

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2017, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 713-722.DOI: 10.11983/CBB16239
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Liu Kaige, Qi Shuanghui, Duan Shaowei, Li Dong, Jin Changyu, Gao Chenhao, Liu Mingxun Chen Xuanxia*( )
)
Received:2016-12-05
Accepted:2017-04-03
Online:2017-11-01
Published:2017-11-22
Contact:
Liu Mingxun Chen Xuanxia
Liu Kaige, Qi Shuanghui, Duan Shaowei, Li Dong, Jin Changyu, Gao Chenhao, Liu Mingxun Chen Xuanxia. Functional Analysis of Brassica napus BnTTG1-1 Gene[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(6): 713-722.
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) | Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| AtACTIN7-F | GCCCCTGAGGAGCACCCAGTT | RT-PCR |
| AtACTIN7-R | CCGGTTGTACGACCACTGGCA | |
| BnTTG1-1-F | GCCAGTATCCGTCCTCAACA | RT-PCR |
| BnTTG1-1-R | CTCCCAGATAAGAGCCTGCG | |
| BnACTIN7-F | GGAGCTGAGAGATTCCGTTG | qRT-PCR |
| BnACTIN7-R | GAACCACCACTGAGGACGAT | |
| BnTTG1-1-F | CTGCAGTGGTCTTCTTCGTT | qRT-PCR |
| BnTTG1-1-R | GTTACAATCACATAGATGCAGAGAC | |
| BnTTG1-1-Xma1-F | TATTcccgggATGGACAACTCAGCTCCAGACTC | 35S:BnTTG1-1-GFP and 35S:BnTTG1-1 |
| BnTTG1-1-Spe1-R | GGactagtAACTCTAAGGAGCTGCATTTTGTTAGC |
Table 1 Sequences of primers
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) | Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| AtACTIN7-F | GCCCCTGAGGAGCACCCAGTT | RT-PCR |
| AtACTIN7-R | CCGGTTGTACGACCACTGGCA | |
| BnTTG1-1-F | GCCAGTATCCGTCCTCAACA | RT-PCR |
| BnTTG1-1-R | CTCCCAGATAAGAGCCTGCG | |
| BnACTIN7-F | GGAGCTGAGAGATTCCGTTG | qRT-PCR |
| BnACTIN7-R | GAACCACCACTGAGGACGAT | |
| BnTTG1-1-F | CTGCAGTGGTCTTCTTCGTT | qRT-PCR |
| BnTTG1-1-R | GTTACAATCACATAGATGCAGAGAC | |
| BnTTG1-1-Xma1-F | TATTcccgggATGGACAACTCAGCTCCAGACTC | 35S:BnTTG1-1-GFP and 35S:BnTTG1-1 |
| BnTTG1-1-Spe1-R | GGactagtAACTCTAAGGAGCTGCATTTTGTTAGC |
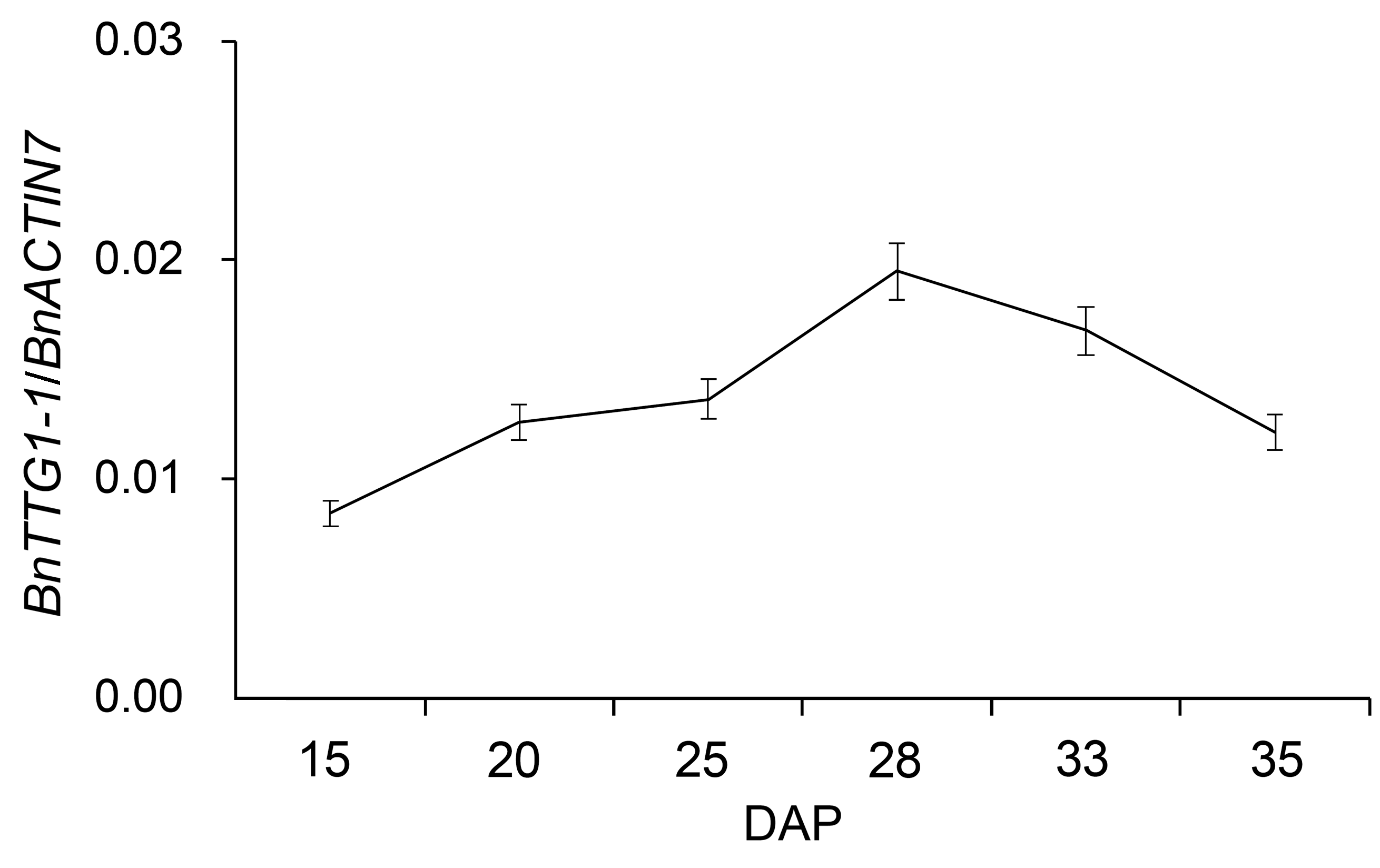
Figure 1 qRT-PCR analysis of BnTTG1-1 expression in de- veloping seeds at different developmental stages in Brassica napus cv. ‘QINYOU Seven’ (means±SD)DAP: Days after pollination. The qRT-PCR result was normaliz- ed against the expression of BnACTIN7 as an internal control.
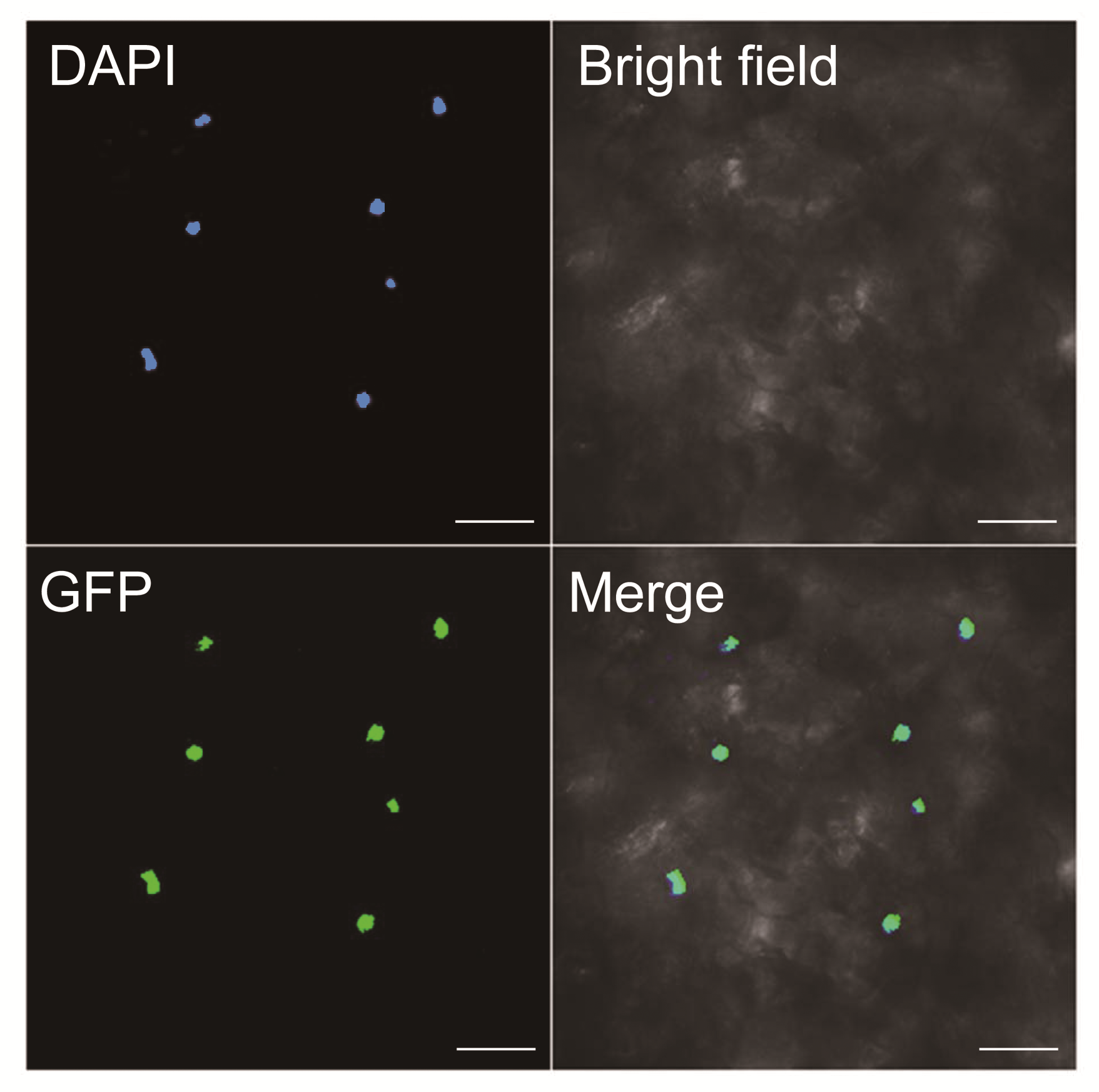
Figure 2 Subcellular localization of BnTTG1-1 protein fus- ed with GFP (35S:BnTTG1-1-GFP) in tobacco (Nicotiana ben- thamiana) leave cellsDAPI: 4’, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride; GFP: Green fluorescent protein; Merge: Merged picture of bright, DAPI, and GFP fields. Bars=5 μm
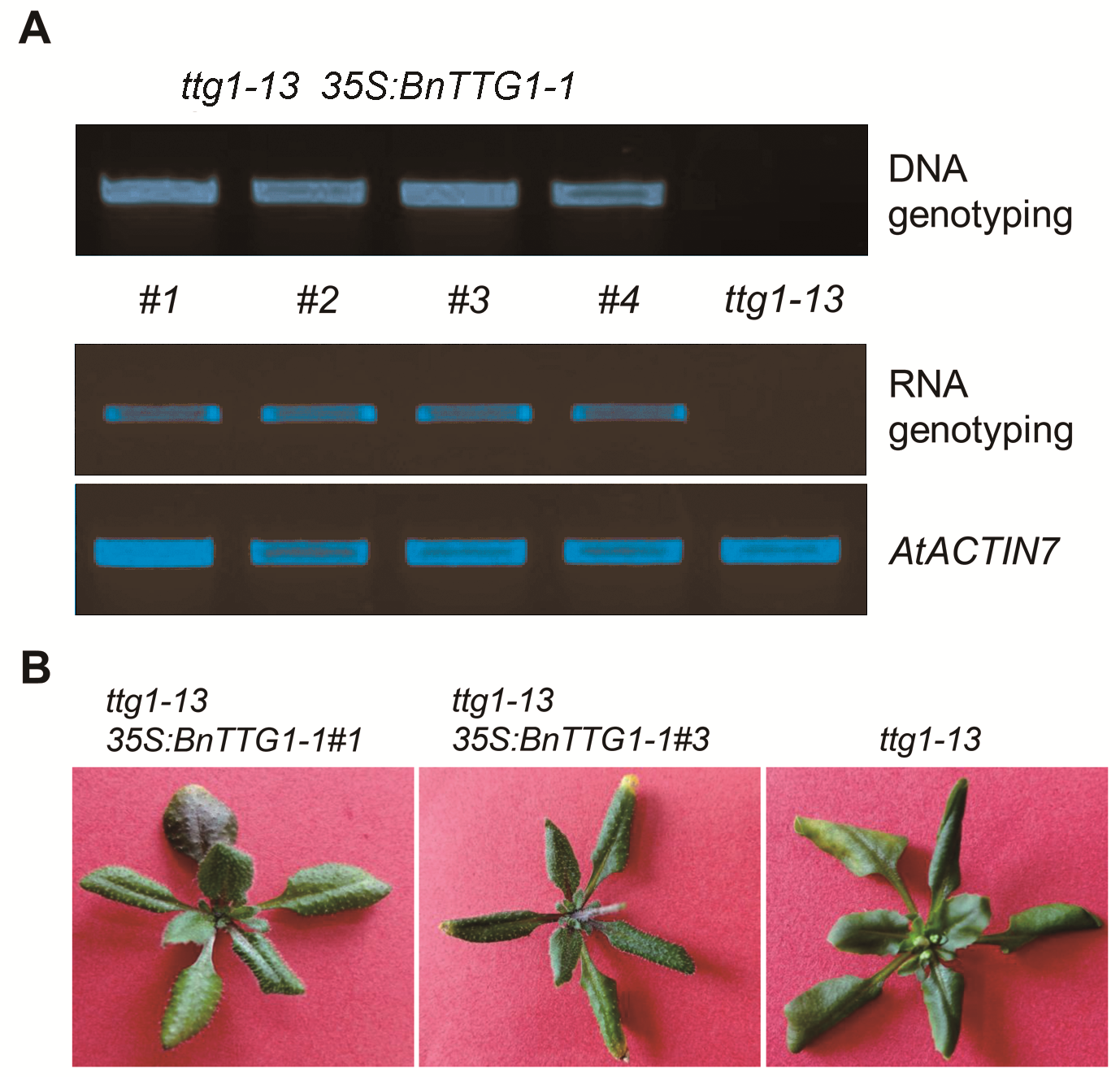
Figure 3 Identification of ttg1-13 35S:BnTTG1-1 transgenic plants(A) PCR-based DNA and RNA genotyping of ttg1-13 35S: BnTTG1-1 transgenic plants, AtACTIN7 was regarded as an internal control; (B) Heterologous expression of BnTTG1-1 in the ttg1-13 background fully rescued no trichomes and anthocyanins phenotypes of ttg1-13.
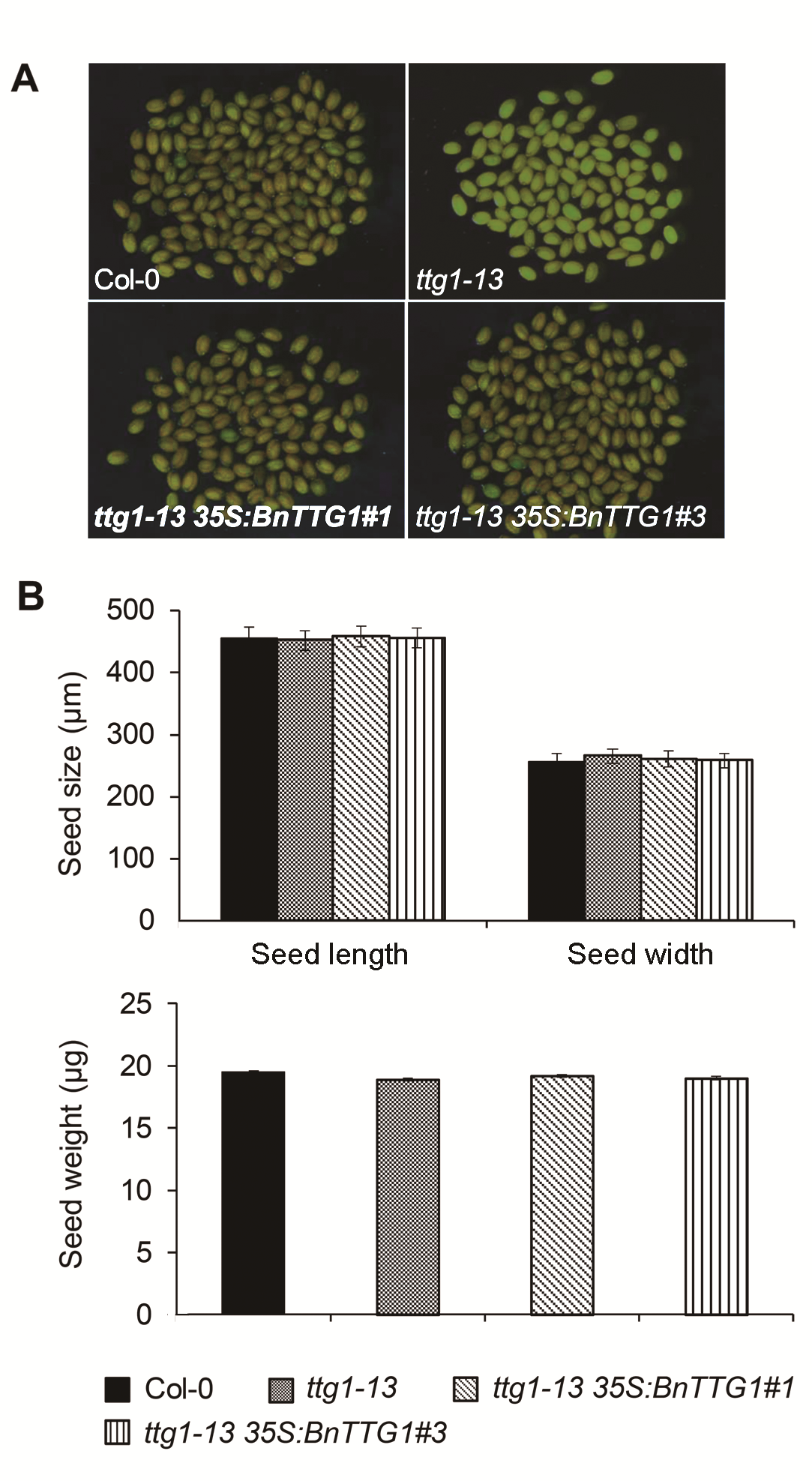
Figure 4 Comparison of seed coat color, seed size and se- ed weight among the wild-type (Col-0), ttg1-13, and ttg1-13 35S:BnTTG1-1 transgenic plants of Arabidopsis (means±SD)(A) Microscopic observation of mature seeds; (B) Comparison of seed size and weight of mature seeds
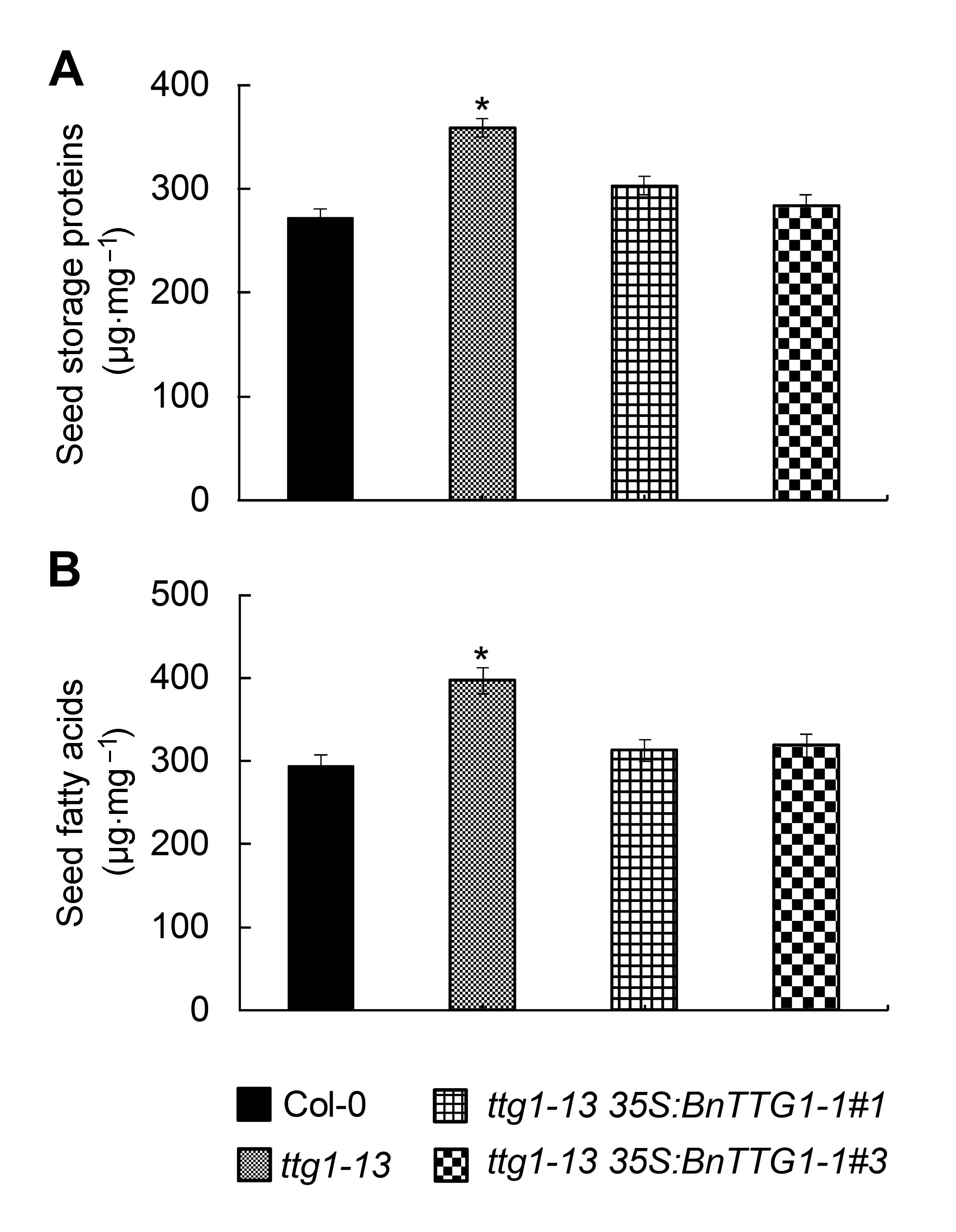
Figure 5 Comparison of seed storage compounds among the wild-type (Col-0), ttg1-13, and ttg1-13 35S:BnTTG1-1 trans- genic plants of Arabidopsis (means±SD)(A) The content of seed storage proteins in different lines; (B) The content of seed fatty acids in different lines. Asterisks de- note statistically signi?cant differences between the wild-type and ttg1-13 mutant (Student’s t test, P<0.05).
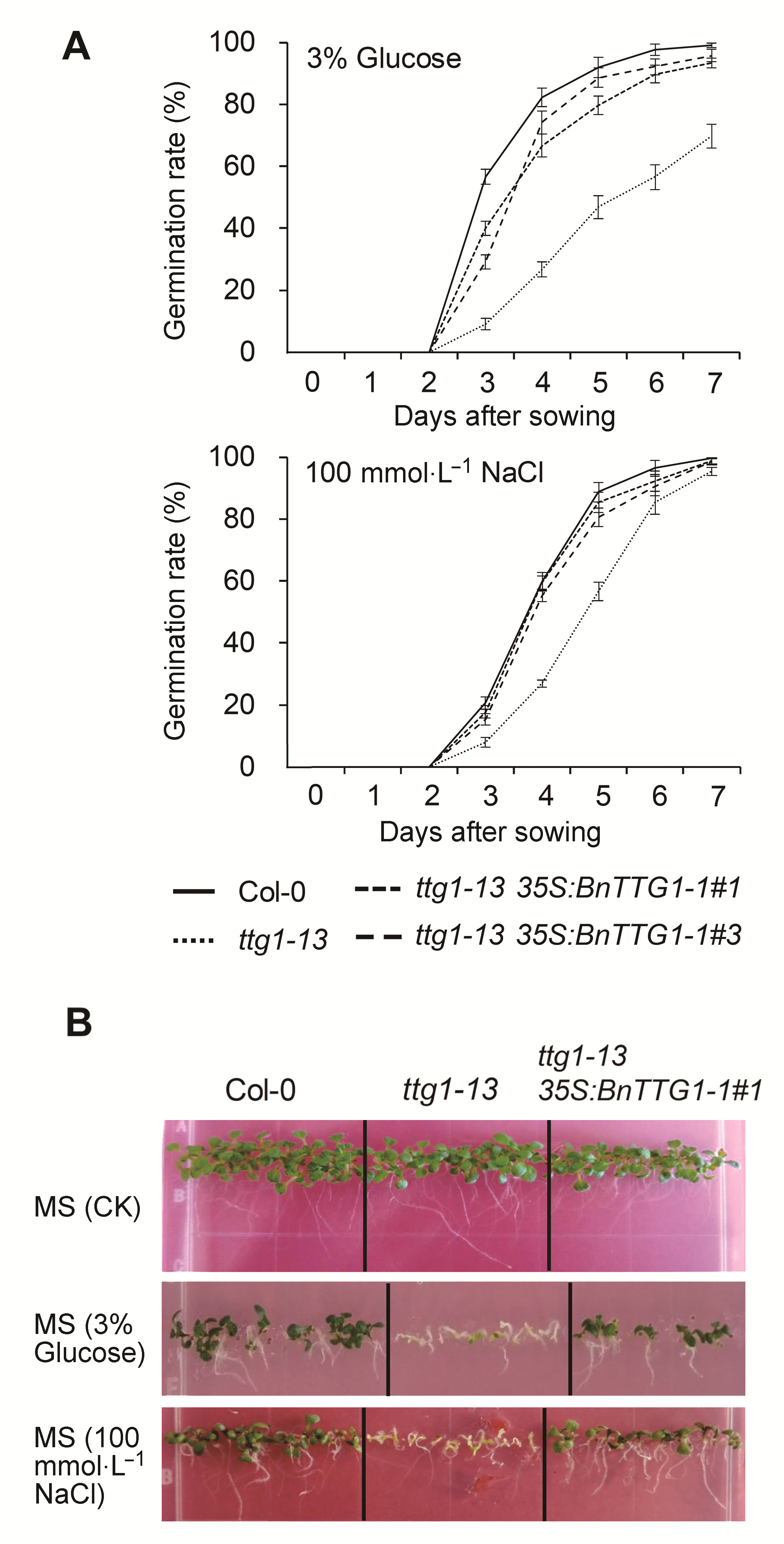
Figure 6 Seed germination rate and seedling establishment on MS agar medium containing 3% (w/v) Glucose and containing 100 mmol·L-1 NaCl among the wild-type (Col-0), ttg1- 13, and ttg1-13 35S:BnTTG1-1 transgenic plants of Arabidopsis(A) Seed germination rate; (B) Seedling establishment. Values are the means±SD from three independent experiments evaluating 100 seeds.
| [1] | 刘后利, 傅廷栋, 陈怀庆, 易淑梅, 熊双娥 (1979). 甘蓝型黄籽油菜的发现及其遗传行为的初步研究. 遗传学报 6, 54. |
| [2] |
张子龙, 李加纳 (2001). 甘蓝型黄籽油菜粒色遗传及其育种研究进展. 作物杂志 (6), 37-40.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Bradford MM (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the |
| [4] | principle of protein-dye binding.Anal Biochem 72, 248-254. |
| [5] | Cavell AC, Lydiate DJ, Parkin IAP, Dean C, Trick M (1998). Collinearity between a 30-centimorgan segment of Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 4 and duplicated regions within the Brassica napus genome. Genome 41, 62-69. |
| [6] |
Cernac A, Andre C, Hoffmann-Benning S, Benning C (2006). WRI1 is required for seed germination and seedling establishment.Plant Physiol 141, 745-757.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Chen MX, Du X, Zhu Y, Wang Z, Hua SJ, Li ZL, Guo WL, Zhang GP, Peng JR, Jiang LX (2012a).Seed Fatty Acid Reducer acts downstream of gibberellin signaling pathway to lower seed fatty acid storage in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 35, 2155-2169.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] | Chen MX, Wang Z, Zhu YN, Li ZL, Hussain N, Xuan LJ, Guo WL, Zhang GP, Jiang LX (2012b). The effect of TRANSPARENT TESTA2 on seed fatty acid biosynthesis and tolerance to environmental stresses during young seedling establishment in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 160, 1023-1036. |
| [9] |
Chen MX, Xuan LJ, Wang Z, Zhou LH, Li ZL, Du X, Ali E, Zhang GP, Jiang LX (2014). TRANSPARENT TESTA8 inhibits seed fatty acid accumulation by targeting several seed development regulators in Arabidopsis.Plant Phy- siol 165, 905-916.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] | Chen MX, Zhang B, Li CX, Kulaveerasingam H, Chew FT, Yu H (2015). TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA1 regulates the accumulation of seed storage reserves in Ara- bidopsis. Plant Physiol 169, 391-402. |
| [11] | Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998). Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16, 735-743. |
| [12] |
Cutler SR, Rodriguez PL, Finkelstein RR, Abrams SR (2010). Abscisic acid: emergence of a core signaling network.Annu Rev Plant Biol 61, 651-679.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Debeaujon I, Léon-Kloosterziel KM, Koornneef M (2000). Influence of the testa on seed dormancy, germination, and longevity in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 122, 403-414.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Debeaujon I, Nesi N, Perez P, Devic M, Grandjean O, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2003). Proanthocyanidin- accumulating cells in Arabidopsis testa: regulation of differentiation and role in seed development.Plant Cell 15, 2514-2531.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
Finkelstein RR, Gampala SSL, Rock CD (2002). Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings.Plant Cell 14, S15-S45.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
Gibson SI (2001). Plant sugar-response pathways. Part of a complex regulatory web.Plant Physiol 125, 2203-2203.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
Hong JK, Choi HW, Hwang IS, Kim DS, Kim NH, Choi DS, Kim YJ, Hwang BK (2008). Function of a novel GDSL- type pepper lipase gene, CaGLIP1, in disease susceptibility and abiotic stress tolerance. Planta 227, 539-558.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
Koes RE, Quattrocchio F, Mol JNM (1994). The flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in plants: function and evolution.BioEssays 16, 123-132.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Koornneef M (1981). The complex syndrome of ttg mutants. Arabidopsis Inf Serv 18, 45-51. |
| [20] |
Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Baudry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N, Caboche M (2006). Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids.Annu Rev Plant Biol 57, 405-430.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
Liu KG, Qi SH, Li D, Jin CY, Gao CH, Duan SW, Feng BL, Chen MX (2017). TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA 1 ubiquitously regulates plant growth and development from Arabidopsis to foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Plant Sci 254, 60-69.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method.Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Lu J, Li JN, Lei B, Wang SG, Chai YR (2009). Molecular cloning and characterization of two Brassica napus TTG1 genes reveal genus-specific nucleotide preference, extreme protein-level conservation and fast divergence of organ-specificity. Genes Genom 31, 129-142.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Mol J, Grotewold E, Koes R (1998). How genes paint flowers and seeds.Trends Plant Sci 3, 212-217.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Mu JY, Tan HL, Zheng Q, Fu FY, Liang Y, Zhang J, Yang XH, Wang T, Chong K, Wang XJ, Zuo JR (2008). LEAFY COTYLEDON1 is a key regulator of fatty acid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 148, 1042-1054. |
| [26] |
Nakabayashi R, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Urano K, Suzuki M, Yamada Y, Nishizawa T, Matsuda F, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Shinozaki K, Michael AJ, Tohge T, Yamazaki M, Saito K (2014). Enhancement of oxidative and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by overaccumulation of antioxidant flavonoids.Plant J 77, 367-379.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] |
Nesi N, Jond C, Debeaujon I, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2001). The Arabidopsis TT2 gene encodes an R2R3 MYB domain protein that acts as a key determinant for proanthocyanidin accumulation in developing seed. Plant Cell 13, 2099-2114.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] |
Nguyen HN, Kim JH, Hyun WY, Nguyen NT, Hong SW, Lee H (2013). TTG1-mediated flavonols biosynthesis alleviates root growth inhibition in response to ABA.Plant Cell Rep 32, 503-514.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] | Osborn TC, Kole C, Parkin IAP, Sharpe AG, Kuiper M, Lydiate DJ, Trick M (1997). Comparison of flowering time genes inBrassica rapa, B. napus and Arabidopsis tha- liana. Genetics 146, 1123-1129. |
| [30] |
Peer WA, Murphy AS (2007). Flavonoids and auxin transport: modulators or regulators?Trends Plant Sci 12, 556-563.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] |
Petrussa E, Braidot E, Zancani M, Peresson C, Bertolini A, Patui S, Vianello A (2013). Plant flavonoids-biosyn- thesis, transport and involvement in stress responses.Int J Mol Sci 14, 14950-14973.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Shi L, Katavic V, Yu YY, Kunst L, Haughn G (2012). Arabidopsis glabra2 mutant seeds deficient in mucilage biosynthesis produce more oil. Plant J 69, 37-46.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] |
Shirley BW (1996). Flavonoid biosynthesis: ‘new’ functions for an ‘old’ pathway.Trends Plant Sci 1, 377-382.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Shirley BW, Kubasek WL, Storz G, Bruggemann E, Koornneef M, Ausubel FM, Goodman HM (1995). Analysis of Arabidopsis mutants deficient in flavonoid bio- synthesis.Plant J 8, 659-671.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] |
Szymanski DB, Lloyd AM, Marks MD (2000). Progress in the molecular genetic analysis of trichome initiation and morphogenesis in Arabidopsis.Trends Plant Sci 5, 214-219.
DOI URL PMID |
| [36] |
Tsuchiya Y, Nambara E, Naito S, McCourt P (2004). The FUS3 transcription factor functions through the epidermal regulator TTG1 during embryogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 37, 73-81.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] | Walker AR, Davison PA, Bolognesi-Winfield AC, James CM, Srinivasan N, Blundell TL, Esch JJ, Marks MD, Gray JC (1999). The TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA1 locus, which regulates trichome differentiation and anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis, encodes a WD40 repeat protein. Plant Cell 11, 1337-1350. |
| [38] | Wang Z, Chen MX, Chen TL, Xuan LJ, Li ZL, Du X, Zhou LH, Zhang GP, Jiang LX (2014). TRANSPARENT TESTA2 regulates embryonic fatty acid biosynthesis by targeting FUSCA3 during the early developmental stage of Arabidopsis seeds. Plant J 77, 757-769. |
| [39] |
Western TL, Burn J, Tan WL, Skinner DJ, Martin- McCaffrey L, Moffatt BA, Haughn GW (2001). Isolation and characterization of mutants defective in seed coat mucilage secretory cell development in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 127, 998-1011.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Winkel-Shirley B (2002). Biosynthesis of flavonoids and ef- fects of stress.Curr Opin Plant Biol 5, 218-223.
DOI URL PMID |
| [41] |
Xu WJ, Grain D, Bobet S, Le Gourrierec J, Thévenin J, Kelemen Z, Lepiniec L, Dubos C (2014). Complexity and robustness of the flavonoid transcriptional regulatory network revealed by comprehensive analyses of MYB- bHLH-WDR complexes and their targets in Arabidopsis seed.New Phytol 202, 132-144.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] |
Zhang YM, Rock CO (2004). Evaluation of epigallocatechin gallate and related plant polyphenols as inhibitors of the FabG and FabI reductases of bacterial type II fatty-acid synthase.J Biol Chem 279, 30994-31001.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Zhang Yingchuan, Wu Xiaomingyu, Tao Baolong, Chen Li, Lu Haiqin, Zhao Lun, Wen Jing, Yi Bin, Tu Jinxing, Fu Tingdong, Shen Jinxiong. Bna-miR43 Mediates the Response of Drought Tolerance in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 701-711. |
| [2] | Nan Wu, Lei Qin, Kan Cui, Haiou Li, Zhongsong Liu, Shitou Xia. Cloning of Brassica napus EXA1 Gene and Its Regulation on Plant Disease Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| [3] | Zhenmei He,Dongming Li,Yanhua Qi. Advances in Biofunctions of the ABCB Subfamily in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 688-698. |
| [4] | Min Song,Yao Zhang,Liying Wang,Xiangyong Peng. Genome-wide Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Zinc Finger Homeodomain Family Genes in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 699-710. |
| [5] | Gao Huhu, Zhang Yunxiao, Hu Shengwu, Guo Yuan. Genome-wide Survey and Phylogenetic Analysis of MADS-box Gene Family in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(6): 699-712. |
| [6] | Jia Ledong, Li Shimeng, Xu Daixiang, Qu Cunmin, Li Jiana, Wang Rui. Bioinformatics Analysis of BnMYB80 Genes in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(5): 620-630. |
| [7] | Yuying Qi, Yanli Zhan, Cuibo Wang, Fadi Chen, Jiafu Jiang. Mechanism of AtCPL1 in Regulating Flowering of Arabidopsis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(1): 9-15. |
| [8] | Yang Lu, Hong Long. The Effect of Leaf Number-altered Mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(3): 331-336. |
| [9] | YANG Chun, TAN Tai-Long, YU Jia-Ling, LIAO Qiong, ZHANG Xiao-Long, ZHANG Zhen-Hua, SONG Hai-Xing, GUAN Chun-Yun. Effects of atmospheric CO2 enrichment on phloem sap composition and root nitrogen accumulation in oilseed rape [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2014, 38(7): 776-784. |
| [10] | MAI Bo-Ru, ZHENG You-Fei, WU Rong-Jun, LIANG Jun, LIU Xia. Effects of simulated sulfur-rich, nitric-rich and mixed acid rain on the physiology, growth and yield of rape (Brassica napus) [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2010, 34(4): 427-437. |
| [11] | Lichuan Dai, Minglong Zhang, Jiye Liu, Xiaobai Li, Hairui Cui. Genetic diversity in Chinese rapeseed (Brassica napus) cultivars based on EST-SSR markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(5): 482-489. |
| [12] | JU Chang-Hua, TIAN Yong-Chao, ZHU Yan, YAO Xia, CAO Wei-Xing. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN DERIVATIVE SPECTRA AND PHOTOSYNTHETIC ORGAN AREA IN RAPESEED (BRASSICA NAPUS) [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2008, 32(3): 664-672. |
| [13] | Wu Ningfeng, Li Rugang, Wu Xiaoming, Zhu Li, Fan Yunliu, Qian Xiuzhen, . RAPD molecular markers and genetic diversity among 40 cultivars of Brassica napus in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 1997, 05(4): 246-250. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||