

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 699-710.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19055
收稿日期:2019-03-25
接受日期:2019-07-26
出版日期:2019-11-01
发布日期:2020-07-09
通讯作者:
宋敏
基金资助:
Min Song( ),Yao Zhang,Liying Wang,Xiangyong Peng
),Yao Zhang,Liying Wang,Xiangyong Peng
Received:2019-03-25
Accepted:2019-07-26
Online:2019-11-01
Published:2020-07-09
Contact:
Min Song
摘要: ZF-HD是一类植物特有的转录因子, 在植物生长发育及胁迫响应过程中发挥重要作用。利用生物信息学方法, 在甘蓝型油菜(Brassica napus)基因组中鉴定到62个ZF-HD基因, 其中83.9%的基因缺乏内含子, 93.5%的BnZF-HD等电点大于7, 预测定位于细胞核的蛋白大多由100个以上氨基酸组成。根据进化关系可将其分为6个亚群, 在每个亚群中, 甘蓝(B. oleracea)和白菜(B. rapa)的ZF-HD基因数量相等或近似相等, 而甘蓝型油菜的ZF-HD基因数量接近或等同于甘蓝和白菜的ZF-HD基因数量之和。同一亚群的motif数量和类型高度相似。共线性分析结果显示, 全基因组三倍体化使ZF-HD基因在二倍体祖先得到扩张, 而异源多倍体化又进一步使甘蓝型油菜ZF-HD基因家族扩张。Ka/Ks值说明大多数ZF-HD基因在进化过程中受到了纯化选择。所有BnZF-HD基因都具有光响应元件, 2/3的基因具有MeJA、ABA和厌氧诱导顺式作用元件, 推测这些基因可能参与相关生物学过程。研究结果为进一步挖掘该家族基因的生物学功能奠定基础, 同时为揭示多基因家族在异源多倍体中的进化式样提供借鉴。
宋敏,张瑶,王丽莹,彭向永. 甘蓝型油菜ZF-HD基因家族的鉴定与系统进化分析. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 699-710.
Min Song,Yao Zhang,Liying Wang,Xiangyong Peng. Genome-wide Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Zinc Finger Homeodomain Family Genes in Brassica napus. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 699-710.
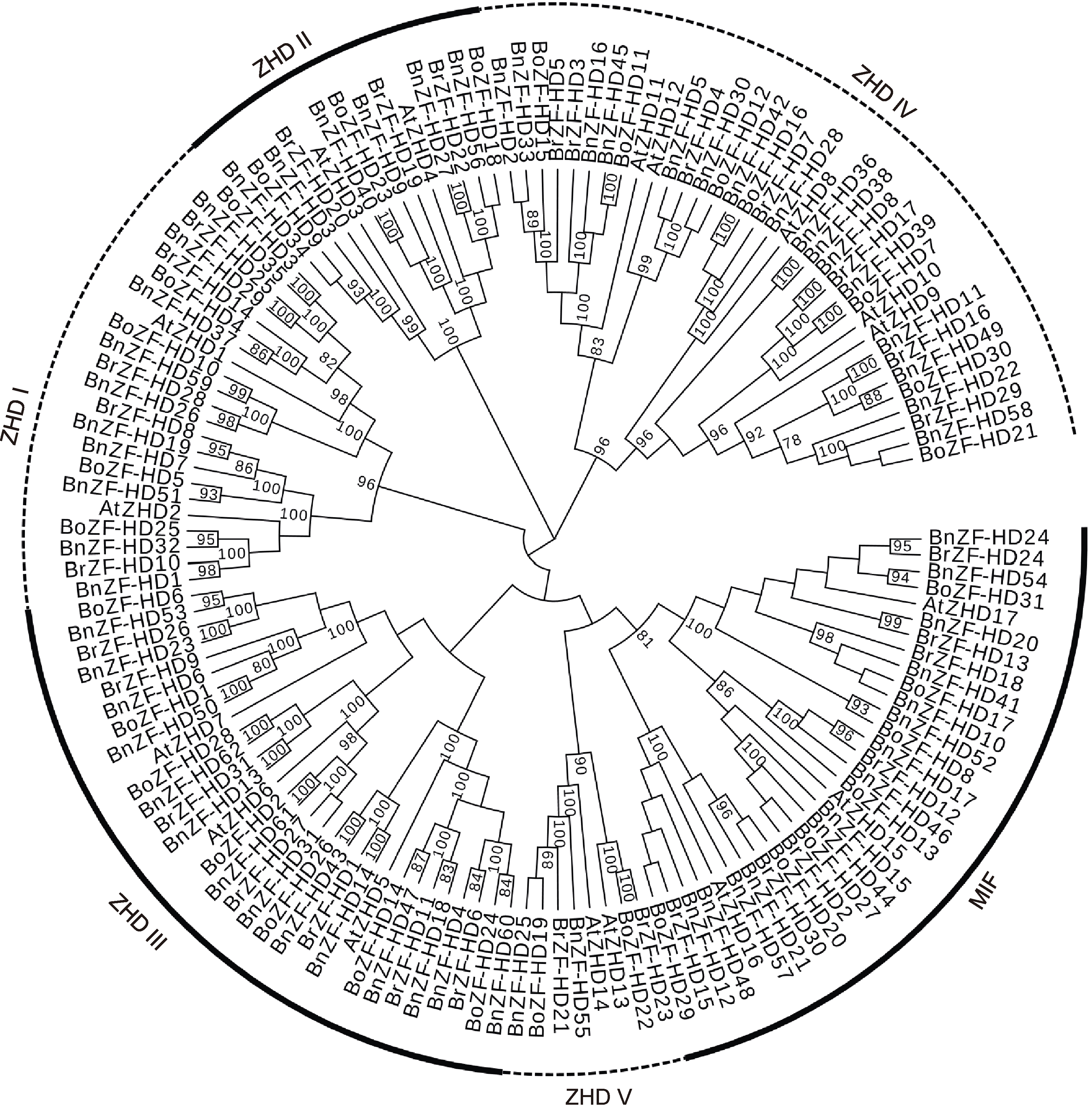
图1 甘蓝型油菜、拟南芥、白菜和甘蓝ZF-HD蛋白的系统发生树 利用MEGA 7.0软件构建邻接树, bootstrap值设为1 000。
Figure 1 Phylogenetic analysis of Brassica napus, Arabidopsis thaliana, B. rapa and B. oleracea ZF-HD proteins This phylogenetic unrooted tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining (NJ) method with MEGA 7.0, with 1 000 bootstrap replicates.

图2 甘蓝型油菜(A, B)、白菜(C)和甘蓝(D) ZF-HD基因在染色体上的分布 基因名称后标注该基因所属亚群。
Figure 2 Chromosomal location of ZF-HD genes from Brassica napus (A, B), B. rapa (C) and B. oleracea (D) The gene name was followed by its subgroup.
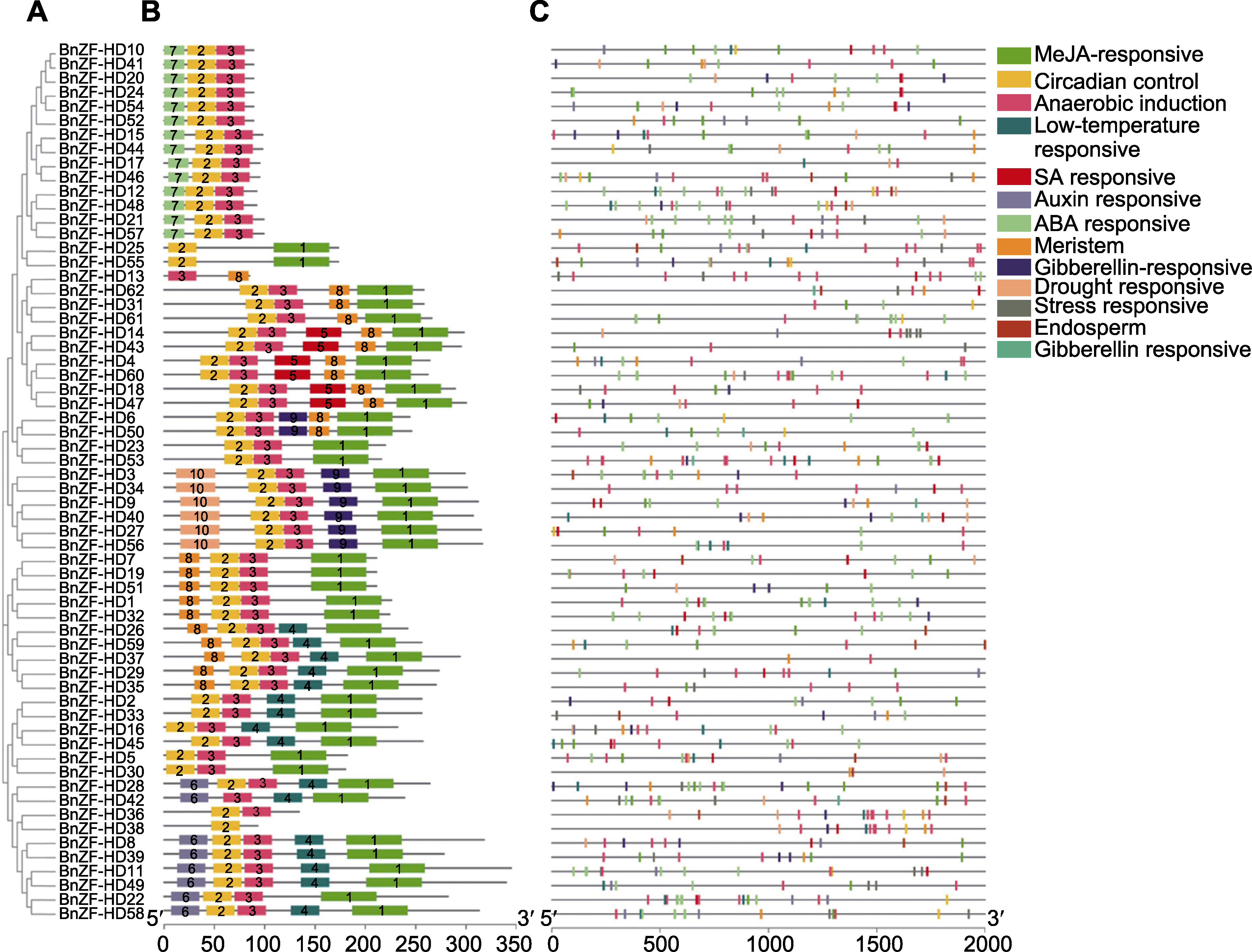
图3 甘蓝型油菜ZF-HD蛋白家族的聚类(A)、motif结构(B)和顺式作用元件(C)
Figure 3 Phylogenetic analysis (A), motif structure (B) and cis-acting element (C) of different ZF-HD protein families in Brassica napus
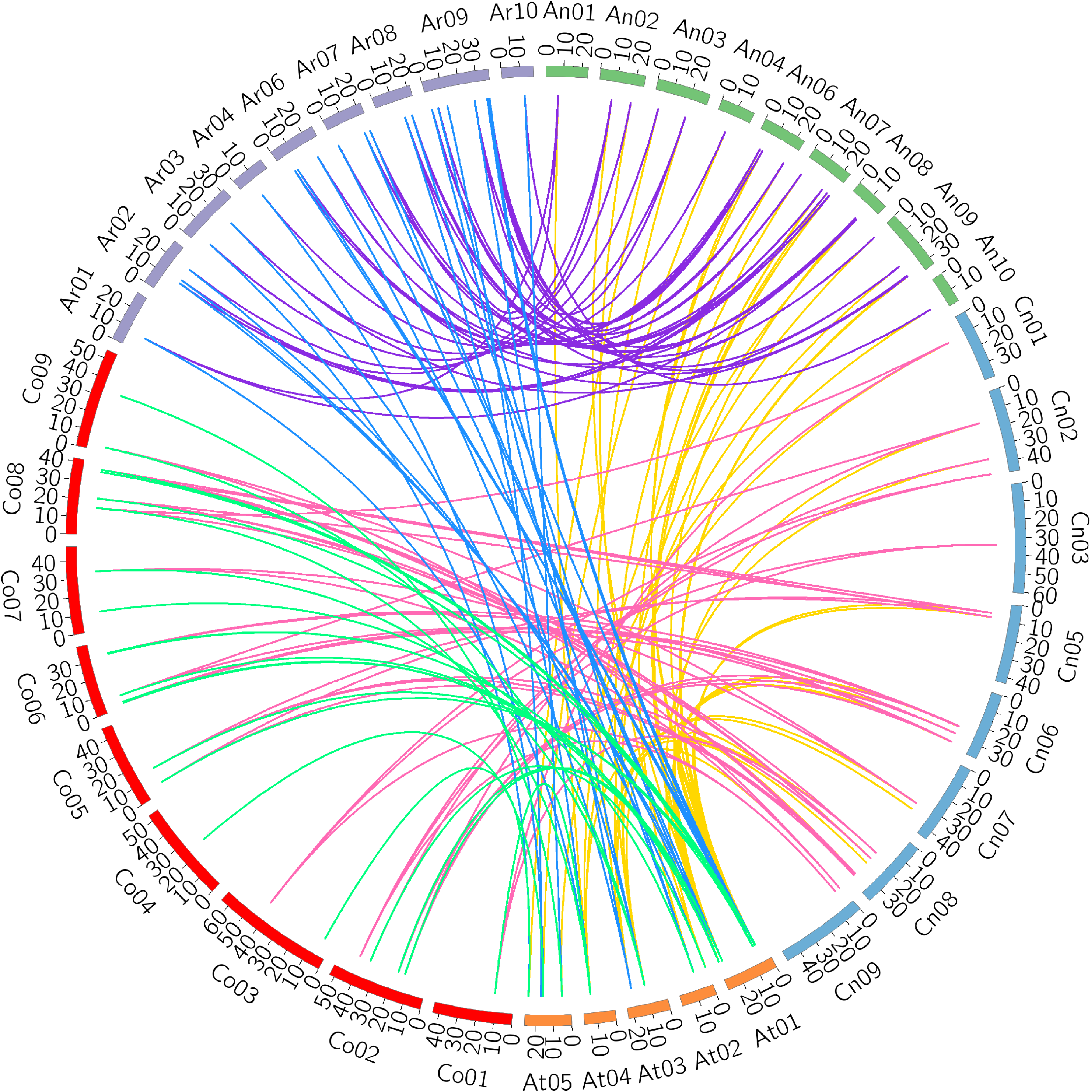
图4 甘蓝型油菜、白菜、甘蓝与拟南芥ZF-HD基因的染色体共线性关系
Figure 4 Collinear relationship of ZF-HD genes among Brassica napus, B. rapa, B. oleracea, and Arabidopsis thaliana chromosomes
| [1] | 高虎虎, 张云霄, 胡胜武, 郭媛 ( 2017). 甘蓝型油菜MADS- box基因家族的鉴定与系统进化分析. 植物学报 52, 699-712. |
| [2] | Abdullah M, Cheng X, Cao YP, Su XQ, Manzoor MA, Gao JS, Cai YP, Lin Y ( 2018). Zinc finger-homeodomain transcriptional factors (ZHDs) in upland cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum ): genome-wide identification and expression analysis in fiber development. Front Genet 9, 357. |
| [3] | Ariel FD, Manavella PA, Dezar CA, Chan RL ( 2007). The true story of the HD-Zip family. Trends Plant Sci 12, 419-426. |
| [4] | Bailey TL, Johnson J, Grant CE, Noble WS ( 2015). The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res 43, W39-W49. |
| [5] | Bateman A, Birney E, Cerruti L, Durbin R, Etwiller L, Eddy SR, Griffiths-Jones S, Howe KL, Marshall M, Sonnhammer ELL ( 2002). The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 30, 276-280. |
| [6] | Bhattacharjee A, Ghangal R, Garg R, Jain M ( 2015). Genome-wide analysis of homeobox gene family in legumes: identification, gene duplication and expression profiling. PLoS One 10, e0119198. |
| [7] | Bhattacharjee A, Jain M (2013). omeobox genes as potential candidates for crop improvement under abiotic stress. In: Tuteja N, Singh Gill S, eds. Plant Acclimation to Environmental Stress. New York: Springer. pp. 163-176. |
| [8] | Chalhoub B, Denoeud F, Liu SY, Parkin IAP, Tang HB, Wang XY, Chiquet J, Belcram H, Tong CB, Samans B, Corréa M, Da Silva C, Just J, Falentin C, Koh CS, Le Clainche I, Bernard M, Bento P, Noel B, Labadie K, Alberti A, Charles M, Arnaud D, Guo H, Daviaud C, Alamery S, Jabbari K, Zhao MX, Edger PP, Chelaifa H, Tack D, Lassalle G, Mestiri I, Schnel N, Le Paslier MC, Fan GY, Renault V, Bayer PE, Golicz AA, Manoli S, Lee TH, Thi VHD, Chalabi S, Hu Q, Fan CC, Tollenaere R, Lu YH, Battail C, Shen JX, Sidebottom CHD, Wang XF, Canaguier A, Chauveau A, Bérard A, Deniot G, Guan M, Liu ZS, Sun FM, Lim YP, Lyons E, Town CD, Bancroft I, Wang XW, Meng JL, Ma JX, Pires JC, King GJ, Brunel D, Delourme R, Renard M, Aury JM, Adams KL, Batley J, Snowdon RJ, Tost J, Edwards D, Zhou YM, Hua W, Sharpe AG, Paterson AH, Guan CY, Wincker P ( 2014). Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 345, 950-953. |
| [9] | Chen CJ, Xia R, Chen H, He YH ( 2018). TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various HTS-data handling tools with a user-friendly interface. bioRxiv [2018-03-27]. . |
| [10] | Cheng F, Liu SY, Wu J, Fang L, Sun SL, Liu B, Li PX, Hua W, Wang XW ( 2011). BRAD, the genetics and genomics database for Brassica plants. BMC Plant Biol 11, 136. |
| [11] | Cheng F, Wu J, Fang L, Wang XW ( 2012). Syntenic gene analysis between Brassica rapa and other Brassicaceae species. Front Plant Sci 3, 198. |
| [12] | Deng X, Phillips J, Meijer AH, Salamini F, Bartels D ( 2002). Characterization of five novel dehydration-responsive homeodomain leucine zipper genes from the resurrection plant Craterostigma plantagineum. Plant Mol Biol 49, 601-610. |
| [13] | Finn RD, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Mistry J, Mitchell AL, Potter SC, Punta M, Qureshi M, Sangrador-Vegas A, Salazar GA, Tate J, Bateman A ( 2016). The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res 44, D279-D285. |
| [14] | He ZL, Zhang HK, Gao SH, Lercher MJ, Chen WH, Hu SN ( 2016). Evolview v2: an online visualization and management tool for customized and annotated phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res 44, W236-W241. |
| [15] | Hu B, Jin JP, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo JC, Gao G ( 2015). GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31, 1296-1297. |
| [16] | Hu W, DePamphilis CW, Ma H ( 2008). Phylogenetic analysis of the plant-specific Zinc finger-Homeobox and Mini zinc finger gene families. J Integr Plant Biol 50, 1031-1045. |
| [17] | Hu W, Ma H ( 2006). Characterization of a novel putative zinc finger gene MIF1: involvement in multiple hormonal regulation of Arabidopsis development. Plant J 45, 399-422. |
| [18] | Jain M, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP ( 2008). Genome-wide identification, classification, evolutionary expansion and expression analyses of homeobox genes in rice. FEBS J 275, 2845-2861. |
| [19] | Jin JP, Tian F, Yang DC, Meng YQ, Kong L, Luo JC, Gao G ( 2017a). PlantTFDB 4.0: toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 45, D1040-D1045. |
| [20] | Jin XL, Ren J, Nevo E, Yin XG, Sun DF, Peng JH ( 2017b). Divergent evolutionary patterns of NAC transcription factors are associated with diversification and gene duplications in angiosperm. Front Plant Sci 8, 1156. |
| [21] | Jørgensen JE, Grønlund M, Pallisgaard N, Larsen K, Marcker KA, Jensen EØ ( 1999). A new class of plant homeobox genes is expressed in specific regions of determinate symbiotic root nodules. Plant Mol Biol 40, 65-77. |
| [22] | Khadiza K, Nath UK, Robin AHK, Park JI, Lee DJ, Kim MB, Kim CK, Lim LB, Nou IS, Chung MY ( 2017). Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of zinc finger homeodomain ( ZHD ) family genes reveal likely roles in organ development and stress responses in tomato. BMC Genomics 18, 695. |
| [23] | Krishna SS, Majumdar I, Grishin NV ( 2003). SURVEY AND SUMMARY: structural classification of zinc fingers. Nucleic Acids Res 31, 532-550. |
| [24] | Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol İ, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ, Marra MA ( 2009). Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res 19, 1639-1645. |
| [25] | Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K ( 2016). MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33, 1870-1874. |
| [26] | Liu SY, Liu YM, Yang XH, Tong CB, Edwards D, Parkin IAP, Zhao MX, Ma JX, Yu JY, Huang SM, Wang XY, Wang JY, Lu K, Fang ZY, Bancroft I, Yang TJ, Hu Q, Wang XF, Yue Z, Li HJ, Yang LF, Wu J, Zhou Q, Wang WX, King GJ, Pires JC, Lu CX, Wu ZY, Sampath P, Wang Z, Guo H, Pan SK, Yang LM, Min JM, Zhang D, Jin DC, Li WS, Belcram H, Tu JX, Guan M, Qi CK, Du DZ, Li JN, Jiang LC, Batley J, Sharpe AG, Park BS, Ruperao P, Cheng F, Waminal NE, Huang Y, Dong CH, Wang L, Li JP, Hu ZY, Zhuang M, Huang Y, Huang JY, Shi JQ, Mei DS, Liu J, Lee TH, Wang JP, Jin HZ, Li ZY, Li X, Zhang JF, Xiao L, Zhou YM, Liu ZS, Liu XQ, Qin R, Tang X, Liu WB, Wang YP, Zhang YY, Lee J, Kim HH, Denoeud F, Xu X, Liang XM, Hua W, Wang XW, Wang J, Chalhoub B, Paterson AH ( 2014). The Brassica oleracea genome reveals the asymmetrical evolution of polyploid genomes. Nat Commun 5, 3930. |
| [27] | Mackay JP, Crossley M ( 1998). Zinc fingers are sticking together. Trends Biochem Sci 23, 1-4. |
| [28] | Mun JH, Kwon SJ, Yang TJ, Seol YJ, Jin M, Kim JA, Lim MH, Kim JS, Baek S, Choi BS, Yu HJ, Kim DS, Kim N, Lim KB, Lee SI, Hahn JH, Lim YP, Bancroft I, Park BS ( 2009). Genome-wide comparative analysis of the Brassica rapa gene space reveals genome shrinkage and differential loss of duplicated genes after whole genome triplication. Genome Biol 10, 211. |
| [29] | Nam J, Nei M ( 2005). Evolutionary change of the numbers of homeobox genes in bilateral animals. Mol Biol Evol 22, 2386-2394. |
| [30] | Nekrutenko A, Makova KD, Li WH ( 2002). The KA/KS ratio test for assessing the protein-coding potential of genomic regions: an empirical and simulation study. Genome Res 12, 198-202. |
| [31] | Park HC, Kim ML, Lee SM, Bahk JD, Yun DJ, Lim CO, Hong JC, Lee SY, Cho MJ, Chung WS ( 2007). Pathogen-induced binding of the soybean zinc finger homeodomain proteins GmZF-HD1 and GmZF-HD2 to two repeats of ATTA homeodomain binding site in the calmodulin isoform 4 (GmCaM4) promoter. Nucleic Acids Res 35, 3612-3623. |
| [32] | Schultz J, Milpetz F, Bork P, Ponting CP ( 1998). SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 5857-5864. |
| [33] | Takatsuji H ( 1999). Zinc-finger proteins: the classical zinc finger emerges in contemporary plant science. Plant Mol Biol 39, 1073-1078. |
| [34] | Tan QKG, Irish VF ( 2006). The Arabidopsis zinc finger-homeodomain genes encode proteins with unique biochemical properties that are coordinately expressed during floral development. Plant Physiol 140, 1095-1108. |
| [35] | Tran LSP, Nakashima K, Sakuma Y, Osakabe Y, Qin F, Simpson SD, Maruyama K, Fujita Y, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K ( 2007). Co-expression of the stress-inducible zinc finger homeodomain ZFHD1 and NAC transcription factors enhances expression of the ERD1 gene in Arabidopsis. Plant J 49, 46-63. |
| [36] | Walther D, Brunnemann R, Selbig J ( 2007). The regulatory code for transcriptional response diversity and its relation to genome structural properties in A. thaliana. PLoS Genet 3, e11. |
| [37] | Wang H, Yin XJ, Li XQ, Wang L, Zheng Y, Xu XZ, Zhang YC, Wang XP ( 2014). Genome-wide identification, evolution and expression analysis of the grape ( Vitis vinifera L.) zinc finger-homeodomain gene family. Int J Mol Sci 15, 5730-5748. |
| [38] | Wang W, Wu P, Li Y, Hou X ( 2016). Genome-wide analysis and expression patterns of ZF-HD transcription factors under different developmental tissues and abiotic stresses in Chinese cabbage. Mol Gen Genomics 291, 1451-1464. |
| [39] | Wang XW, Wang HZ, Wang J, Sun RF, Wu J, Liu SY, Bai YQ, Mun JH, Bancroft I, Cheng F, Huang SW, Li XX, Hua W, Wang JY, Wang XY, Freeling M, Pires JC, Paterson AH, Chalhoub B, Wang B, Hayward A, Sharpe AG, Park BS, Weisshaar B, Liu BH, Li B, Liu B, Tong CB, Song C, Duran C, Peng CF, Geng CY, Koh C, Lin CY, Edwards D, Mu D, Shen D, Soumpourou E, Li F, Fraser F, Conant G, Lassalle G, King GJ, Bonnema G, Tang HB, Wang HP, Belcram H, Zhou HL, Hirakawa H, Abe H, Guo H, Wang H, Jin HZ, Parkin IAP, Batley J, Kim JS, Just J, Li JW, Xu JH, Deng J, Kim JA, Li JP, Yu JY, Meng JL, Wang JP, Min JM, Poulain J, Wang J, Hatakeyama K, Wu K, Wang L, Fang L, Trick M, Links MG, Zhao MX, Jin MN, Ramchiary N, Drou N, Berkman PJ, Cai QL, Huang QF, Li RQ, Tabata S, Cheng SF, Zhang S, Zhang SJ, Huang SM, Sato S, Sun SL, Kwon SJ, Choi SR, Lee TH, Fan W, Zhao X, Tan X, Xu X, Wang Y, Qiu Y, Yin Y, Li YR, Du YC, Liao YC, Lim Y, Narusaka Y, Wang YP, Wang ZY, Li ZY, Wang ZW, Xiong ZY, Zhang ZH ( 2011). The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat Genet 43, 1035-1039. |
| [40] | Windhövel A, Hein I, Dabrowa R, Stockhaus J ( 2001). Characterization of a novel class of plant homeodomain proteins that bind to the C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene of Flaveria trinervia. Plant Mol Biol 45, 201-214. |
| [41] | Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K ( 2005). Organization of cis -acting regulatory elements in osmotic-and cold- stress-responsive promoters. Trends Plant Sci 10, 88-94. |
| [42] | Yang JH, Liu DY, Wang XW, Ji CM, Cheng F, Liu BN, Hu ZY, Chen S, Pental D, Ju YH, Yao P, Li XM, Xie K, Zhang JH, Wang JL, Liu F, Ma WW, Shopan J, Zheng HK, Mackenzie SA, Zhang MF ( 2016). The genome sequence of allopolyploid Brassica juncea and analysis of differential homoeolog gene expression influencing selection. Nat Genet 48, 1225-1232. |
| [1] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [2] | 张盈川, 吴晓明玉, 陶保龙, 陈丽, 鲁海琴, 赵伦, 文静, 易斌, 涂金星, 傅廷栋, 沈金雄. Bna-miR43介导甘蓝型油菜响应干旱胁迫[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 701-711. |
| [3] | 吴楠, 覃磊, 崔看, 李海鸥, 刘忠松, 夏石头. 甘蓝型油菜EXA1的克隆及其对植物抗病的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| [4] | 沈诗韵, 潘远飞, 陈丽茹, 土艳丽, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草原产地和入侵地种群的植物-土壤反馈差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22436-. |
| [5] | 席念勋, 张原野, 周淑荣. 群落生态学中的植物-土壤反馈研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(2): 170-182. |
| [6] | 戚海迪, 张定海, 单立山, 陈国鹏, 张勃. 昆虫病原真菌感染昆虫宿主的机制和宿主昆虫的防御策略研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23273-. |
| [7] | 俄广旭, 白天天, 朱振宇, 郭雪峰. 动物消化道微生物多样性与宿主协同进化关系的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23214-. |
| [8] | 邹金莲, 张志强. 性选择与性冲突理论在植物繁殖生态学中的应用与进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(9): 984-994. |
| [9] | 葛颂. 中国植物系统和进化生物学研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22385-. |
| [10] | 王芸芸, 郝占庆. 被子植物性系统的多样性、生态功能及分布规律[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22065-. |
| [11] | 薛成, 李波卡, 雷天宇, 山红艳, 孔宏智. 生物多样性起源与进化研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22460-. |
| [12] | 王少鹏, 罗明宇, 冯彦皓, 储诚进, 张大勇. 生物多样性理论最新进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22410-. |
| [13] | 邓铭先, 黄河燕, 沈诗韵, 吴纪华, 拉琼, 斯确多吉, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草在青藏高原对模拟增温的可塑性: 引入地和原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1198-1205. |
| [14] | 陈旸康, 王益, 李家亮, 王文韬, 冯端宇, 毛康珊. 主流分子钟定年方法的原理、误差来源和使用建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 629-646. |
| [15] | 黄河燕, 朱政财, 吴纪华, 拉琼, 周永洪, 潘晓云. 喜旱莲子草对模拟全天增温的可塑性: 引入地和原产地种群的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 419-427. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||