

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2016, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 130-143.DOI: 10.11983/CBB14216
Zhen Liu, Xia Liu, Jianzhong Liu*
Received:2014-12-25
Accepted:2015-03-30
Online:2016-01-01
Published:2016-02-01
Contact:
Liu Jianzhong
About author:? These authors contributed equally to this paper
Zhen Liu, Xia Liu, Jianzhong Liu. The Roles of Protein S-nitrosylation in Plant Cell Death and Disease Resistance[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(1): 130-143.
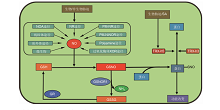
Figure 1 The homeostasis of cellular S-nitrosylation level in plantsThe level of S-nitrosylation in plant cells is determined by balance between the production of NO and the capacity of de-nitrosylation. There are multiple routes for NO production in plants such as NOA1-dependent pathway, NR pathway, plasma-membrane NR/NiNOR pathway, mitochondrial pathway, polyamines pathway, peroxisome (XOR) pathway and apoplast pathway. In addition, micro-organisms also contribute to the NO accumulation in plants (Crawford and Guo, 2005; Yu et al., 2014). Both biotic and abiotic stresses can induce the production of NO. Under stress conditions, NO level is increased in plant cells and as a results, the GSNO is formed in the presence of GSH; GSNO is a major donor of S-nitrosylation and S-nitrosylation is mediated by GSNO rather than by NO directly; NO moiety is transferred from GSNO to proteins in trans and thus the protein functions are altered by this modification (Liu et al., 2001; Feechan et al., 2005). GSNOR1 and thioredoxins (TRX) are two key enzymes involved in de-nitrosylation. Whereas GSNOR1 achieves the protein de-nitrosylation indirectly through reducing cellular level of GSNO, TRX (TRX-h3 and TRX-h5) catalyzes de-nitrosylation directly (Tada et al., 2008).
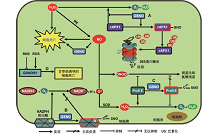
Figure 2 Regulation of cell death by S-nitrosylation in plants(A) NO promotes cell death through increasing the accumulation of H2O2 excessively by inhibiting H2O2 detoxifying enzymes. cAPX is a target of S-nitrosylation and its enzyme activity is severely inhibited by S-nitrosylation. In addition, S-nitrosylation of cAPX results in its ubiquitination and degradation by proteasome and thus leads to the cell death by over-accumulation of H2O2 (de Pinto et al., 2013). (B) NO can feedback inhibit H2O2 production through S-nitrosylation of Cys890 of AtRBOHD, a subunit of NADPH oxidase on the plasmamembrane, and as a result, excessive accumulation of H2O2 is relieved and cell death is alleviated (Yun et al., 2011). (C) NO inhibits H2O2 reduction and ONOO- detoxification of PrxII E through S-nitrosylation at Cys121. ONOO- can irreversibly alter protein functions through nitration. PrxII E is an enzyme that can prevent proteins from nitration (Romero-Puertas et al., 2007). (D) GSNOR1 functions as a positive regulator that participates in the cell death induced by paraquat. Application of herbicide paraquat can kill the wild type Arabidopsis Col-0 but not par2-1, a missense mutant of GSNOR1. ROS has an effect in increasing the level of GSNOR1, whereas RSN has the opposite effect. GSNOR1 participates paraquat-induced cell death downstream of ROS (Chen et al., 2009).
| 1 | 汪达丽, 张双双, 刘建中 (2014). 蛋白质亚硝基化检测和鉴定方法的研究进展. 植物生理学报 50, 1079-1088. |
| 2 | 王鹏程, 杜艳艳, 宋纯鹏 (2009). 植物细胞一氧化氮信号转导研究进展. 植物学报 44, 517-525. |
| 3 | 姚涛, 白素兰, 李苗苗, 张耀川, 何奕昆 (2011). DELLA蛋白参与拟南芥幼苗对一氧化氮逆境的抵抗. 植物学报 46, 481-488. |
| 4 | Astier J, Besson-Bard A, Lamotte O, Bertoldo J, Bo- urque S, Terenzi H, Wendehenne D (2012). Nitric oxide inhibits the ATPase activity of the chaperone-like AAA+ ATPase CDC48, a target for S-nitrosylation in cryptogein signaling in tobacco cells.Biochem J 447, 249-260. |
| 5 | Baek GH, Cheng H, Choe V, Bao X, Shao J, Luo S, Rao H (2013). Cdc48: a swiss army knife of cell biology.J Amino Acids 2013, 183421. |
| 6 | Begara-Morales JC, Sánchez-Calvo B, Chaki M, Valde- rrama R, Mata-Pérez C, López-Jaramillo J, Padilla MN, Carreras A, Corpas FJ, Barroso JB (2014). Dual regulation of cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase (APX) by tyrosine nitration and S-nitrosylation.J Exp Bot 65, 527-538. |
| 7 | Belenghi B, Romero-Puertas MC, Vercammen D, Brack- enier A, Inzé D, Delledonne M, Van Breusegem F (2007). Metacaspase activity of Arabidopsis thaliana is regulated by S-nitrosylation of a critical cysteine residue.J Biol Chem 282, 1352-1358. |
| 8 | Benhar M, Forrester MT, Hess DT, Stamler JS (2008). Regulated protein denitrosylation by cytosolic and mito- chondrial thioredoxins.Science 320, 1050-1054. |
| 9 | Bonfoco E, Krainc D, Ankarcrona M, Nicotera P, Lipton SA (1995). Apoptosis and necrosis: two distinct events induced, respectively, by mild and intense insults with N-methyl-D-aspartate or nitric oxide/superoxide in cortical cell cultures.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92, 7162-7166. |
| 10 | Chen R, Sun S, Wang C, Li Y, Liang Y, An F, Li C, Dong H, Yang X, Zhang J, Zuo J (2009). The Arabidopsis PARAQUAT RESISTANT2 gene encodes an S-nitro- soglutathione reductase that is a key regulator of cell death.Cell Res 19, 1377-1387. |
| 11 | Crawford NM, Guo FQ (2005). New insights into nitric oxide metabolism and regulatory functions.Trends Plant Sci 10, 195-200. |
| 12 | de Pinto MC, Locato V, Sgobba A, Romero-Puertas Mdel C, Gadaleta C, Delledonne M, De Gara L (2013). S- nitrosylation of ascorbate peroxidase is part of pro- grammed cell death signaling in tobacco Bright Yellow-2 cells.Plant Physiol 163, 1766-1775. |
| 13 | Delledonne M, Xia Y, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1998). Nitric oxide functions as a signal in plant disease resistance.Nature 394, 585-588. |
| 14 | Durner J, Wendehenne D, Klessig DF (1998). Defense gene induction in tobacco by nitric oxide, cyclic GMP, and cyclic ADP-ribose.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 10328-10333. |
| 15 | Elsasser S, Finley D (2005). Delivery of ubiquitinated sub- strates to protein-unfolding machines.Nat Cell Biol 7, 742-749. |
| 16 | Feechan A, Kwon E, Yun BW, Wang Y, Pallas JA, Loake GJ (2005). A central role for S-nitrosothiols in plant dis- ease resistance.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 8054-8059. |
| 17 | Feng X, Sun T, Bei Y, Ding S, Zheng W, Lu Y, Shen P (2013). S-nitrosylation of ERK inhibits ERK phosphoryla- tion and induces apoptosis.Sci Rep 3, 1814. |
| 18 | Groß F, Durner J, Gaupels F (2013). Nitric oxide, antioxidants and prooxidants in plant defence responses.Front Plant Sci 4, 419. |
| 19 | Gupta KJ (2011). Protein S-nitrosylation in plants: photorespiratory metabolism and NO signaling. Sci Signal 4, jc1. |
| 20 | Hara MR, Agrawal N, Kim SF, Cascio MB, Fujimuro M, Ozeki Y, Takahashi M, Cheah JH, Tankou SK, Hester LD, Ferris CD, Hayward SD, Snyder SH, Sawa A (2005). S-nitrosylated GAPDH initiates apoptotic cell de- ath by nuclear translocation following Siah1 binding.Nat Cell Biol 7, 665-674. |
| 21 | He Y, Tang RH, Hao Y, Stevens RD, Cook CW, Ahn SM, Jing L, Yang Z, Chen L, Guo F, Fiorani F, Jackson RB, Crawford NM, Pei ZM (2004). Nitric oxide represses the Arabidopsis floral transition.Science 305, 1968-1971. |
| 22 | Hess DT, Stamler JS (2012). Regulation by S-nitrosylation of protein post-translational modification.J Biol Chem 287, 4411-4418. |
| 23 | Kim SM, Bae C, Oh SK, Choi D (2013). A pepper (Capsicum annuum L) metacaspase 9 (Camc9) plays a role in pathogen-induced cell death in plants.Mol Plant Pathol 14, 557-566. |
| 24 | Klessig DF, Durner J, Noad R, Navarre DA, Wendehenne D, Kumar D, Zhou JM, Shah J, Zhang S, Kachroo P, Trifa Y, Pontier D, Lam E, Silva H (2000). Nitric oxide and salicylic acid signaling in plant defense.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 8849-8855. |
| 25 | Lamattina L, Garcia-Mata C, Graziano M, Pagnussat G (2003). Nitric oxide: the versatility of an extensive signal molecule.Annu Rev Plant Biol 54, 109-136. |
| 26 | Lee TY, Chen YJ, Lu CT, Ching WC, Teng YC, Huang HD, Chen YJ (2012). dbSNO: a database of cysteine S-nitro- sylation.Bioinformatics 28, 2293-2295. |
| 27 | Leitner M, Vandelle E, Gaupels F, Bellin D, Delledonne M (2009). NO signals in the haze: nitric oxide signaling in plant defence.Curr Opin Plant Biol 12, 451-458. |
| 28 | Li H, Wan A, Xu G, Ye D (2013). Small changes huge im- pact: the role of thioredoxin 1 in the regulation of apopto- sis by S-nitrosylation.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 45, 153-161. |
| 29 | Lin A, Wang Y, Tang J, Xue P, Li C, Liu L, Hu B, Yang F, Loake GJ, Chu C (2012). Nitric oxide and protein S- nitrosylation are integral to hydrogen peroxide-induced leaf cell death in rice.Plant Physiol 158, 451-464. |
| 30 | Lindermayr C, Durner J (2009). S-nitrosylation in plants: pattern and function.J Proteomics 73, 1-9. |
| 31 | Lindermayr C, Saalbach G, Bahnweg G, Durner J (2006). Differential inhibition of Arabidopsis methionine adeno- syltransferases by protein S-nitrosylation.J Biol Chem 281, 4285-4291. |
| 32 | Lindermayr C, Saalbach G, Durner J (2005). Proteomic identification of S-nitrosylated proteins in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 137, 921-930. |
| 33 | Lindermayr C, Sell S, Müller B, Leister D, Durner J (2010). Redox regulation of the NPR1-TGA1 system of Arabidopsis thaliana by nitric oxide.Plant Cell 22, 2894-2907. |
| 34 | Lipton SA (1993). Prospects for clinically tolerated NMDA antagonists: open-channel blockers and alternative redox states of nitric oxide.Trends Neurosci 16, 527-532. |
| 35 | Liu L, Hausladen A, Zeng M, Que L, Heitman J, Stamler JS (2001). A metabolic enzyme for S-nitrosothiol con- served from bacteria to humans.Nature 410, 490-494. |
| 36 | Liu L, Yan Y, Zeng M, Zhang J, Hanes MA, Ahearn G, McMahon TJ, Dickfeld T, Marshall HE, Que LG, Stamler JS (2004). Essential roles of S-nitrosothiols in vascular homeostasis and endotoxic shock.Cell 116, 617-628. |
| 37 | Mannick JB (2007). Regulation of apoptosis by protein S-nitrosylation.Amino Acids 32, 523-526. |
| 38 | Mannick JB, Hausladen A, Liu L, Hess DT, Zeng M, Miao QX, Kane LS, Gow AJ, Stamler JS (1999). Fas-induced caspase denitrosylation.Science 284, 651-654. |
| 39 | Marshall HE, Hess DT, Stamler JS (2004). S-nitrosylation: physiological regulation of NF-kappaB.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 8841-8842. |
| 40 | Matthews JR, Botting CH, Panico M, Morris HR, Hay RT (1996). Inhibition of NF-kb DNA binding by nitric oxide.Nucleic Acids Res 24, 2236-2242. |
| 41 | Meyer H, Bug M, Bremer S (2012). Emerging functions of the VCP/p97 AAA-ATPase in the ubiquitin system.Nat Cell Biol 14, 117-123. |
| 42 | Michelet L, Zaffagnini M, Massot V, Keryer E, Vanacker H, Miginiac-Maslow M, Issakidis-Bourguet E, Lemaire SD (2006). Thioredoxins glutaredoxins and glutathionyla- tion: new crosstalks to explore.Photosynth Res 89, 225-245. |
| 43 | Mou Z, Fan W, Dong X (2003). Inducers of plant systemic acquired resistance regulate NPR1 function through redox changes.Cell 113, 935-944. |
| 44 | Nakamura T, Wang L, Wong CC, Scott FL, Eckelman BP, Han X, Tzitzilonis C, Meng F, Gu Z, Holland EA, Clemente AT, Okamoto S, Salvesen GS, Riek R, Yates III JR, Lipton SA (2010). Transnitrosylation of XIAP regulates caspase-dependent neuronal cell death.Mol Cell 39, 184-195. |
| 45 | Neill SJ, Desikan R, Clarke A, Hancock JT (2002). Nitric oxide is a novel component of abscisic acid signaling in stomatal guard cells.Plant Physiol 128, 13-16. |
| 46 | Niehl A, Amari K, Gereige D, Brandner K, Mély Y, Hein- lein M (2012). Control of tobacco mosaic virus movement protein fate by CELL-DIVISION-CYCLE protein48.Plant Physiol 160, 2093-2108. |
| 47 | Ortega-Galisteo AP, Rodríguez-Serrano M, Pazmiño DM, Gupta DK, Sandalio LM, Romero-Puertas MC (2012). S-nitrosylated proteins in pea (Pisum sativum L.) leaf per- oxisomes: changes under abiotic stress.J Exp Bot 63, 2089-2103. |
| 48 | Reynaert NL, Ckless K, Korn SH, Vos N, Guala AS, Wouters EF, van der Vliet A, Janssen-Heininger YM (2004). Nitric oxide represses inhibitory kappaB kinase through S-nitrosylation.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 8945-8950. |
| 49 | Romero-Puertas MC, Campostrini N, Mattè A, Righetti PG, Perazzolli M, Zolla L, Roepstorff P, Delledonne M (2008). Proteomic analysis of S-nitrosylated proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana undergoing hypersensitive response.Proteomics 8, 1459-1469. |
| 50 | Romero-Puertas MC, Laxa M, Matte A, Zaninotto F, Finkemeier I, Jones AM, Perazzolli M, Vandelle E, Dietz KJ, Delledonne M (2007). S-nitrosylation of peroxiredoxin II promotes peroxynitrite-mediated tyrosine nitration.Plant Cell 19, 4120-4130. |
| 51 | Romero-Puertas MC, Rodríguez-Serrano M, Sandalio LM (2013). Protein S-nitrosylation in plants under abiotic stress: an overview.Front Plant Sci 4, 373. |
| 52 | Rustérucci C, Espunya MC, Díaz M, Chabannes M, Martínez MC (2007). S-nitrosoglutathione reductase affo- rds protection against pathogens in Arabidopsis, both locally and systemically.Plant Physiol 143, 1282-1292. |
| 53 | Ryals JA, Neuenschwander UH, Willits MG, Molina A, Steiner HY, Hunt MD (1996). Systemic acquired resistance.Plant Cell 8, 1809-1819. |
| 54 | Sell S, Lindermayr C, Durner J (2008). Identification of S-nitrosylated proteins in plants.Methods Enzymol 440, 283-293. |
| 55 | Sen N, Hara MR, Kornberg MD, Cascio MB, Bae BI, Sha- hani N, Thomas B, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, Snyder SH, Sawa A (2008). Nitric oxide-induced nuclear GAPDH activates p300/CBP and mediates apoptosis.Nat Cell Biol 10, 866-873. |
| 56 | Slaymaker DH, Navarre DA, Clark D, del Pozo O, Martin GB, Klessig DF (2002). The tobacco salicylic acid-bind- ing protein 3 (SABP3) is the chloroplast carbonic anhydrase, which exhibits antioxidant activity and plays a role in the hypersensitive defense response.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 11640-11645. |
| 57 | Stamler JS (1994). Redox signaling: nitrosylation and related target interactions of nitric oxide.Cell 78, 931-936. |
| 58 | Stamler JS, Toone EJ, Lipton SA, Sucher NJ (1997). (S)NO signals: translocation, regulation, and a consensus motif.Neuron 18, 691-696. |
| 59 | Tada Y, Spoel SH, Pajerowska-Mukhtar K, Mou Z, Song J, Wang C, Zuo J, Dong X (2008). Plant immunity requi- res conformational charges of NPR1 via S-nitrosylation and thioredoxins.Science 321, 952-956. |
| 60 | Trapet P, Kulik A, Lamotte O, Jeandroz S, Bourque S, Nicolas-Francès V, Rosnoblet C, Besson-Bard A, Wendehenne D (2014). NO signaling in plant immunity: a tale of messengers.Phytochemistry 112, 72-79. |
| 61 | Trujillo M, Shirasu K (2010). Ubiquitination in plant immu- nity.Curr Opin Plant Biol 13, 402-408. |
| 62 | Vannini C, Marsoni M, Cantara C, De Pinto MC, Locato V, De Gara L, Bracale M (2012). The soluble proteome of tobacco Bright Yellow-2 cells undergoing H2O2-induced programmed cell death.J Exp Bot 63, 3137-3155. |
| 63 | Wang Y, Chen C, Loake GJ, Chu C (2010). Nitric oxide: promoter or suppressor of programmed cell death.Protein Cell 1, 133-142. |
| 64 | Wang YQ, Feechan A, Yun BW, Shafiei R, Hofmann A, Taylor P, Xue P, Yang FQ, Xie ZS, Pallas JA, Chu CC, Loake GJ (2009). S-nitrosylation of AtSABP3 antagoni- zes the expression of plant immunity.J Biol Chem 284, 2131-2137. |
| 65 | Wawer I, Bucholc M, Astier J, Anielska-Mazur A, Dahan J, Kulik A, Wysłouch-Cieszynska A, Zareba-Kozioł M, Krzywinska E, Dadlez M, Dobrowolska G, Wendehe- nne D (2010). Regulation of Nicotiana tabacum osmotic stress-activated protein kinase and its celluar partner GAPDH by nitric oxide in response to salinity.Biochem J 429, 73-83. |
| 66 | Wendehenne D, Durner J, Klessig DF (2004). Nitric oxide: a new player in plant signaling and defence responses.Curr Opin Plant Biol 7, 449-455. |
| 67 | Wildermuth MC, Dewdney J, Wu G, Ausubel FM (2001). Isochorismate synthase is required to synthesize salicylic acid for plant defence.Nature 414, 562-565. |
| 68 | Yan S, Dong X (2014). Perception of the plant immune signal salicylic acid.Curr Opin Plant Biol 20, 64-68. |
| 69 | Yu M, Lamattina L, Spoel SH, Loake GJ (2014). Nitric oxide function in plant biology: a redox cue in deconvolu- tion.New Phytol 202, 1142-1156. |
| 70 | Yu M, Yun BW, Spoel SH, Loake GJ (2012). A sleigh ride through the SNO: regulation of plant immune function by protein S-nitrosylation.Curr Opin Plant Biol 15, 424-430. |
| 71 | Yun BW, Feechan A, Yin M, Saidi NB, Le Bihan T, Yu M, Moore JW, Kang JG, Kwon E, Spoel SH, Pallas JA, Loake GJ (2011). S-nitrosylation of NADPH oxidase regulates cell death in plant immunity.Nature 478, 264-268. |
| 72 | Zaffagnini M, Fermani S, Costa A, Lemaire SD, Trost P (2013). Plant cytoplasmic GAPDH: redox post-transla- tional modifications and moonlighting properties.Front Plant Sci 4, 450. |
| 73 | Zeidler D, Zähringer U, Gerber I, Dubery I, Hartung T, Bors W, Hutzler P, Durner J (2004). Innate immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana: lipopolysaccharides activate nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and induce defense genes.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 15811-15816. |
| 74 | Zhang X, Huang B, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Guo X, Qiao X, Chen C (2012). SNObase, a database for S-nitrosation modification.Protein Cell 3, 929-933. |
| [1] | Nan Wu, Lei Qin, Kan Cui, Haiou Li, Zhongsong Liu, Shitou Xia. Cloning of Brassica napus EXA1 Gene and Its Regulation on Plant Disease Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| [2] | Tiantian Zhi, Zhou Zhou, Chengyun Han, Chunmei Ren. PAD4 Mutation Accelerating Programmed Cell Death in Arabidopsis thaliana Tyrosine Degradation Deficient Mutant sscd1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 288-298. |
| [3] | Jian-Min Zhou. A Ca2+-ROS Signaling Axis in Rice Provides Clues to Rice-pathogen Coevolution and Crop Improvements [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(5): 513-515. |
| [4] | Tiantian Shi, Ying Gao, Huan Wang, Jun Liu. Nucleo-cytoplasmic Transport and Transport Receptors in Plant Disease Resistance Defense Response [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 480-487. |
| [5] | Weiqin Zhang, Hang Zou, Nina Zhang, Xueyuan Lin, Juan Chen. Influence Mechanisms of Nitric Oxide on Nodulation and Nitrogen Fixation in Legumes [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 623-633. |
| [6] | Jian-Min Zhou. Fighting Fusarium Head Blight in Wheat—a Remedy from Afar [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(2): 123-125. |
| [7] | Na Zhang,Xiuxia Liu,Xuesen Chen,Shujing Wu. Identifying Genes Responsive to Jasmonates in Apple Based on Transcriptome Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 733-743. |
| [8] | Lichao Chen,Ni Zhan,Yansha Li,Jian Feng,Jianru Zuo. Detection and Analysis of Protein S-nitrosylation in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(4): 497-502. |
| [9] | Tingting Shan,Xiaomei Chen,Shunxing Guo,Lixia Tian,Lin Yan,Xin Wang. Advances in Molecular Regulation of Sphingolipids in Plant-fungus Interactions [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(3): 396-404. |
| [10] | He Guangming, Deng Xingwang. Death Signal Transduction: Chloroplast-to-Mitochondrion Communication Regulates Programmed Cell Death in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(4): 441-444. |
| [11] | Zhao Xijuan, Qian Lichao, Liu Yule. Chinese Scientists Made Breakthrough Progresses in Plant Programmed Cell Death [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(4): 447-450. |
| [12] | Zhang Xian-sheng. Chinese Scientists Have Made a Great Breakthrough in the Mechanism of Programmed Cell Death [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(4): 445-446. |
| [13] | Yan Jia, Liu Yaqiong, Hou Suiwen. Recent Advances in Disease Resistance Proteins in Plant Immunity [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(2): 250-263. |
| [14] | Wang Yu, He Yikun. The Molecular Mechanism of Nitric Oxide-mediated S-nitrosylation Coordinating with Protein Methylation During Abiotic Stress Responses [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(6): 681-684. |
| [15] | Lingling Zhang, Dan Wu, Zijie Zhao, Liqun Zhao. Research Progress in Nitric Oxide Signaling Molecule in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(3): 337-345. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||