a circadian photoreceptor stabilized by GIGANTEA in blue light. Nature 449, 356-360. |
| [72] | Kim Y, Yeom M, Kim H, Lim J, Koo HJ, Hwang D, Somers D, Nam HG (2012). GIGANTEA and EARLY FLOWERING 4 in Arabidopsis exhibit differential phase-specific genetic influences over a diurnal cycle. Mol Plant 5, 678-687. |
| [73] | Kolmos E, Chow BY, Pruneda-Paz JL, Kay SA (2014). HsfB2b-mediated repression of PRR7 directs abiotic stress responses of the circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 16172-16177. |
| [74] | Koo BH, Yoo SC, Park JW, Kwon CT, Lee BD, An G, Zhang ZY, Li JJ, Li ZC, Paek NC (2013). Natural variation in OsPRR37 regulates heading date and contributes to rice cultivation at a wide range of latitudes. Mol Plant 6, 1877-1888. |
| [75] | Kumar SV, Wigge PA (2010). H2A. Z-containing nucleosomes mediate the thermosensory response in Arabidopsis. Cell 140, 136-147. |
| [76] | Kwon CT, Koo BH, Kim D, Yoo SC, Paek NC (2015). Casein kinases I and 2αphosphorylate Oryza sativa Pseudo Response Regulator 37 (OsPRR37) in photoperiodic flowering in rice. Mol Cells 38, 81-88. |
| [77] | Lau OS, Huang X, Charron JB, Lee JH, Li G, Deng X (2011). Interaction of Arabidopsis DET1 with CCA1 and LHY in mediating transcriptional repression in the plant circadian clock. Mol Cells 43, 703-712. |
| [78] | Lee CM, Feke A, Li MW, Adamchek C, Webb K, Pruneda- Paz J, Bennett EJ, Kay SA, Gendron JM (2018). Decoys untangle complicated redundancy and reveal targets of circadian clock F-box proteins. Plant Physiol 177, 1170-1186. |
| [79] | Lee K, Seo PJ (2018). The HAF2 protein shapes histone acetylation levels of PRR5 and LUX loci in Arabidopsis. Planta 248, 513-518. |
| [80] | Lee SJ, Kang K, Lim JH, Paek NC (2022). Natural alleles of CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED1 contribute to rice cultivation by fine-tuning flowering time. Plant Physiol 190, 640-656. |
| [81] | Legris M, Klose C, Burgie ES, Rojas CCR, Neme M, Hiltbrunner A, Wigge PA, Sch?fer E, Vierstra RD, Casal JJ (2016). Phytochrome B integrates light and temperature signals in Arabidopsis. Science 354, 897-900. |
| [82] | Leivar P, Monte E (2014). PIFs: systems integrators in plant development. Plant Cell 26, 56-78. |
| [83] | Li G, Siddiqui H, Teng YB, Lin RC, Wan XY, Li JG, Lau OS, Ouyang XH, Dai MQ, Wan JM, Devlin PF, Deng XW, Wang HY (2011). Coordinated transcriptional regulation underlying the circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Nat Cell Biol 13, 616-622. |
| [84] | Li J, Qiu JX, Zeng QH, Zhuang Y, Zhang N, Xu SX, Jin J, Dong ZC, Chen L, Huang W (2023a). OsTOC1 plays dual roles in the regulation of plant circadian clock by functioning as a direct transcription activator or repressor. Cell Rep 42, 112765. |
| [85] | Li KN, Zhang SN, Tang S, Zhang J, Dong HZ, Yang SH, Qu HY, Xuan W, Gu M, Xu GH (2022). The rice transcription factor Nhd1 regulates root growth and nitrogen uptake by activating nitrogen transporters. Plant Physiol 189, 1608-1624. |
| [86] | Li MN, Cao LJ, Mwimba M, Zhou Y, Li L, Zhou M, Schnable PS, O'rourke JA, Dong XN, Wang W (2019). Comprehensive mapping of abiotic stress inputs into the soybean circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 23840-23849. |
| [87] | Li N, Zhang YY, He YQ, Wang Y, Wang L (2020). Pseudo response regulators regulate photoperiodic hypocotyl growth by repressing PIF4/5transcription. Plant Physiol 183, 686-699. |
| [88] | Li X, Ma DB, Lu SX, Hu XY, Huang RF, Liang T, Xu TD, Tobin EM, Liu HT (2016). Blue light- and low temperature-regulated COR27 and COR28 play roles in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 28, 2755-2769. |
| [89] | Li ZM, Gao FR, Liu YJ, Abou-Elwafa SF, Qi JL, Pan HB, Hu XM, Ren ZZ, Zeng HX, Liu ZX, Zhang DL, Xi ZY, Liu TX, Chen YH, Su HH, Xiong SP, Ku L (2023b). ZmGI2 regulates flowering time through multiple flower development pathways in maize. Plant Sci 332, 111701. |
| [90] | Liang LW, Zhang ZY, Cheng NN, Liu HY, Song S, Hu Y, Zhou XC, Zhang J, Xing YZ (2021). The transcriptional repressor OsPRR73 links circadian clock and photoperiod pathway to control heading date in rice. Plant Cell Environ 44, 842-855. |
| [91] | Lin XY, Dong LD, Tang Y, Li HY, Cheng Q, Li H, Zhang T, Ma LX, Xiang HL, Chen LN, Nan HY, Fang C, Lu SJ, Li JG, Liu BH, Kong FJ (2022). Novel and multifaceted regulations of photoperiodic flowering by phytochrome A in soybean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119, e2208708119. |
| [92] | Litthauer S, Battle MW, Jones MA (2015). Phototropins do not alter accumulation of evening-phased circadian transcripts under blue light. Plant Signal Behav 11, e1126029. |
| [93] | Liu BH, Kanazawa A, Matsumura H, Takahashi R, Harada K, Abe J (2008). Genetic redundancy in soybean photoresponses associated with duplication of the phytochrome A gene. Genetics 180, 995-1007. |
| [94] | Liu XL, Covington MF, Fankhauser C, Chory J, Wagner DR (2001). ELF3 encodes a circadian clock-regulated nuclear protein that functions in an Arabidopsis PHYB signal transduction pathway. Plant Cell 13, 1293-1304. |
| [95] | Liu Y, Ma MD, Li G, Yuan L, Xie YR, Wei HB, Ma XJ, Li QQ, Devlin PF, Xu XD, Wang HY (2020). Transcription factors FHY3 and FAR1 regulate light-induced CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED1 gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 32, 1464-1478. |
| [96] | Liu Y, Sun Y, Yao H, Zheng Y, Cao S, Wang H (2022). Arabidopsis circadian clock repress phytochrome A signaling. Front Plant Sci 13, 809563. |
| [97] | Lu SJ, Dong LD, Fang C, Liu SL, Kong LP, Cheng Q, Chen LY, Su T, Nan HY, Zhang D, Zhang L, Wang ZJ, Yang YQ, Yu DY, Liu XL, Yang QY, Lin XY, Tang Y, Zhao XH, Yang XQ, Tian CG, Xie QG, Li X, Yuan XH, Tian ZX, Liu BH, Weller JL, Kong FJ (2020). Stepwise selection on homeologous PRR genes controlling flowering and maturity during soybean domestication. Nat Genet 52, 428-436. |
| [98] | Lu SJ, Zhao XH, Hu YL, Liu SL, Nan HY, Li XM, Fang C, Cao D, Shi XY, Kong LP, Su T, Zhang FG, Li SC, Wang Z, Yuan XH, Cober ER, Weller JL, Liu BH, Hou XL, Tian ZX, Kong FJ (2017). Natural variation at the soybean J locus improves adaptation to the tropics and enhances yield. Nat Genet 49, 773-779. |
| [99] | Lu SX, Knowles SM, Webb CJ, Celaya RB, Cha C, Siu JP, Tobin EM (2011). The Jumonji C domain-containing protein JMJ30 regulates period length in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Physiol 155, 906-915. |
| [100] | Malapeira J, Khaitova LC, Mas P (2012). Ordered changes in histone modifications at the core of the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 21540-21545. |
| [101] | Marcolino-Gomes J, Rodrigues FA, Fuganti-Pagliarini R, Bendix C, Nakayama TJ, Celaya B, Molinari HBC, Oliveira MCND, Harmon FG, Nepomuceno A (2014). Diurnal oscillations of soybean circadian clock and drought responsive genes. PLoS One 9, e86402. |
| [102] | Marshall CM, Tartaglio V, Duarte M, Harmon FG (2016). The Arabidopsis sickle mutant exhibits altered circadian clock responses to cool temperatures and temperature- dependent alternative splicing. Plant Cell 28, 2560-2575. |
| [103] | Martín G, Rovira A, Veciana N, Soy J, Toledo-Ortiz G, Gommers CMM, Boix M, Henriques R, Minguet EG, Alabadí D, Halliday KJ, Leivar P, Monte E (2018). Circadian waves of transcriptional repression shape PIF-regulated photoperiod-responsive growth in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 28, 311-318. |
| [104] | Más P, Kim WY, Somers DE, Kay SA (2003) Targeted degradation of TOC 1 by ZTL modulates circadian function in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 426, 567-570. |
| [105] | Mizuno T, Nomoto Y, Oka H, Kitayama M, Takeuchi A, Tsubouchi M, Yamashino T (2014). Ambient temperature signal feeds into the circadian clock transcriptional circuitry through the EC night-time repressor in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 55, 958-976. |
| [106] | Nagel DH, Doherty CJ, Pruneda-Paz JL, Schmitz RJ, Ecker JR, Kay SA (2015). Genome-wide identification of CCA1 targets uncovers an expanded clock network in Ara- bidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, E4802-E4810. |
| [107] | Nakamichi N, Kiba T, Henriques R, Mizuno T, Chua NH, Sakakibara H (2010). PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATORS 9, 7, and 5 are transcriptional repressors in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 22, 594-605. |
| [108] | Nakamichi N, Kiba T, Kamioka M, Suzuki T, Yamashino T, Higashiyama T, Sakakibara H, Mizuno T (2012). Transcriptional repressor PRR5 directly regulates clock-output pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 17123-17128. |
| [109] | Nakamichi N, Kita M, Niinuma K, Ito S, Yamashino T, Mizoguchi T, Mizuno T (2007). Arabidopsis clock-associated pseudo-response regulators PRR9, PRR7 and PRR5 coordinately and positively regulate flowering time through the canonical CONSTANS-dependent photoperiodic pathway. Plant Cell Physiol 48, 822-832. |
| [110] | Ni W, Xu SL, Gonzalez-Grandio E, Chalkley RJ, Huhmer AFR, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY, Quail PH (2017). PPKs mediate direct signal transfer from phytochrome photoreceptors to transcription factor PIF3. Nat Commun 8, 15236. |
| [111] | Nieto C, López-Salmerón V, Davière JM, Prat S (2015). ELF3-PIF4 interaction regulates plant growth independently of the Evening Complex. Curr Biol 25, 187-193. |
| [112] | Ning YS, Shi XT, Wang RY, Fan JB, Park CH, Zhang CY, Zhang T, Ouyang XH, Li SG, Wang GL (2015). OsELF3-2, an ortholog of Arabidopsis ELF3, interacts with the E 3 ligase APIP6 and negatively regulates immunity against Magnaporthe Oryzae in rice. Mol Plant 8, 1679-1682. |
| [113] | Niwa Y, Yamashino T, Mizuno T (2009). The circadian clock regulates the photoperiodic response of hypocotyl elongation through a coincidence mechanism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 50, 838-854. |
| [114] | Nohales MA, Liu WL, Duffy T, Nozue K, Sawa M, Pruneda-Paz JL, Maloof JN, Jacobsen SE, Kay SA (2019). Multi-level modulation of light signaling by GIGANTEA regulates both the output and pace of the circadian clock. Dev Cell 49, 840-851. |
| [115] | Nozue K, Covington MF, Duek PD, Lorrain S, Fankhauser C, Harmer SL, Maloof JN (2007). Rhythmic growth explained by coincidence between internal and external cues. Nature 448, 358-361. |
| [116] | Nusinow DA, Helfer A, Hamilton EE, King JJ, Imaizumi T, Schultz TF, Farré EM, Kay SA (2011). The ELF4-ELF3- LUX complex links the circadian clock to diurnal control of hypocotyl growth. Nature 475, 398-402. |
| [117] | Ohama N, Sato H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2017). Transcriptional regulatory network of plant heat stress response. Trends Plant Sci 22, 53-65. |
| [118] | Para A, Farré EM, Imaizumi T, Pruneda-Paz JL, Harmon FG, Kay SA (2007). PRR3 is a vascular regulator of TOC1 stability in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 19, 3462-3473. |
| [119] | Park BS, Eo HJ, Jang IC, Kang HG, Song JT, Seo HS (2010). Ubiquitination of LHY by SINAT5 regulates flowering time and is inhibited by DET1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 398, 242-246. |
| [120] | Perez-Santángelo S, Mancini E, Francey LJ, Schlaen RG, Chernomoretz A, Hogenesch JB, Yanovsky MJ (2014). Role for LSM genes in the regulation of circadian rhythms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 15166-15171. |
| [121] | Portolés S, Más P (2010). The functional interplay between protein kinase CK2 and CCA1 transcriptional activity is essential for clock temperature compensation in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 6, e1001201. |
| [122] | Pruneda-Paz JL, Breton G, Para A, Kay SA (2009). A functional genomics approach reveals CHE as a component of the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Science 323, 1481-1485. |
| [123] | Qin C, Li HY, Zhang SR, Lin XY, Jia ZW, Zhao F, Wei XZ, Jiao YC, Li Z, Niu ZY, Zhou YG, Li XJ, Li HY, Zhao T, Liu J, Li HY, Lu YP, Kong FJ, Liu B (2023). GmEID1 modulates light signaling through the Evening Complex to control flowering time and yield in soybean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 120, e2212468120. |
| [124] | Quint M, Delker C, Franklin KA, Wigge PA, Halliday KJ, Van Zanten M (2016). Molecular and genetic control of plant thermomorphogenesis. Nat Plants 2, 15190. |
| [125] | Rawat R, Takahashi N, Hsu PY, Jones MA, Schwartz J, Salemi MR, Phinney BS, Harmer SL (2011). REVEILLE8 and PSEUDO-REPONSE REGULATOR5 form a negative feedback loop within the Arabidopsis circadian clock. PLoS Genet 7, e1001350. |
| [126] | Rugnone ML, Soverna AF, Sanchez SE, Schlaen RG, Hernando CE, Seymour DK, Mancini E, Chernomoretz A, Weigel D, Más P, Yanovsky MJ (2013). LNK genes integrate light and clock signaling networks at the core of the Arabidopsis oscillator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 12120-12125. |
| [127] | Salomé PA, Weigel D, McClung CR (2010). The role of the Arabidopsis morning loop components CCA1, LHY, PRR7, and PRR9 in temperature compensation. Plant Cell 22, 3650-3661. |
| [128] | Sanchez SE, Petrillo E, Beckwith EJ, Zhang X, Rugnone ML, Hernando CE, Cuevas JC, Godoy Herz MA, Depetris-Chauvin A, Simpson CG, Brown JWS, Cerdán PD, Borevitz JO, Mas P, Ceriani MF, Kornblihtt AR, Yanovsky MJ (2010). A methyltransferase links the circadian clock to the regulation of alternative splicing. Nature 468, 112-116. |
| [129] | Sanchez SE, Rugnone ML, Kay SA (2020). Light perception: a matter of time. Mol Plant 13, 363-385. |
| [130] | Sawa M, Nusinow DA, Kay SA, Imaizumi T (2007). FKF1 and GIGANTEA complex formation is required for day-length measurement in Arabidopsis. Science 318, 261-265. |
| [131] | Schlaen RG, Mancini E, Sanchez SE, Perez-Santángelo S, Rugnone ML, Simpson CG, Brown JWS, Zhang X, Chernomoretz A, Yanovsky MJ (2015). The spliceosome assembly factor GEMIN2 attenuates the effects of temperature on alternative splicing and circadian rhythms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 9382-9387. |
| [132] | Seo PJ, Park MJ, Lim MH, Kim SG, Lee M, Baldwin IT, Park CM (2012). A self-regulatory circuit of CIRCADIAN CLOCK-ASSOCIATED1 underlies the circadian clock regulation of temperature responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 2427-2442. |
| [133] | Shalit-Kaneh A, Kumimoto RW, Filkov V, Harmer SL (2018). Multiple feedback loops of the Arabidopsis circadian clock provide rhythmic robustness across environmental conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, 7147-7152. |
| [134] | Silva CS, Nayak A, Lai XL, Hutin S, Hugouvieux V, Jung JH, López-Vidriero I, Franco-Zorrilla JM, Panigrahi KCS, Nanao MH, Wigge PA, Zubieta C (2020). Molecular mechanisms of evening complex activity in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117, 6901-6909. |
| [135] | Somers DE, Devlin PF, Kay SA (1998). Phytochromes and cryptochromes in the entrainment of the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Science 282, 1488-1490. |
| [136] | Somers DE, Kim WY, Geng RS (2004). The F-box protein ZEITLUPE confers dosage-dependent control on the circadian clock, photomorphogenesis, and flowering time. Plant Cell 16, 769-782. |
| [137] | Song HR, Carre IA (2005). DET1 regulates the proteasomal degradation of LHY, a component of the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Mol Biol 57, 761-771. |
| [138] | Song YH, Kubota A, Kwon MS, Covington MF, Lee N, Taagen ER, Laboy Cintrón D, Hwang DY, Akiyama R, Hodge SK, Huang H, Nguyen NH, Nusinow DA, Millar AJ, Shimizu KK, Imaizumi T (2018). Molecular basis of flowering under natural long-day conditions in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 4, 824-835. |
| [139] | Song YH, Shim JS, Kinmonth-Schultz HA, Imaizumi T (2015). Photoperiodic flowering: time measurement mechanisms in leaves. Annu Rev Plant Biol 66, 441-464. |
| [140] | Song YH, Smith RW, To BJ, Millar AJ, Imaizumi T (2012). FKF1 conveys timing information for CONSTANS stabilization in photoperiodic flowering. Science 336, 1045-1049. |
| [141] | Soy J, Leivar P, González-Schain N, Martín G, Diaz C, Sentandreu M, Al-Sady B, Quail PH, Monte E (2016). Molecular convergence of clock and photosensory pathways through PIF3-TOC1 interaction and co-occupancy of target promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 4870-4875. |
| [142] | Soy J, Leivar P, González-Schain N, Sentandreu M, Prat S, Quail PH, Monte E (2012). Phytochrome-imposed oscillations in PIF3 protein abundance regulate hypocotyl growth under diurnal light/dark conditions in Arabidopsis. Plant J 71, 390-401. |
| [143] | Steed G, Ramirez DC, Hannah MA, Webb AAR (2021). Chronoculture, harnessing the circadian clock to improve crop yield and sustainability. Science 372, eabc9141. |
| [144] | Su Y, Wang S, Zhang F, Zheng H, Liu Y, Huang T, Ding Y (2017) Phosphorylation of histone H2A at serine 95: a plant-specific mark involved in flowering time regulation and H2A.Z deposition. Plant Cell 29, 2197-2213. |
| [145] | Sun QB, Wang SL, Xu G, Kang XJ, Zhang M, Ni M (2019). SHB1 and CCA1 interaction desensitizes light responses and enhances thermomorphogenesis. Nat Commun 10, 3110. |
| [146] | Syed NH, Prince SJ, Mutava RN, Patil G, Li S, Chen W, Babu V, Joshi T, Khan S, Nguyen HT (2015). Core clock, SUB1, and ABAR genes mediate flooding and drought responses via alternative splicing in soybean. J Exp Bot 66, 7129-7149. |
| [147] | Tian L, Zhao XY, Liu HH, Ku L, Wang SX, Han ZP, Wu LC, Shi Y, Song XH, Chen YH (2019). Alternative splicing of ZmCCA1 mediates drought response in tropical maize. PLoS One 14, e0211623. |
| [148] | Tian WW, Wang RY, Bo CP, Yu YJ, Zhang YY, Shin GI, Kim WY, Wang L (2021). SDC mediates DNA methylation-controlled clock pace by interacting with ZTL in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 49, 3764-3780. |
| [149] | Tong M, Lee K, Ezer D, Cortijo S, Jung J, Charoensawan V, Box MS, Jaeger KE, Takahashi N, Mas P, Wigge PA, Seo PJ (2020). The evening complex establishes repressive chromatin domains via H2A.Z deposition. Plant Physiol 182, 612-625. |
| [150] | Uehara TN, Mizutani Y, Kuwata K, Hirota T, Sato A, Mizoi J, Takao S, Matsuo H, Suzuki T, Ito S, Saito AN, Nishiwaki-Ohkawa T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Yoshimura T, Kay SA, Itami K, Kinoshita T, Yamaguchi J, Nakamichi N (2019). Casein kinase 1 family regulates PRR5 and TOC1 in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 11528-11536. |
| [151] | Venkat A, Muneer S (2022). Role of circadian rhythms in major plant metabolic and signaling pathways. Front Plant Sci 13, 836244. |
| [152] | Wang CQ, Sarmast MK, Jiang JS, Dehesh K (2015). The transcriptional regulator BBX19 promotes hypocotyl growth by facilitating COP1-mediated EARLY FLOWERING 3 degradation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 27, 1128-1139. |
| [153] | Wang L, Kim J, Somers DE (2013). Transcriptional corepressor TOPLESS complexes with pseudoresponse regulator proteins and histone deacetylases to regulate circadian transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 761-766. |
| [154] | Wang LS, Li HY, He ML, Dong LD, Huang ZR, Chen LY, Nan HY, Kong FJ, Liu BH, Zhao XH (2023). GIGANTEA orthologs, E2 members, redundantly determine photoperiodic flowering and yield in soybean. J Integr Plant Biol 65, 188-202. |
| [155] | Wang X, Jiang BC, Gu LF, Chen YD, Mora M, Zhu MLM, Noory E, Wang Q, Lin CT (2021a). A photoregulatory mechanism of the circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 7, 1397-1408. |
| [156] | Wang XL, He YQ, Wei H, Wang L (2021b). A clock regulatory module is required for salt tolerance and control of heading date in rice. Plant Cell Environ 44, 3283-3301. |
| [157] | Wang XX, Wu FM, Xie QG, Wang HM, Wang Y, Yue YL, Gahura O, Ma SS, Liu L, Cao Y, Jiao YL, Puta F, Mcclung CR, Xu XD, Ma LG (2012). SKIP is a component of the spliceosome linking alternative splicing and the circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 3278-3295. |
| [158] | Wang Y, He YQ, Su C, Zentella R, Sun TP, Wang L (2020a). Nuclear localized O-fucosyltransferase SPY facilitates PRR5 proteolysis to fine-tune the pace of Arabidopsis circadian clock. Mol Plant 13, 446-458. |
| [159] | Wang Y, Su C, Yu YJ, He YQ, Wei H, Li N, Li H, Duan J, Li B, Li JG, Davis SJ, Wang L (2022a). TIME FOR COFFEE regulates phytochrome A-mediated hypocotyl growth through dawn-phased signaling. Plant Cell 34, 2907-2924. |
| [160] | Wang Y, Wu JF, Nakamichi N, Sakakibara H, Nam HG, Wu SH (2011). LIGHT-REGULATED WD1 and PSEUDO- RESPONSE REGULATOR9 form a positive feedback regulatory loop in the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Plant Cell 23, 486-498. |
| [161] | Wang Y, Yuan L, Su T, Wang Q, Gao Y, Zhang SY, Jia Q, Yu GL, Fu YF, Cheng Q, Liu BH, Kong FJ, Zhang X, Song CP, Xu XD, Xie QG (2020b). Light- and temperature-entrainable circadian clock in soybean development. Plant Cell Environ 43, 637-648. |
| [162] | Wang YP, Wu FQ, Zhou SR, Chen WW, Li CY, Duan EC, Wang JC, Cheng ZJ, Zhang X, Lin QB, Ren YL, Lei CL, Guo XP, Wu ZM, Zhu SS, Wan JM (2022b). Clock component OsPRR59 delays heading date by repressing transcription of Ehd3 in rice. Crop J 10, 1570-1579. |
| [163] | Wei H, Wang XL, He YQ, Xu H, Wang L (2021). Clock component OsPRR73 positively regulates rice salt tolerance by modulating OsHKT2;1-mediated sodium homeostasis. EMBO J 40, e105086. |
| [164] | Wei H, Xu H, Su C, Wang XL, Wang L (2022). Rice CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1 transcriptionally regulates ABA signaling to confer multiple abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Physiol 190, 1057-1073. |
| [165] | Wu JF, Tsai HL, Joanito I, Wu YC, Chang CW, Li YH, Wang Y, Hong JC, Chu JW, Hsu CP, Wu SH (2016). LWD-TCP complex activates the morning gene CCA1 in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 7, 13181. |
| [166] | Xie QG, Wang P, Liu X, Yuan L, Wang LB, Zhang CG, Li Y, Xing HY, Zhi LY, Yue ZL, Zhao CS, Mcclung CR, Xu XD (2014). LNK1 and LNK2 are transcriptional coactivators in the Arabidopsis circadian oscillator. Plant Cell 26, 2843-2857. |
| [167] | Xie QG, Xu XD (2024). Plant circadian clock in agricultural production in response to global warming. Chin Bull Bot 59, 635-650. (in Chinese) |
| 谢启光, 徐小冬 (2024). 植物生物钟在农业生产中应对全球变暖的应用. 植物学报 59, 635-650. | |
| [168] | Xu P, Zhang YX, Wen XX, Yang QQ, Liu L, Hao SL, Li JX, Wu ZZ, Shah L, Sohail A, Liu QE, Sun LP, Hong YB, Chen DB, Shen XH, Zhan XD, Cheng SH, Cao LY, Wu WX (2023). The clock component OsLUX regulates rice heading through recruiting OsELF3-1 and OsELF4s to repress Hd1 and Ghd7. J Adv Res 48, 17-31. |
| [169] | Xu T, Wu XW, Wong CE, Fan S, Zhang Y, Zhang SY, Liang Z, Yu H, Shen LS (2022a). FIONA1-mediated m6A modification regulates the floral transition in Arabidopsis. Adv Sci 9, e2103628. |
| [170] | Xu XD, Yuan L, Yang X, Zhang X, Wang L, Xie QG (2022b). Circadian clock in plants: linking timing to fitness. J Integr Plant Biol 64, 792-811. |
| [171] | Xu ZH, Zhao XG, He YK (2005). Research progress of molecular mechanism of the circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Chin Bull Bot 22, 341-349. (in Chinese) |
| 徐张红, 赵晓刚, 何奕昆 (2005). 拟南芥生物钟分子机制研究进展. 植物学报 22, 341-349. | |
| [172] | Xue MD, Zhang HR, Zhao FY, Zhao T, Li H, Jiang DH (2021). The INO80 chromatin remodeling complex promotes thermomorphogenesis by connecting H2A. Z eviction and active transcription in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 14, 1799-1813. |
| [173] | Yan JP, Li SB, Kim YJ, Zeng QN, Radziejwoski A, Wang L, Nomura Y, Nakagami H, Somers DE (2021). TOC1 clock protein phosphorylation controls complex formation with NF-YB/C to repress hypocotyl growth. EMBO J 40, e108684. |
| [174] | Yanovsky MJ, Mazzella MA, Whitelam GC, Casal JJ (2001). Resetting of the circadian clock by phytochromes and cryptochromes in Arabidopsis. J Biol Rhythms 16, 523-530. |
| [175] | Yeom M, Kim H, Lim J, Shin AY, Hong S, Kim JI, Nam HG (2014). How do phytochromes transmit the light quality information to the circadian clock in Arabidopsis? Mol Plant 7, 1701-1704. |
| [176] | Yoshida T, Ohama N, Nakajima J, Kidokoro S, Mizoi J, Nakashima K, Maruyama K, Kim JM, Seki M, Todaka D, Osakabe Y, Sakuma Y, Sch?ffl F, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011). Arabidopsis HsfA1 transcription factors function as the main positive regulators in heat shock-responsive gene expression. Mol Genet Genomics 286, 321-332. |
| [177] | Yu JW, Rubio V, Lee NY, Bai SL, Lee SY, Kim SS, Liu LJ, Zhang YY, Irigoyen ML, Sullivan JA, Zhang Y, Lee I, Xie Q, Paek NC, Deng XW (2008). COP1 and ELF3 control circadian function and photoperiodic flowering by regulating GI stability. Mol Cell 32, 617-630. |
| [178] | Yu YJ, Su C, He YQ, Wang L (2023). B-Box proteins BBX28 and BBX29 interplay with PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATORS to fine-tune circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 46, 2810-2826. |
| [179] | Yuan L, Xie GZ, Zhang SY, Li BZ, Wang XL, Li Y, Liu T, Xu XD (2021b). GmLCLs negatively regulate ABA perception and signaling genes in soybean leaf dehydration response. Plant Cell Environ 44, 412-424. |
| [180] | Yuan L, Yu YJ, Liu MM, Song Y, Li HM, Sun JQ, Wang Q, Xie QG, Wang L, Xu XD (2021a). BBX19 fine-tunes the circadian rhythm by interacting with PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR proteins to facilitate their repressive effect on morning-phased clock genes. Plant Cell 33, 2602-2617. |
| [181] | Zhao JM, Huang X, Ouyang XH, Chen WL, Du AP, Zhu L, Wang SG, Deng XW, Li SG (2012). OsELF3-1, an or- tholog of Arabidopsis EARLY FLOWERING 3, regulates rice circadian rhythm and photoperiodic flowering. PLoS One 7, e43705. |
| [182] | Zhao XH, Li HY, Wang LS, Wang JH, Huang ZR, Du HP, Li YR, Yang JH, He ML, Cheng Q, Lin XY, Liu BH, Kong FJ (2024). A critical suppression feedback loop determines soybean photoperiod sensitivity. Dev Cell 59, 1750-1763. |
| [183] | Zhao YP, Zhao BB, Xie YR, Jia H, Li YX, Xu MY, Wu GX, Ma XJ, Li QQ, Hou M, Li CY, Xia ZC, He G, Xu H, Bai ZJ, Kong DX, Zheng ZG, Liu Q, Liu YT, Zhong JS, Tian F, Wang BB, Wang HY (2023). The evening complex promotes maize flowering and adaptation to temperate re- gions. Plant Cell 35, 369-389. |
| [184] | Zheng TH, Sun J, Zhou SR, Chen SH, Lu J, Cui S, Tian YL, Zhang H, Cai MH, Zhu SS, Wu MM, Wang YH, Jiang L, Zhai HQ, Wang HY, Wan JM (2019). Post-transcriptional regulation of Ghd7 protein stability by phytochrome and OsGI in photoperiodic control of flowering in ri-ce. New Phytol 224, 306-320. |