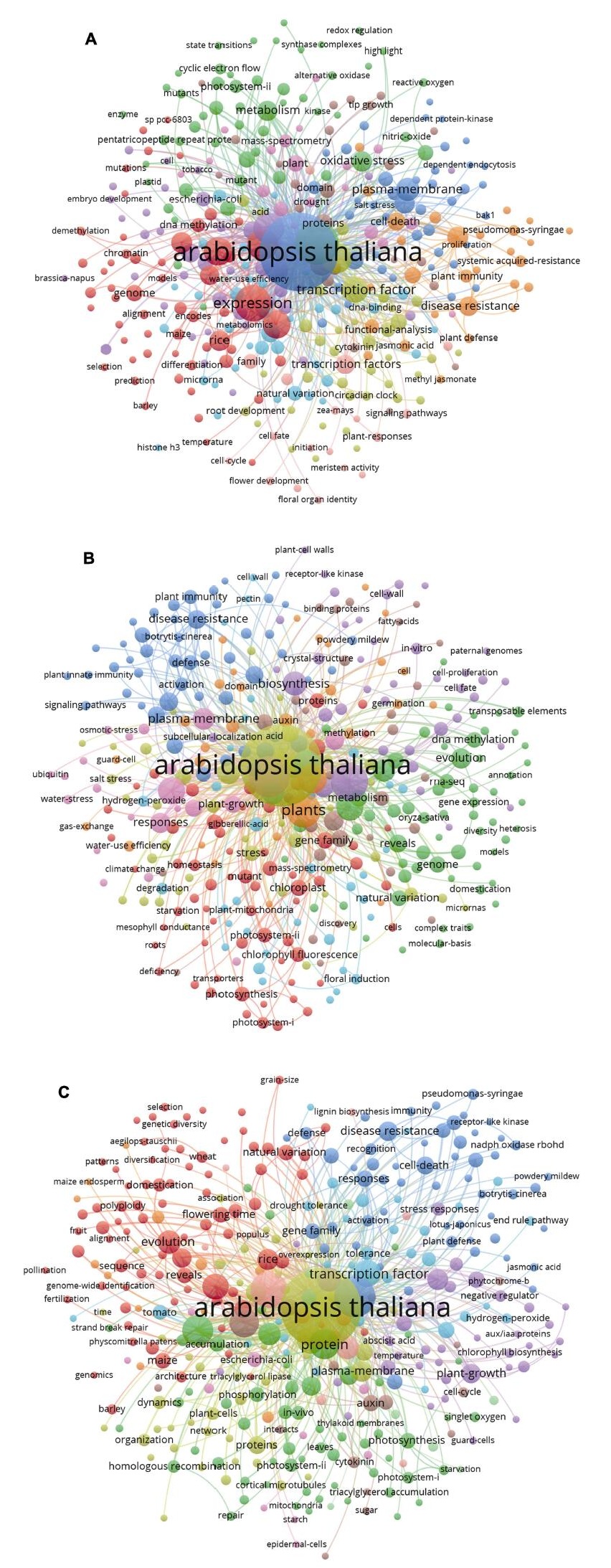
图1. 2016-2018年中国科学家在植物科学主流期刊Molecular Plant、The Plant Cell、Plant Physiology和The Plant Journal上发表论文的研究主题(数据来源: Web of Science, 绘制时间: 2019年7月2日)
使用VOSviewer软件对2016-2018年中国科学家在这4个学术期刊发表的研究论文进行关键词共现聚类。(A) 2016年的研究主题: 拟南芥蛋白激酶及盐胁迫下质膜依赖性内吞作用(蓝色); 水稻基因差异表达和编码基因预测(玉米和大麦)及基因组共线性和DNA甲基化与脱甲基化(红色); 丁香假单胞菌诱导的细胞死亡、系统获得性抗性等抗病性及植物免疫防御反应(橘色); 物质代谢关键酶(如交替氧化酶和合酶复合物)、NO对氧化胁迫的调节、PSII循环电子流状态转换及三角状五肽重复蛋白研究(绿色); 转录因子的功能及生物钟和根发育研究(黄绿色); 花发育和花器官特征及信号通路(淡粉色)。(B) 2017年的研究主题: 植物先天免疫、免疫激活、抗病性和防御机制(蓝色); PSI和PSII的叶绿素荧光, 线粒体、叶绿体基因家族及相关突变体(红色); 水稻基因组、相关代谢和自然变异, RNA序列的基因表达、进化发育与DNA甲基化(绿色); 拟南芥盐胁迫(黄绿色); 植物生长发育与水分利用效率(淡粉色)。(C) 2018年的研究主题: 丁香假单胞菌诱导的细胞死亡、抗病性鉴定及基因家族对逆境的响应(蓝色); 多倍体物种的进化和驯化、水稻开花时间和自然变异及玉米和大麦等的基因组, 小麦(节节麦)的遗传多样性, 序列的共线性(红色); 光合作用的类囊体膜(PSI和PSII)蛋白、体内磷酸化作用、同源重组及三酰甘油积累(绿色); 植物生长发育及其负调节子、叶绿素的生物合成与激素(生长素和脱落酸)蛋白(紫色); 拟南芥质膜蛋白及细胞组织动态(黄绿色)。
Figure 1. Research themes of Chinese scientists published in major journals of plant sciences (Molecular Plant, The Plant Cell, Plant Physiology and The Plant Journal) from 2016 to 2018 (data sources: Web of Science; data collected by July 2, 2019)
Keyword co-occurence cluster of papers published by Chinese scientists in four plant science journals from 2016 to 2018 was constructed by VOSviewer. (A) The themes of 2016: Arabidopsis protein kinases and plasma membrane-dependent endocytosis under salt stress (blue); differentially expressed genes in rice and coding genes prediction (maize and barley), genome colinea- rity and DNA methylation and demethylation (red); Pseudomonas syringae induced cell death and systemic acquired resistance and immunity (orange); key enzymes of metabolism (such as alternative oxidase and synthase complexes), roles of NO in oxidative stress, cyclic electron flow of PSII and pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) (green); transcription factors, circadian clock and root development (yellow-green); flower development and floral organ identity and signaling pathways (light pink). (B) The themes of 2017: plant innate immunity, immunity activation, disease resistance and defense mechanism (blue); chlorophyll fluorescence of PSI and PSII, mitochondria and chloroplast gene family and related mutants (red); rice genome, metabolism and natural variation, RNA-seq, evolution and DNA methylation (green); salt stress of Arabidopsis (yellow-green); plant growth and development and water use efficiency (light pink). (C) The themes of 2018: Pseudomonas syringae induced cell death, disease resistance recognition and gene family response on stress (blue); evolution and domestication of polyploid species, flowering time and natural variation of rice, genome (maize, barley, etc.), genetic diversity of wheat (Aegilops tauschii), and collinear analysis (red); thylakoid membrane protein of PSI and PSII; phosphorylation in vivo, homologous recombination and triacylglycerol accumulation (green); plant growth and development and negative regulators; biosynthesis of chlorophyll and hormone (auxin and abscisic acid) proteins (purple); Arabidopsis plasma membrane proteins and cell tissue dynamics (yellow green).