

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 497-502.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19108
• TECHNIQUES AND METHODS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lichao Chen,Ni Zhan,Yansha Li,Jian Feng,Jianru Zuo*( )
)
Received:2019-06-13
Accepted:2019-06-20
Online:2019-07-10
Published:2020-01-08
Contact:
Jianru Zuo
Lichao Chen,Ni Zhan,Yansha Li,Jian Feng,Jianru Zuo. Detection and Analysis of Protein S-nitrosylation in Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(4): 497-502.
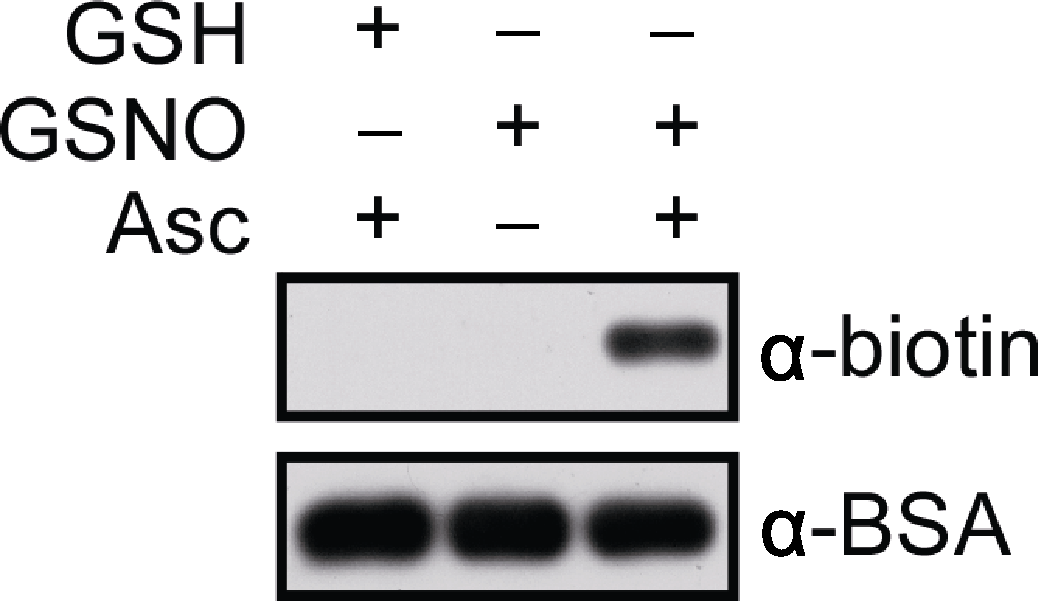
Figure 1 In vitro analysis of S-nitrosylated bovine serum albumin (BSA) BSA is labelled with biotin-maleimide, subjected to SDS- PAGE and western blotting. Anti-biotin and anti-BSA antibodies are used as primary antibodies, respectively (dilution in 1:20 000) and anti-mouse IgG as a secondary antibody. Signals are detected by using the SuperSignal Western Femto Maximun Sensitivity Substrate Kit. The blots are exposed for 20 sec (top) and 30 sec (bottom), respectively. GSH: Glutathione; GSNO: S-nitrosoglutathione; Asc: Sodium ascorbate
| [1] | Albertos P, Romero-Puertas MC, Tatematsu K, Mateos I, Sánchez-Vicente I, Nambara E, Lorenzo O ( 2015). S-nitrosylation triggers ABI5 degradation to promote seed germination and seedling growth. Nat Commun 6, 8669. |
| [2] | Chen R, Sun S, Wang C, Li Y, Liang Y, An F, Li C, Dong H, Yang X, Zhang J, Zuo J ( 2009). The Arabidopsis PARAQUAT RESISTANT2 gene encodes an S-nitrosoglutathione reductase that is a key regulator of cell death. Cell Res 19, 1377. |
| [3] | Cui B, Pan Q, Clarke D, Villarreal MO, Umbreen S, Yuan B, Shan W, Jiang J, Loake GJ ( 2018). S-nitrosylation of the zinc finger protein SRG1 regulates plant immunity. Nat Commun 9, 4226. |
| [4] | Feng J, Chen L, Zuo J ( 2019). Protein S-nitrosylation in plants: current progresses and challenges. J Integr Plant Biol doi. org/10.1111/jipb.12780. |
| [5] | Feng J, Wang C, Chen Q, Chen H, Ren B, Li X, Zuo J ( 2013). S-nitrosylation of phosphotransfer proteins represses cytokinin signaling. Nat Commun 4, 1529. |
| [6] | He Y, Tang RH, Hao Y, Stevens RD, Cook CW, Ahn SM, Jing L, Yang Z, Chen L, Guo F, Fiorani F, Jackson RB, Crawford NM, Pei ZM ( 2004). Nitric oxide represses the Arabidopsis floral transition. Science 305, 1968-1971. |
| [7] | Hess DT, Matsumoto A, Kim SO, Marshall HE, Stamler JS ( 2005). Protein S-nitrosylation: purview and parameters. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6, 150-166. |
| [8] | Hess DT, Stamler JS ( 2012). Regulation by S-nitrosylation of protein post-translational modification. J Biol Chem 287, 4411-4418. |
| [9] | Hu J, Huang X, Chen L, Sun X, Lu C, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zuo J ( 2015). Site-specific nitrosoproteomic identification of endogenously S-nitrosylated proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 167, 1731-1746. |
| [10] | Hu J, Yang H, Mu J, Lu T, Peng J, Deng X, Kong Z, Bao S, Cao X, Zuo J ( 2017). Nitric oxide regulates protein methylation during stress responses in plants. Mol Cell 67, 702-710. |
| [11] | Iglesias MJ, Terrile MC, Correa-Aragunde N, Colman SL, Izquierdo-Álvarez A, Fiol DF, París R, Sánchez-López N, Marina A, Calderón Villalobos LIA, Estelle M, Lamattina L, Martínez-Ruiz A, Casalongué CA ( 2018). Regulation of SCFTIR1/AFBs E3 ligase assembly by S-nitrosylation of Arabidopsis SKP1-like1 impacts on auxin signaling. Redox Biol 18, 200-210. |
| [12] | Jaffrey SR, Snyder SH ( 2001). The biotin switch method for the detection of S-nitrosylated proteins. Sci STKE 2001,pl1. |
| [13] | Ling T, Bellin D, Vandelle E, Imanifard Z, Delledonne M ( 2017). Host-mediated S-nitrosylation disarms the bacterial effector HopAI1 to reestablish immunity. Plant Cell 29, 2871-2881. |
| [14] | Lytvyn DI, Raynaud C, Yemets AI, Bergounioux C, Blume YB ( 2016). Involvement of inositol biosynthesis and nitric oxide in the mediation of UV-B induced oxidative stress. Front Plant Sci 7, 430. |
| [15] | Pan QN, Geng CC, Li DD, Xu SW, Mao DD, Umbreen S, Loake GJ, Cui BM ( 2019). Nitrate reductase-mediated nitric oxide regulates the leaf shape in Arabidopsis by mediating the homeostasis of reactive oxygen species. Int J Mol Sci 20, 2235. |
| [16] | París R, Vazquez MM, Graziano M, Terrile MC, Miller ND, Spalding EP, Otegui MS, Casalongué CA ( 2018). Distribution of endogenous NO regulates early gravitropic response and PIN2 localization in Arabidopsis roots. Front Plant Sci 9, 495. |
| [17] | Seth D, Hess DT, Hausladen A, Wang L, Wang YJ, Stamler JS ( 2018). A multiplex enzymatic machinery for cellular protein S-nitrosylation. Mol Cell 69, 451-464. |
| [18] | Seth P, Hsieh PN, Jamal S, Wang L, Gygi SP, Jain MK, Coller J, Stamler JS ( 2019). Regulation of microRNA machinery and development by interspecies S-nitrosylation. Cell 176, 1014-1025. |
| [19] | Shekariesfahlan A, Lindermayr C ( 2018). Identification of NO-sensitive cysteine residues using cysteine mutants of recombinant proteins. In: Mengel A, Lindermayr C, eds. Nitric Oxide: Methods and Protocols. New York: Springer New York. pp. 183-203. |
| [20] | Shi H, Liu W, Wei Y, Ye T ( 2017). Integration of auxin/ indole-3-acetic acid 17 and RGA-LIKE3 confers salt stress resistance through stabilization by nitric oxide in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 68, 1239-1249. |
| [21] | Tada Y, Spoel SH, Pajerowska-Mukhtar K, Mou Z, Song J, Wang C, Zuo J, Dong X ( 2008). Plant immunity requires conformational charges of NPR1 via S-nitrosylation and thioredoxins. Science 321, 952-956. |
| [22] | Wang P, Zhu JK, Lang Z ( 2015). Nitric oxide suppresses the inhibitory effect of abscisic acid on seed germination by S-nitrosylation of SnRK2 proteins. Plant Signal Behav 10, e1031939. |
| [23] | Willems P, Horne A, Van Parys T, Goormachtig S, De Smet I, Botzki A, Van Breusegem F, Gevaert K ( 2019). The Plant PTM Viewer, a central resource for exploring plant protein modifications. Plant J 99, 752-762. |
| [24] | Xue Y, Liu Z, Gao X, Jin C, Wen L, Yao X, Ren J ( 2010). GPS-SNO: computational prediction of protein S-nitrosylation sites with a modified GPS algorithm. PLoS One 5, e11290. |
| [25] | Yang H, Mu J, Chen L, Feng J, Hu J, Li L, Zhou JM, Zuo J ( 2015). S-nitrosylation positively regulates ascorbate peroxidase activity during plant stress responses. Plant Physiol 167, 1604. |
| [26] | Zhan N, Wang C, Chen L, Yang H, Feng J, Gong X, Ren B, Wu R, Mu J, Li Y, Liu Z, Zhou Y, Peng J, Wang K, Huang X, Xiao S, Zuo J ( 2018). S-nitrosylation targets GSNO reductase for selective autophagy during hypoxia responses in plants. Mol Cell 71, 142-154. |
| [27] | Zhang L, Shi X, Zhang Y, Wang J, Yang J, Ishida T, Jiang W, Han X, Kang J, Wang X, Pan L, Lv S, Cao B, Zhang Y, Wu J, Han H, Hu Z, Cui L, Sawa S, He J, Wang G ( 2019 a). CLE9 peptide-induced stomatal closure is mediated by abscisic acid, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 42, 1033-1044. |
| [28] | Zhang ZW, Fu YF, Zhou YH, Wang CQ, Lan T, Chen GD, Zeng J, Chen YE, Yuan M, Yuan S, Hu JY ( 2019 b). Nitrogen and nitric oxide regulate Arabidopsis flowering differently. Plant Sci 284, 177-184. |
| [1] | Yun Han, Xiaofeng Chi, Jingya Yu, Xujie Ding, Shilong Chen, Faqi Zhang. A checklist of wild vascular plants in Qinghai, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23280-. |
| [2] | Yousheng Chen, Zhuqiu Song, Ran Wei, Yan Luo, Wenli Chen, Fusheng Yang, Lianming Gao, Yuan Xu, Zhuoxin Zhang, Pengcheng Fu, Chunlei Xiang, Huanchong Wang, Jiachen Hao, Shiyong Meng, Lei Wu, Bo Li, Shengxiang Yu, Shuren Zhang, Li He, Xinqiang Guo, Wenguang Wang, Yihua Tong, Qi Gao, Wenqun Fei, Youpai Zeng, Lin Bai, Zichao Jin, Xingjie Zhong, Buyun Zhang, Siyi Du. A dataset on inventory and geographical distribution of vascular plants in Xizang, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23188-. |
| [3] | Zhuqiu Song, Wen Ye, Shiyong Dong, Zichao Jin, Xingjie Zhong, Zhen Wang, Buyun Zhang, Yechun Xu, Wenli Chen, Shijin Li, Gang Yao, Zhoufeng Xu, Shuai Liao, Yihua Tong, Youpai Zeng, Yunbao Zeng, Yousheng Chen. A dataset on inventory and geographical distributions of higher plants in Guangdong, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23177-. |
| [4] | Shifeng Wen, Zhihua Zhou, Tuo He, Hui Dong, Liangchen Yuan, Zeyang Lu, Yongteng Wang, Lin Guo, Jiangping Shu, Kaifan Li. Formulating the National Botanical Garden System Layout Plan of China: Background, procedures, ideas and key considerations [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23193-. |
| [5] | Yong Li, Sanqing Li, Huan Wang. A dataset of wild vascular plants and their distributions in Tianjin, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23128-. |
| [6] | Tingting Deng, Yan Wei, Siyuan Ren, Yan Zhu. Effects of topography and stand structure of warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest on understory herb diversity in Donglingshan, Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 22671-. |
| [7] | Xinjing Wu, Jinfeng Chen, Guofa Cui. Proposals for updating the List of National Key Protected Wild Plants—Based on an analysis of existing conservation lists [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 22622-. |
| [8] | Caiqun Liang, Yukai Chen, Xiaobo Yang, Kai Zhang, Donghai Li, Yuexin Jiang, Jinghan Li, Chongyang Wang, Shunwei Zhang, Zicheng Zhu. A dataset on inventory and geographical distributions of wild vascular plants in Hainan Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 23067-. |
| [9] | Chang An, Yixue Zhuang, Ping Zheng, Yanxiang Lin, Chengzi Yang, Yuan Qin. A checklist of vascular plants in Fujian Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22537-. |
| [10] | Cheng Du, Yuan Wang, Xiaoling Yan, Jing Yan, Huiru Li, Qingfei Zhang, Yonghong Hu. Composition and historical changes of plant species diversity in Shanghai and the updated checklist of Shanghai vascular plants (2022) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 23093-. |
| [11] | Yi Li, Xi Zhang, Yanhui Yuan, Pichang Gong, Jinxing Lin. Aptamers and Their Applications in Plant Science Researches [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 935-945. |
| [12] | Zhaoyang Jing, Keguang Cheng, Heng Shu, Yongpeng Ma, Pingli Liu. Whole genome resequencing approach for conservation biology of endangered plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22679-. |
| [13] | Yu Xiao, Yuran Li, Hexiang Duan, Zhengtao Ren, Shengbi Feng, Zhicheng Jiang, Jiahua Li, Pin Zhang, Jinming Hu, Yupeng Geng. Invasion status and control measures for alien plants within the Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 23011-. |
| [14] | Yaochu Sun, Yuanfei Pan, Mu Liu, Xiaoyun Pan. The specialist-to-generalist ratio affects growth and defense strategy of invasive plant Alternanthera philoxeroides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22632-. |
| [15] | Yexi Zhao, Jiayu Zhang, Zihan Li, Qinmijia Xie, Xin Deng, Nan Wang. Use of native and alien plants during night roosting by urban birds in Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22399-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||